Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide

Electricity is the lifeblood of modern households, powering everything from lighting and heating to appliances and entertainment systems. Understanding how much electricity a household consumes and the factors influencing this consumption is crucial for responsible energy management and financial well-being. This article delves into the intricacies of normal household electricity usage, providing a comprehensive overview of the various factors at play and offering insights into ways to optimize energy consumption.
Factors Influencing Household Electricity Consumption:
Several factors contribute to the overall electricity consumption of a household. These factors can be broadly categorized as follows:
1. Size and Composition of the Household:
- Number of occupants: Larger households naturally consume more electricity as they require more lighting, heating, and appliances to cater to the needs of multiple individuals.
- Occupant activities: The habits and lifestyles of household members significantly impact energy consumption. For instance, a household with individuals who work from home or engage in hobbies that require high energy usage will consume more electricity than a household with members who are primarily away from home during the day.
2. Housing Characteristics:
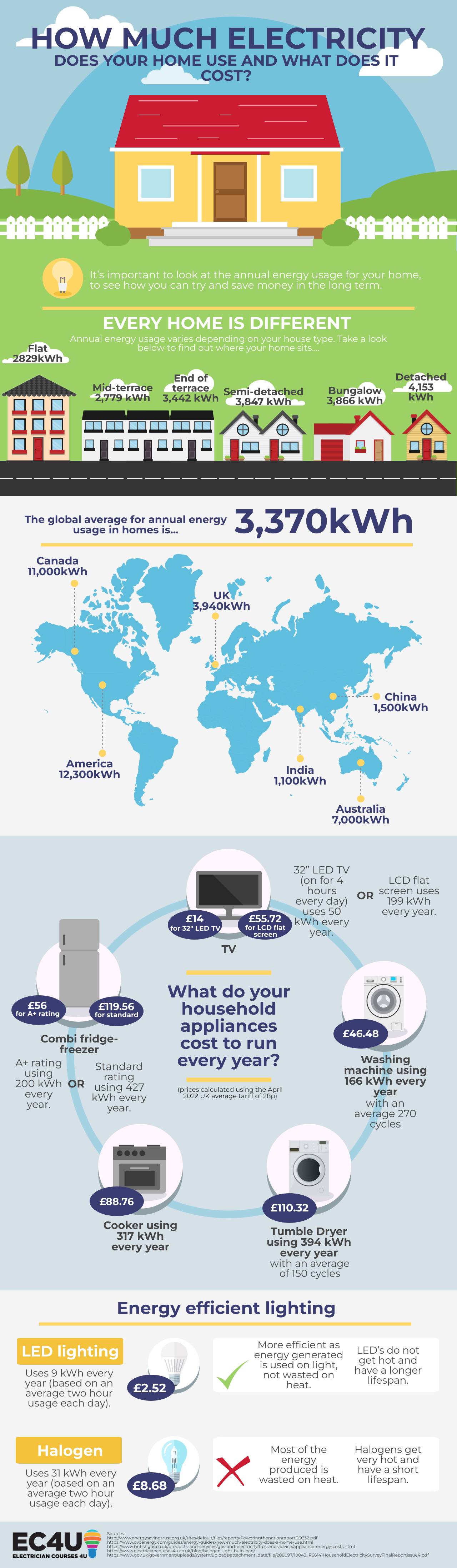
- Size and insulation: Larger homes with poor insulation require more energy for heating and cooling, leading to higher electricity consumption.
- Number of rooms and appliances: The number of rooms and appliances in a home directly correlates with electricity usage. Homes with numerous rooms, multiple bathrooms, and a wide range of appliances will consume more energy than smaller homes with fewer amenities.
- Climate: The climate in which a home is located plays a significant role in energy consumption. Homes in areas with extreme temperatures require more energy for heating or cooling, resulting in higher electricity bills.
3. Appliance Usage:
- Type and age of appliances: Newer, energy-efficient appliances consume less electricity than older models.
- Frequency and duration of appliance usage: The frequency and duration of appliance use have a direct impact on electricity consumption. For instance, using the dishwasher only when it is full and avoiding unnecessary laundry loads can significantly reduce energy usage.
- Appliance settings: The settings used for various appliances, such as the temperature on the refrigerator or the heat setting on the oven, can influence electricity consumption.
4. Lighting:
- Type of bulbs: Incandescent bulbs consume significantly more energy than LED or CFL bulbs. Replacing traditional bulbs with energy-efficient alternatives can lead to substantial savings.
- Lighting usage: The amount of time spent using lights, especially during daylight hours, contributes to overall electricity consumption.
5. Other Factors:
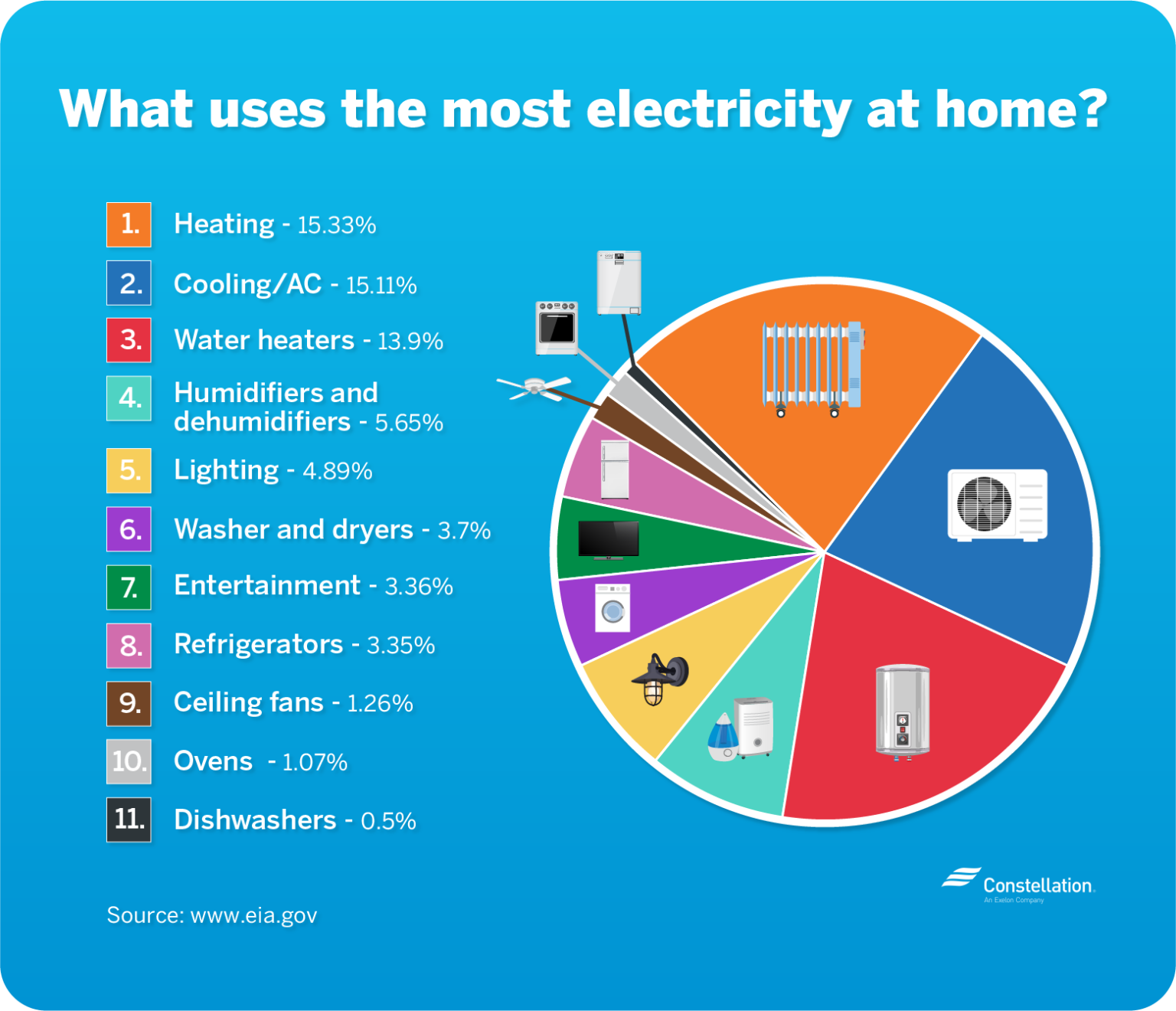
- Heating and cooling systems: The type and efficiency of heating and cooling systems used in a home significantly impact electricity consumption.
- Water heating: Water heating can account for a significant portion of household electricity usage. Using energy-efficient water heaters and taking shorter showers can reduce consumption.
- Electronic devices: The increasing prevalence of electronic devices, such as computers, televisions, and gaming consoles, has contributed to rising household electricity usage.
Understanding Average Household Electricity Consumption:
The average household electricity consumption varies significantly depending on factors such as location, climate, household size, and lifestyle. However, some general insights can be gleaned from data collected by energy providers and government agencies:
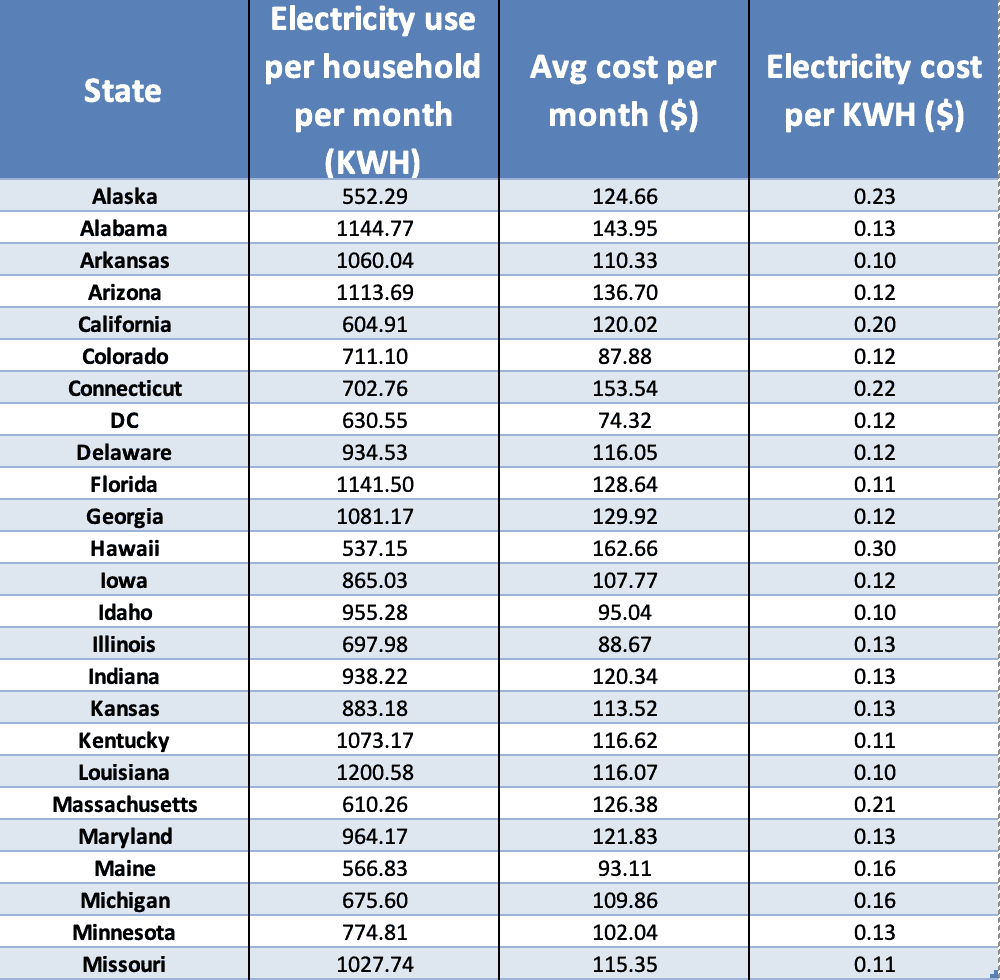
- National averages: The average American household consumes around 10,715 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity annually. This translates to approximately 893 kWh per month.
- Regional variations: Electricity consumption patterns can vary significantly across different regions of the country. For example, households in warmer climates tend to use more electricity for cooling, while households in colder climates use more electricity for heating.
- Seasonal fluctuations: Electricity consumption tends to be higher during summer months due to increased air conditioning usage and lower during winter months due to increased heating usage.
Benefits of Understanding Household Electricity Consumption:
Understanding household electricity consumption offers numerous benefits:
- Financial savings: By identifying areas where electricity consumption can be reduced, households can save money on their energy bills.
- Environmental sustainability: Reducing electricity consumption helps minimize greenhouse gas emissions and promotes a more sustainable lifestyle.
- Energy independence: By using energy more efficiently, households can become less reliant on external energy sources and contribute to a more resilient energy system.
FAQs about Normal Household Electricity Usage:
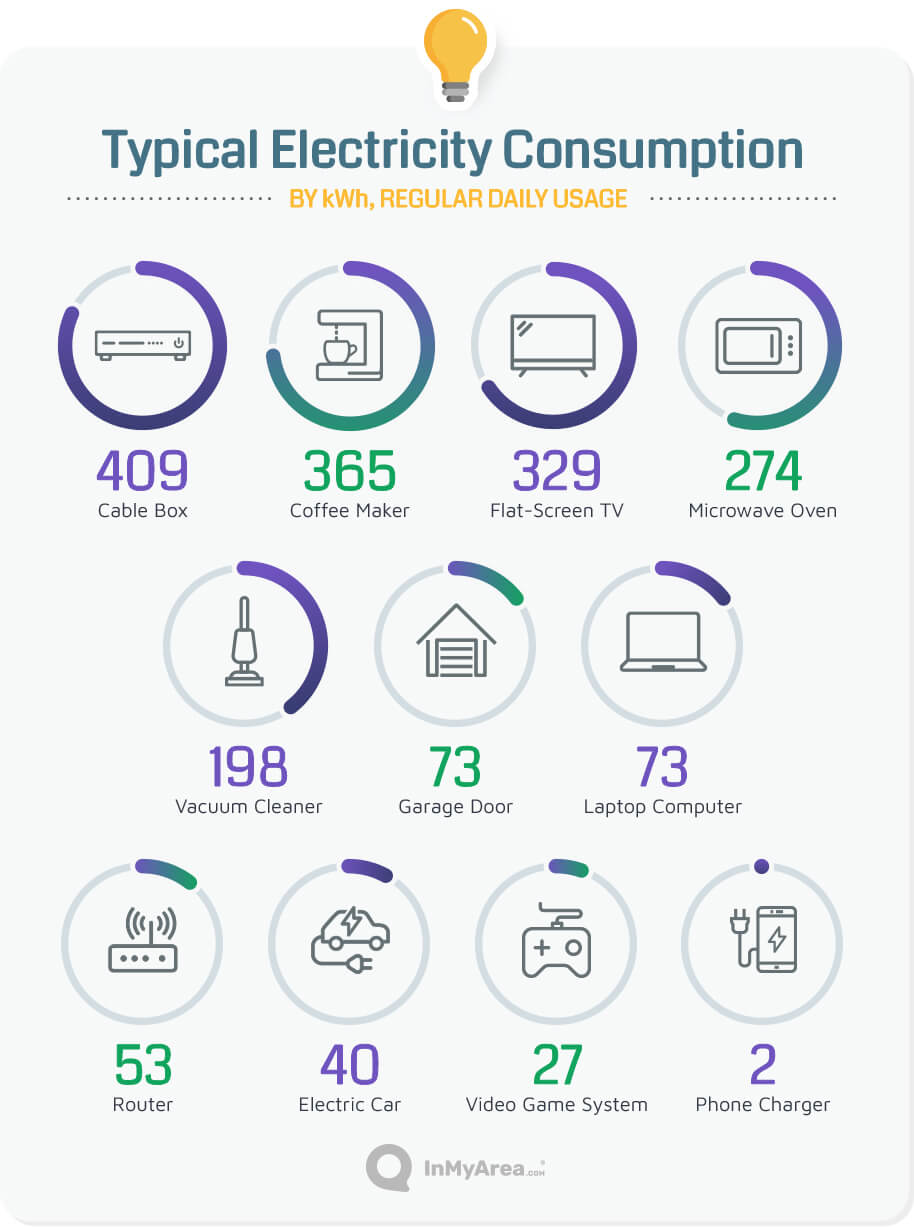
1. What are the most energy-intensive appliances in a household?
- Refrigerator: Refrigerators run continuously and can account for a significant portion of household electricity consumption.
- Water heater: Water heaters, especially electric tank-style models, are also major energy consumers.
- Clothes dryer: Electric clothes dryers are energy-intensive appliances, especially when used frequently.
- Oven: Electric ovens require a substantial amount of energy to reach high temperatures.
2. How can I track my household electricity consumption?
- Energy monitoring devices: Smart plugs and energy monitors can provide real-time information on appliance energy usage.
- Utility bill analysis: Carefully analyzing utility bills can help identify patterns of energy consumption and pinpoint areas for improvement.
- Online tools: Many utility providers offer online tools that allow customers to track their energy consumption and compare it to average usage for their area.
3. What are some simple ways to reduce household electricity consumption?
- Turn off lights when leaving a room.
- Unplug electronic devices when not in use.
- Use energy-efficient appliances.
- Wash clothes in cold water and air-dry them whenever possible.
- Reduce the use of the dishwasher and hand-wash dishes when possible.
- Set the thermostat to a comfortable temperature and use fans to circulate air.
- Install energy-efficient windows and insulation.
- Use natural light whenever possible.
Tips for Optimizing Household Electricity Consumption:
- Conduct an energy audit: A professional energy audit can identify areas for improvement and suggest specific measures to reduce energy consumption.
- Utilize energy-efficient lighting: Replace traditional incandescent bulbs with LED or CFL bulbs.
- Install a programmable thermostat: A programmable thermostat can automatically adjust heating and cooling settings to optimize energy usage.
- Take advantage of natural light: Use curtains or blinds to maximize natural light during the day and reduce the need for artificial lighting.
- Use energy-efficient appliances: Choose appliances with Energy Star ratings, which indicate higher energy efficiency.
- Practice energy-saving habits: Turn off lights when leaving a room, unplug electronic devices when not in use, and avoid running appliances when they are not fully loaded.
- Consider solar panels: Installing solar panels can generate electricity from renewable sources and reduce reliance on the grid.
Conclusion:
Understanding normal household electricity usage is essential for responsible energy management and financial well-being. By understanding the factors influencing consumption and implementing energy-saving strategies, households can reduce their environmental impact, save money, and contribute to a more sustainable energy future. From simple habits like turning off lights to investing in energy-efficient appliances and renewable energy sources, there are numerous ways to optimize household electricity consumption and create a more responsible and efficient energy usage pattern.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!