Unveiling the Science Behind Metal Polishing Compounds: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Science Behind Metal Polishing Compounds: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Science Behind Metal Polishing Compounds: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Science Behind Metal Polishing Compounds: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Science Behind Metal Polishing Compounds: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Science of Polishing: A Journey From Rough to Refined
- 3.2 The Importance of Polishing Compounds in Diverse Industries
- 3.3 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Metal Polishing Compounds
- 3.4 Tips for Achieving Optimal Polishing Results
- 3.5 Conclusion: A Legacy of Precision and Refinement
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Science Behind Metal Polishing Compounds: A Comprehensive Guide

The pursuit of a lustrous, blemish-free surface on metal objects has captivated artisans and manufacturers alike for centuries. The key to achieving this desired aesthetic lies in the art of polishing, a process that utilizes specialized compounds to refine and enhance the surface of metals. This article delves into the fascinating world of metal polishing compounds, unraveling their composition, application, and significance in various industries.
The Science of Polishing: A Journey From Rough to Refined
Polishing compounds, often referred to as abrasives, are meticulously engineered mixtures designed to remove surface imperfections and impart a desired sheen to metal surfaces. The effectiveness of a polishing compound hinges on its abrasive particles, which are classified by their size, shape, and hardness.
Abrasive Particles: The Cornerstones of Polishing
-
Size: The size of abrasive particles dictates the degree of surface refinement. Coarse particles, ranging from several hundred microns to several millimeters, are ideal for removing deep scratches and imperfections. As the particle size diminishes, the polishing action becomes finer, resulting in a smoother and more reflective surface.
-
Shape: The shape of abrasive particles influences their cutting action. Angular particles, such as those found in silicon carbide and aluminum oxide, are highly effective at removing material quickly. Rounded particles, commonly found in rouge and diamond compounds, offer a gentler polishing action, leaving a smoother finish.
-
Hardness: The hardness of abrasive particles determines their ability to cut through the metal surface. Harder abrasives, like diamond and silicon carbide, are capable of removing more material than softer abrasives like rouge and cerium oxide.
The Polishing Process: A Symphony of Friction and Abrasion
The polishing process involves applying a polishing compound to the metal surface using a rotating wheel, pad, or cloth. The abrasive particles in the compound, under the influence of friction, cut into the surface, removing imperfections and irregularities. The pressure applied, the speed of rotation, and the duration of the polishing process all contribute to the final finish.
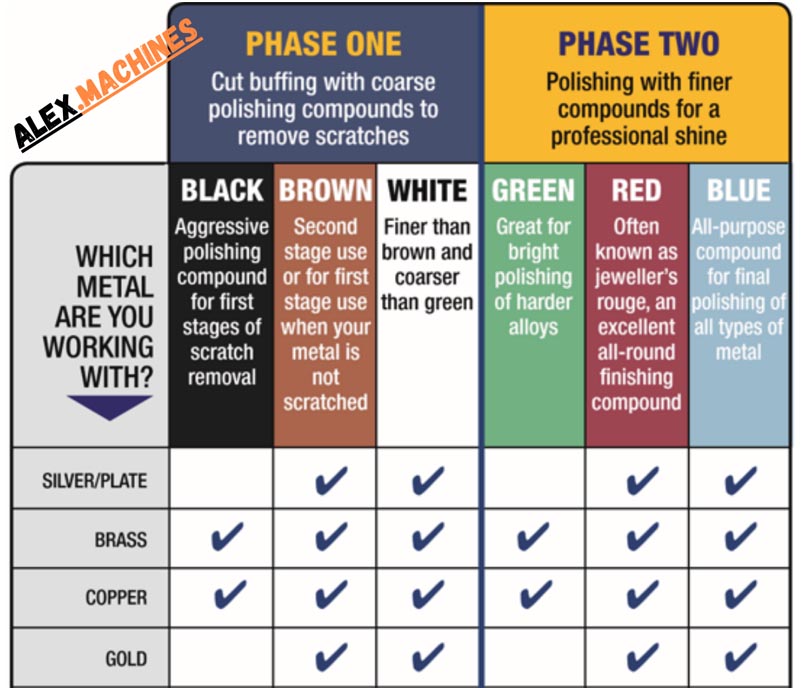
Types of Polishing Compounds: A Diverse Arsenal for Diverse Needs
The world of polishing compounds encompasses a diverse array of formulations, each tailored to specific metal types and desired finishes.
-
Coarse Compounds: These compounds, typically containing large abrasive particles, are used for initial rough grinding and removing deep scratches or imperfections. Examples include silicon carbide, aluminum oxide, and emery.
-
Medium Compounds: These compounds, with smaller abrasive particles, are used for intermediate polishing, refining the surface and preparing it for finer polishing stages. Examples include tripoli, pumice, and rouge.
-
Fine Compounds: These compounds, containing extremely fine abrasive particles, are used for final polishing, achieving a high gloss and mirror-like finish. Examples include jeweler’s rouge, cerium oxide, and diamond compounds.
Beyond Abrasives: Additives for Enhanced Performance
Polishing compounds often incorporate additives to enhance their performance and characteristics. These additives can include:
-
Lubricants: Lubricants reduce friction, preventing heat buildup and extending the life of polishing tools. Common lubricants include oils, waxes, and water-based solutions.
-
Binders: Binders hold the abrasive particles together, ensuring a consistent application and preventing premature wear. Common binders include resins, polymers, and waxes.
-
Fillers: Fillers enhance the compound’s texture and consistency, improving its application and preventing clogging of the polishing wheel. Common fillers include silica, alumina, and chalk.
The Importance of Polishing Compounds in Diverse Industries
The applications of polishing compounds extend far beyond the realm of aesthetics, playing a crucial role in various industries, including:
-
Manufacturing: Polishing compounds are essential for achieving desired surface finishes in a wide range of manufactured goods, from automotive parts to medical instruments. The process enhances wear resistance, corrosion protection, and aesthetic appeal.
-
Jewelry: In the jewelry industry, polishing compounds are indispensable for achieving the brilliance and luster that characterize precious metals. They are used to remove scratches, tarnish, and imperfections, enhancing the value and beauty of jewelry pieces.
-
Machining: Polishing compounds are used to refine machined surfaces, removing burrs, tool marks, and other imperfections. This process improves the functionality and longevity of machined parts.
-
Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, polishing compounds are used to achieve extremely smooth and reflective surfaces on aircraft components, reducing drag and improving aerodynamic performance.
-
Electronics: Polishing compounds are used in the electronics industry to create smooth and reflective surfaces on semiconductors and other electronic components, enhancing their performance and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Metal Polishing Compounds
1. What is the difference between polishing and buffing?
Polishing involves removing material from the metal surface using abrasive compounds, resulting in a smoother and more refined finish. Buffing, on the other hand, involves using a soft cloth or wheel to polish a surface that has already been polished, enhancing its shine and luster.
2. How do I choose the right polishing compound for my application?
The selection of the appropriate polishing compound depends on factors such as the metal type, the desired finish, and the severity of surface imperfections. Consulting a polishing compound manufacturer or a knowledgeable professional can provide valuable guidance.
3. How do I apply polishing compound safely and effectively?
Applying polishing compound involves using a rotating wheel, pad, or cloth. The pressure, speed, and duration of application should be carefully controlled to avoid damaging the metal surface. Wearing appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and eye protection, is essential.
4. What are the common safety precautions associated with polishing compounds?
Polishing compounds can pose certain health risks if not handled properly. It is important to avoid inhaling dust or fumes generated during polishing, and to wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, eye protection, and a respirator.
5. How do I dispose of polishing compounds responsibly?
The disposal of polishing compounds should be done according to local regulations. Some compounds may be hazardous and require special handling and disposal procedures.
Tips for Achieving Optimal Polishing Results
-
Start with the right compound: Choose a compound that is appropriate for the metal type and the desired finish.
-
Use a clean polishing wheel: A clean polishing wheel will ensure optimal contact with the metal surface and prevent contamination.
-
Apply the compound evenly: Ensure that the compound is applied evenly across the entire surface.
-
Control the pressure and speed: Apply appropriate pressure and maintain a consistent speed to avoid damaging the surface.
-
Monitor the process: Regularly inspect the surface to assess the progress and adjust the polishing process as needed.
-
Clean the surface thoroughly: After polishing, thoroughly clean the surface to remove any residual compound.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Precision and Refinement
Metal polishing compounds have played a pivotal role in shaping the world around us, contributing to the beauty, functionality, and durability of countless objects. From the intricate details of jewelry to the sleek surfaces of automobiles, these specialized compounds continue to refine and enhance the world of metals, leaving a lasting legacy of precision and refinement. By understanding the science behind polishing compounds and following best practices, individuals and industries can unlock their potential, achieving exceptional finishes that elevate both aesthetics and performance.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Science Behind Metal Polishing Compounds: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!