Unraveling the Origins of Alpha Particles: A Journey into the Heart of Radioactive Decay
Related Articles: Unraveling the Origins of Alpha Particles: A Journey into the Heart of Radioactive Decay
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Origins of Alpha Particles: A Journey into the Heart of Radioactive Decay. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Origins of Alpha Particles: A Journey into the Heart of Radioactive Decay
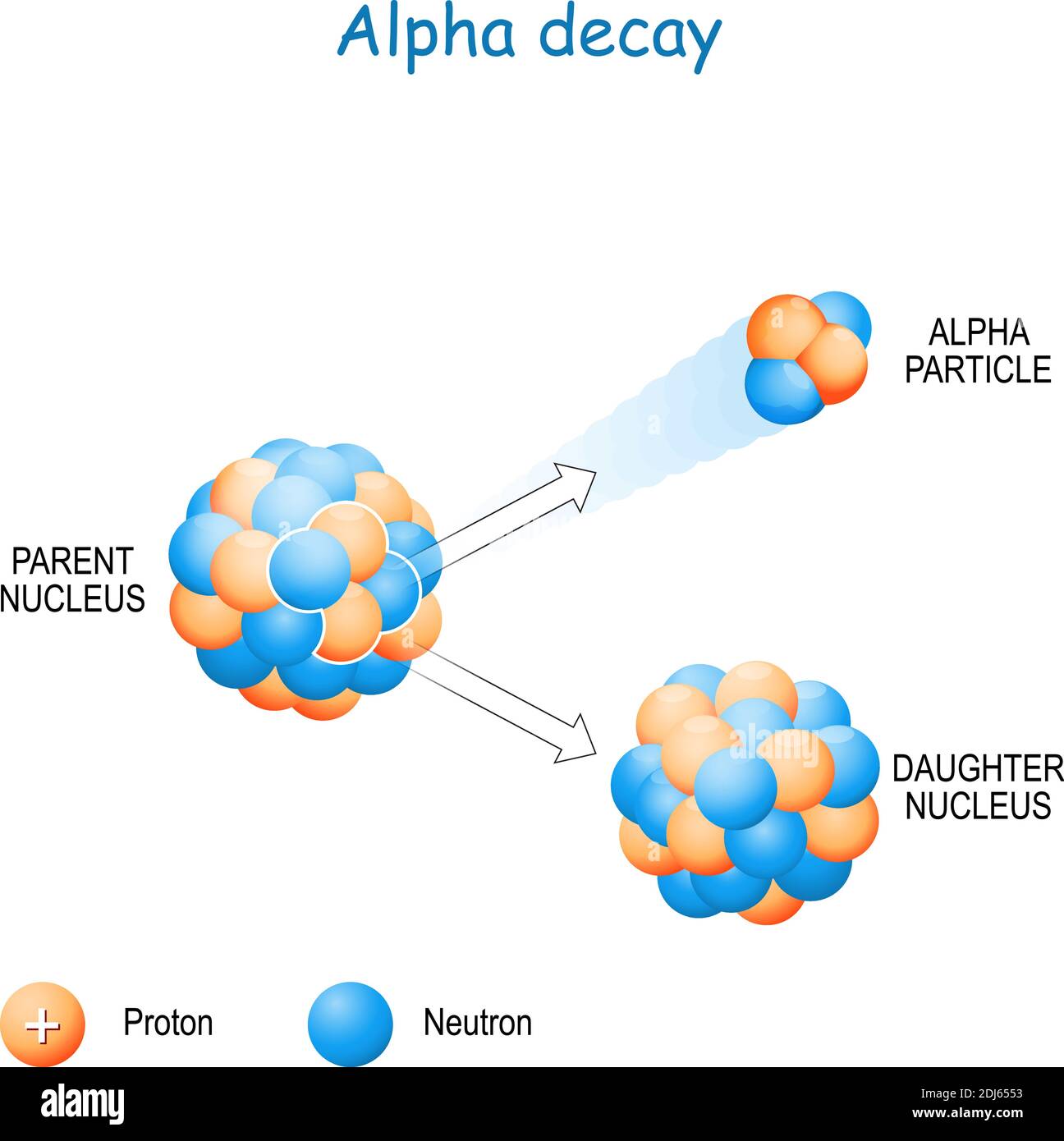
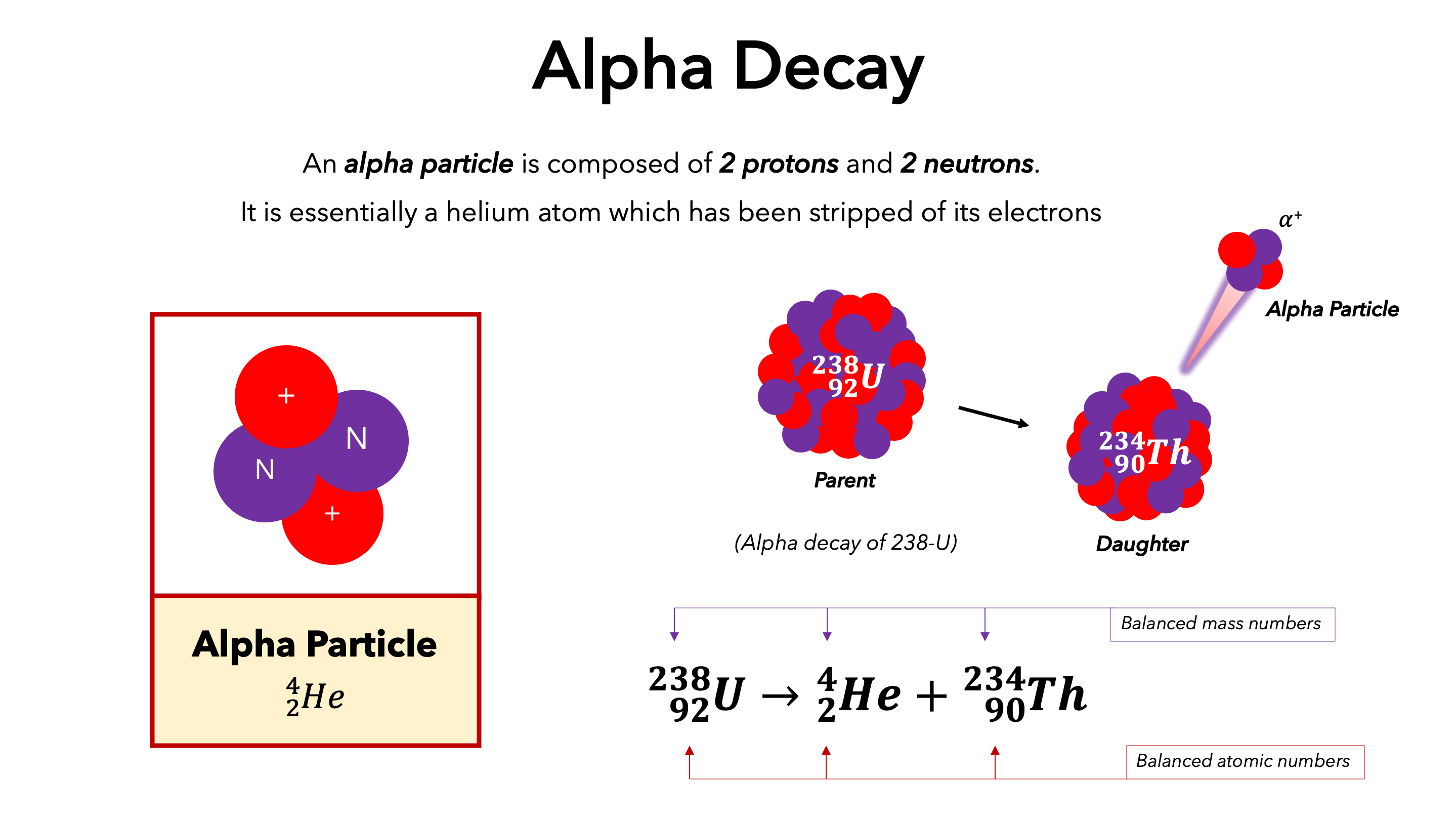
Alpha particles, composed of two protons and two neutrons, are a fundamental component of the radioactive decay process. They are emitted from the nuclei of unstable atoms, carrying a significant amount of energy and leaving behind a daughter nucleus with a reduced atomic number and mass. Understanding the sources of alpha particles is crucial for various applications, from nuclear medicine to geology, as they provide valuable insights into the nature of matter and the processes that shape our world.
The Radioactive Decay Process: The Genesis of Alpha Particles
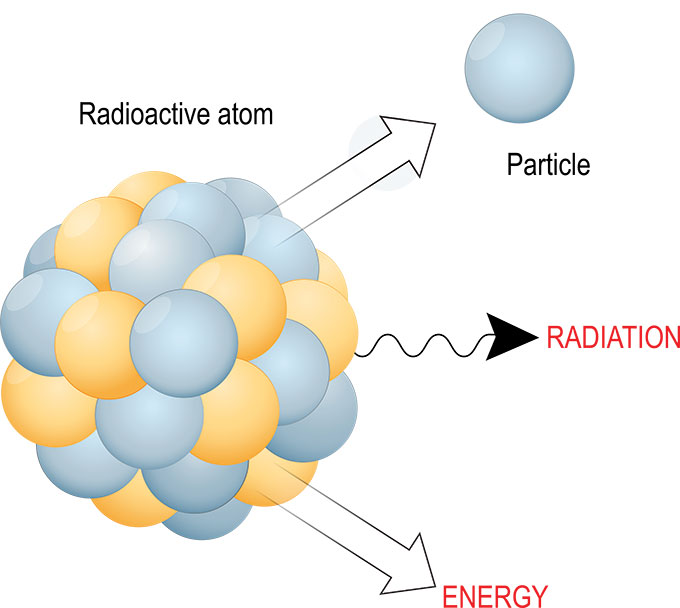
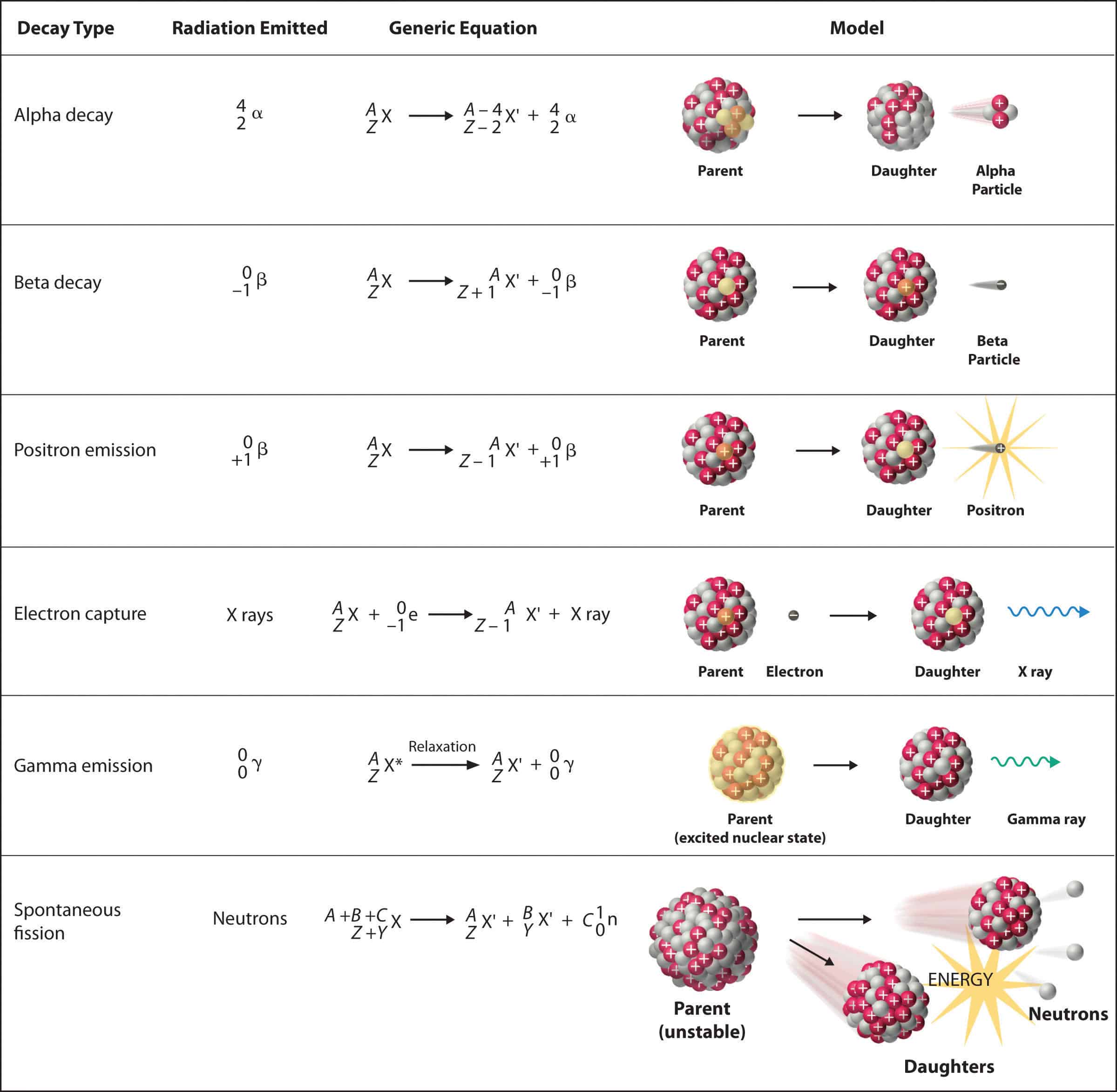
Radioactive decay is a natural phenomenon where unstable atomic nuclei transform into more stable configurations by releasing energy in the form of particles and/or electromagnetic radiation. This process is governed by the laws of nuclear physics, where the nucleus strives to achieve a balance between the strong nuclear force holding the protons and neutrons together and the electrostatic repulsion between protons.
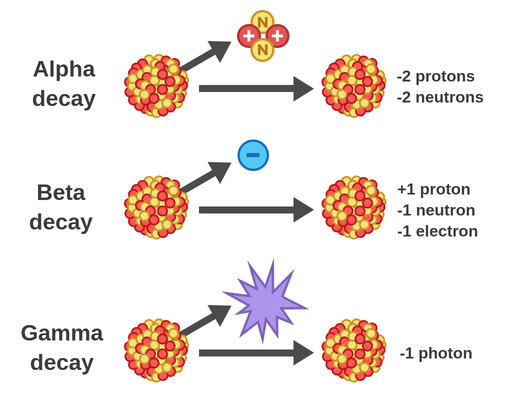
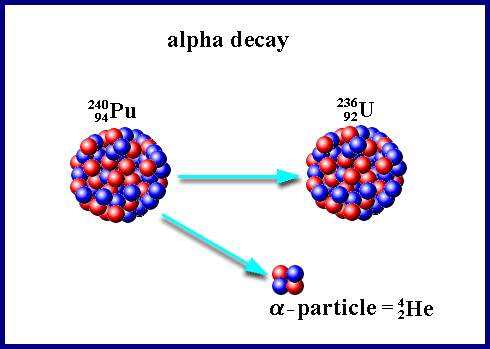
Alpha decay is one of the primary modes of radioactive decay, where an unstable nucleus emits an alpha particle. This emission occurs when the nucleus is too large or has an imbalance of protons and neutrons, leading to an energetically favorable state by shedding the alpha particle.
The Sources of Alpha Particles: A Diverse Spectrum
Alpha particles originate from a diverse range of sources, both natural and man-made. Each source has its unique characteristics, contributing to the multifaceted nature of these particles.
1. Naturally Occurring Radioactive Isotopes:
- Uranium Series: The uranium series is a chain of radioactive decay starting with uranium-238, a naturally occurring isotope found in the Earth’s crust. This series involves multiple alpha decay events, producing a cascade of alpha particles along with other decay products.
- Thorium Series: Similar to the uranium series, the thorium series begins with thorium-232, another naturally occurring isotope. This series also involves multiple alpha decay events, contributing to the natural background radiation we experience.
- Actinium Series: The actinium series starts with uranium-235 and undergoes a series of alpha and beta decays, ultimately leading to the stable lead-207 isotope.
- Potassium-40: While not part of a decay series, potassium-40 is a naturally occurring radioactive isotope that undergoes beta decay and electron capture, but also a small percentage of alpha decay, contributing to the Earth’s natural background radiation.
2. Man-Made Radioactive Isotopes:
- Nuclear Reactors: Nuclear reactors, designed to produce energy through nuclear fission, generate a significant amount of alpha particles. Fission reactions involve the splitting of heavy atomic nuclei, releasing neutrons and alpha particles.
- Radioactive Waste: Nuclear reactors and other nuclear facilities generate radioactive waste, which contains various radioactive isotopes, including alpha emitters. This waste requires careful management due to the potential health risks associated with alpha radiation.
- Medical Isotopes: Some radioactive isotopes, such as americium-241, are used in medical imaging and treatment. These isotopes emit alpha particles, which can be targeted to specific tissues or organs for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
- Nuclear Weapons: The detonation of nuclear weapons releases a tremendous amount of energy, including alpha particles, along with other radioactive materials. This release can have devastating consequences for the environment and human health.
3. Cosmic Rays:
- Solar Flares: The Sun, our nearest star, occasionally emits bursts of high-energy particles, known as solar flares. These flares can release alpha particles into space, which can reach Earth and contribute to the cosmic radiation background.
- Supernovae: Supernovae, the explosive deaths of massive stars, release a vast amount of energy, including alpha particles, into the interstellar medium. These particles contribute to the cosmic radiation background and can have significant effects on the evolution of galaxies.
The Significance of Alpha Particles: A Multifaceted Impact
Alpha particles have a significant impact on various fields, from fundamental science to practical applications.
1. Nuclear Physics and Cosmology:
- Understanding Nuclear Structure: Studying alpha decay provides valuable insights into the structure of atomic nuclei, particularly the interplay of the strong nuclear force and electrostatic repulsion.
- Dating Geological Samples: Alpha decay is a fundamental process used in radiometric dating, which allows scientists to determine the age of geological samples, fossils, and artifacts.
- Cosmic Ray Studies: Analyzing the composition and energy of cosmic rays, including alpha particles, helps scientists understand the origin and evolution of the universe.
2. Medical Applications:
- Radiotherapy: Alpha emitters are increasingly used in targeted radiotherapy, where they deliver high-energy radiation directly to cancerous cells, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- Medical Imaging: Some alpha emitters are used in medical imaging techniques, such as alpha-particle imaging, which provides high-resolution images of biological processes at the cellular level.
3. Industrial Applications:
- Smoke Detectors: Americium-241, an alpha emitter, is commonly used in smoke detectors, where its alpha particles ionize the air, creating a small electrical current. When smoke enters the detector, it disrupts this current, triggering an alarm.
- Static Eliminators: Alpha emitters are also used in static eliminators, which neutralize static charges on surfaces by ionizing the surrounding air.
4. Environmental Concerns:
- Radioactive Waste: Alpha emitters pose a significant environmental hazard due to their high ionizing power. Proper management and disposal of radioactive waste are crucial to minimize the risk of radiation exposure.
- Natural Background Radiation: Alpha particles contribute to the natural background radiation we experience from the Earth’s crust and cosmic rays. While this radiation is generally low, it can pose health risks at high levels.
FAQs on Alpha Particles:
1. Are alpha particles dangerous?
Alpha particles are highly ionizing and can cause significant damage to living tissues if they penetrate the body. However, due to their large size and charge, they have a limited range in air and are easily stopped by a sheet of paper or even a layer of skin. The primary concern with alpha particles is internal exposure, where they can be ingested or inhaled, leading to damage to internal organs.
2. How are alpha particles detected?
Alpha particles can be detected using various methods, including:
- Scintillation Counters: These devices use materials that emit light when struck by alpha particles, which is then detected by a photomultiplier tube.
- Gas Ionization Chambers: These devices use the ionization of gas by alpha particles to generate a measurable electrical signal.
- Solid State Detectors: These devices use semiconductor materials that generate a signal when alpha particles pass through them.
3. What are the applications of alpha particles in medicine?
Alpha emitters are increasingly used in medical applications, particularly in targeted radiotherapy and medical imaging. In radiotherapy, alpha emitters are attached to specific molecules that target cancerous cells, delivering a high dose of radiation directly to the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. In medical imaging, alpha emitters can be used to create high-resolution images of biological processes at the cellular level.
4. What are the environmental concerns associated with alpha particles?
Alpha emitters pose a significant environmental hazard due to their high ionizing power. Improper management and disposal of radioactive waste containing alpha emitters can lead to contamination of the environment and potential health risks to humans and wildlife. Additionally, alpha particles contribute to the natural background radiation, which can pose health risks at high levels.
Tips for Understanding Alpha Particles:
- Visualize the structure: Imagine an alpha particle as a tiny helium nucleus, consisting of two protons and two neutrons.
- Focus on the decay process: Understand that alpha decay is a process where an unstable nucleus sheds an alpha particle to achieve a more stable configuration.
- Consider the sources: Be aware of the various sources of alpha particles, both natural and man-made, and their respective characteristics.
- Explore the applications: Learn about the diverse applications of alpha particles in various fields, from nuclear physics to medicine and industry.
- Understand the risks: Be aware of the potential health risks associated with alpha particles, particularly internal exposure.
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding Alpha Particles
Alpha particles, originating from a diverse range of sources, play a crucial role in our understanding of the universe, the nature of matter, and the processes that shape our world. Their high ionizing power makes them a valuable tool in various fields, particularly in medicine, industry, and scientific research. However, their potential for harm must be carefully considered, especially regarding radioactive waste management and exposure to high levels of alpha radiation. By understanding the sources, properties, and applications of alpha particles, we can harness their potential while mitigating their risks, contributing to a safer and more informed world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Origins of Alpha Particles: A Journey into the Heart of Radioactive Decay. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!