Understanding Household Appliance Power Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
Related Articles: Understanding Household Appliance Power Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Household Appliance Power Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Household Appliance Power Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
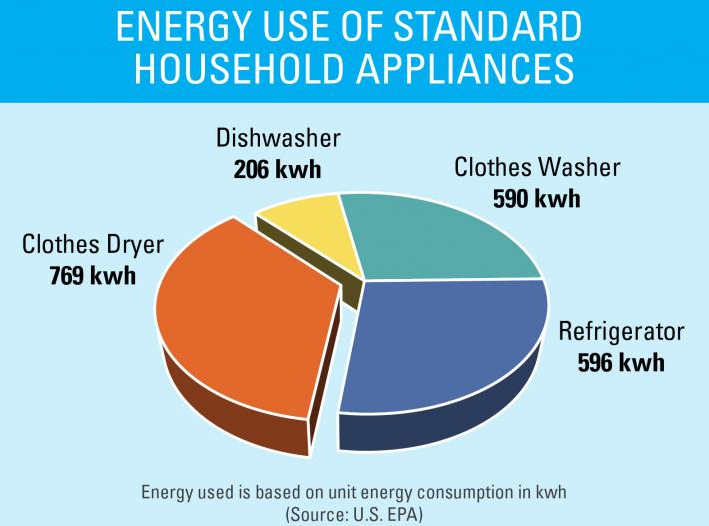
Modern life is inextricably intertwined with household appliances. From refrigerators keeping our food fresh to washing machines cleaning our clothes, these devices have become indispensable in our daily routines. However, their convenience comes at a cost – energy consumption. Understanding the power consumption of various appliances is crucial for managing energy bills, reducing environmental impact, and making informed purchasing decisions.
This article delves into the energy consumption patterns of common household appliances, highlighting their impact on electricity bills and the environment. It provides a comprehensive overview of appliance power consumption, offering insights into efficient usage, energy-saving tips, and the importance of choosing energy-efficient models.
Power Consumption: A Key Factor in Energy Management
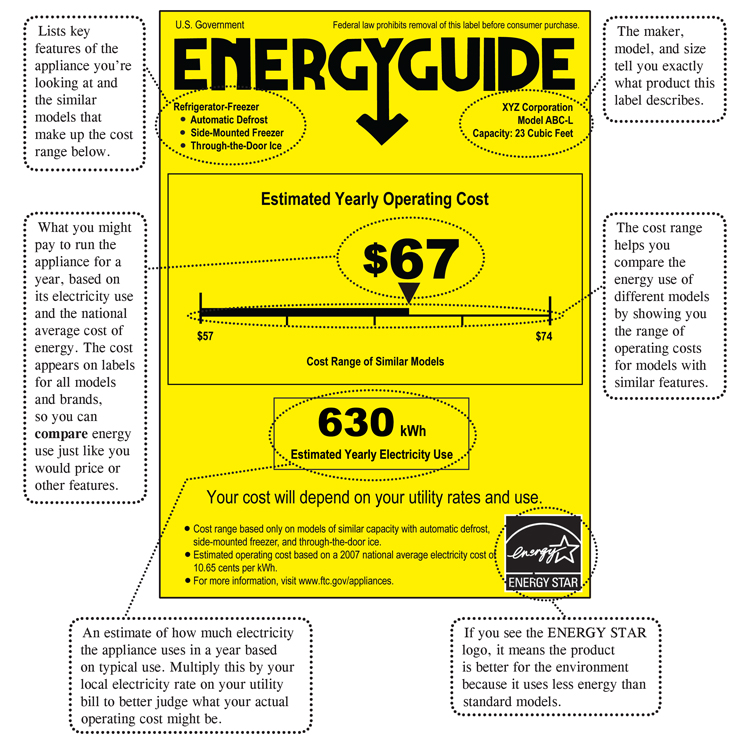
Power consumption, measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW), indicates the rate at which an appliance uses electricity. The higher the wattage, the more energy the appliance consumes. Appliances typically display their power consumption in watts on their energy labels or user manuals.
Factors Influencing Appliance Power Consumption
Several factors influence the energy consumption of household appliances:
- Appliance Type: Different appliances have varying power requirements. For example, a refrigerator operates continuously, consuming significant energy compared to a toaster that is only used intermittently.
- Size and Capacity: Larger appliances, such as refrigerators with greater storage capacity, generally consume more energy.
- Usage Patterns: Frequent use and prolonged operation times increase energy consumption. For instance, running a washing machine multiple times a day consumes more energy than using it once or twice.
- Efficiency Rating: Modern appliances often feature energy efficiency ratings, indicating their energy consumption relative to other models. Energy-efficient appliances consume less energy for the same level of performance.
- Operating Conditions: Environmental factors like ambient temperature can affect energy consumption. For example, a refrigerator in a hot room may need to work harder to maintain a cool temperature, resulting in higher energy use.
Understanding Appliance Power Consumption: A Breakdown
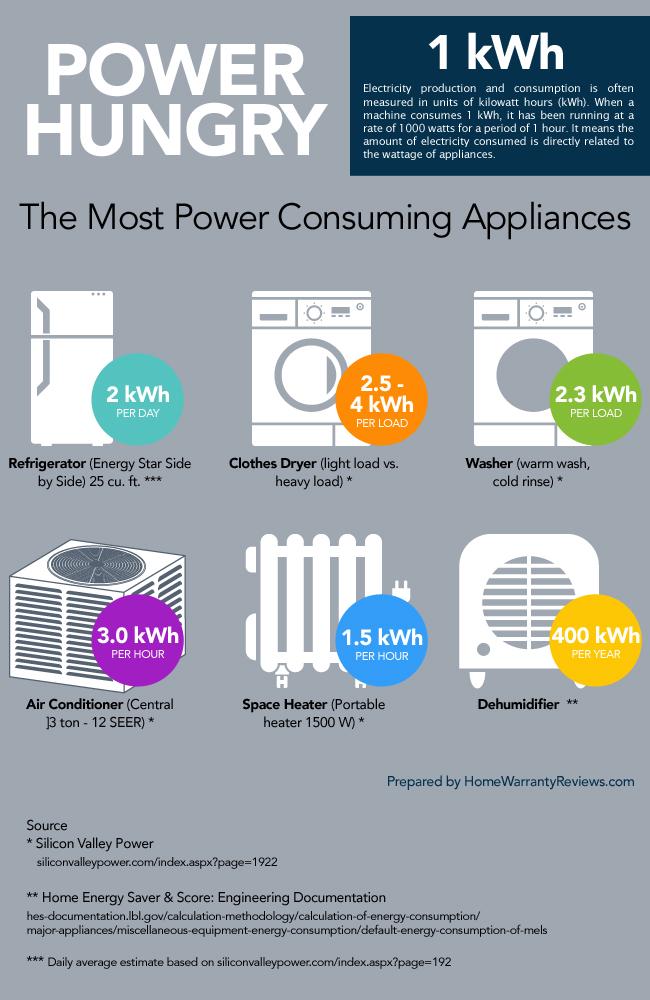
1. Refrigerators and Freezers:
- Average Power Consumption: 150-700 watts
- Energy Consumption per Year: 500-2000 kilowatt-hours (kWh)
- Factors Influencing Consumption: Size, age, ambient temperature, frequency of door openings.
- Tips for Efficient Use: Keep the refrigerator well-stocked to minimize cold air loss, avoid placing hot food inside, ensure proper ventilation, and clean the coils regularly.
2. Washing Machines:
- Average Power Consumption: 300-1500 watts
- Energy Consumption per Year: 200-800 kWh
- Factors Influencing Consumption: Load size, water temperature, wash cycle settings.
- Tips for Efficient Use: Wash full loads, use cold water whenever possible, select energy-efficient cycles, and avoid excessive use of detergent.
3. Dishwashers:
- Average Power Consumption: 1200-2400 watts
- Energy Consumption per Year: 200-600 kWh
- Factors Influencing Consumption: Load size, wash cycle settings, water temperature.
- Tips for Efficient Use: Wash full loads, use the energy-efficient cycle, avoid pre-washing dishes, and ensure the dishwasher door seals properly.
4. Clothes Dryers:
- Average Power Consumption: 2000-4000 watts
- Energy Consumption per Year: 600-1500 kWh
- Factors Influencing Consumption: Load size, drying time, type of dryer (electric or gas).
- Tips for Efficient Use: Dry full loads, use the lowest heat setting possible, clean the lint trap regularly, and consider air drying clothes whenever feasible.
5. Ovens and Cooktops:
- Average Power Consumption: 1000-5000 watts
- Energy Consumption per Year: 200-1000 kWh
- Factors Influencing Consumption: Oven size, cooking temperature, and duration.
- Tips for Efficient Use: Use the oven’s preheating function, cook multiple dishes at once, use pot lids to retain heat, and consider using alternative cooking methods like microwaving or slow cooking.
6. Water Heaters:
- Average Power Consumption: 4500-5500 watts
- Energy Consumption per Year: 1000-2500 kWh
- Factors Influencing Consumption: Water heater size, tank insulation, and water usage patterns.
- Tips for Efficient Use: Install a tankless water heater, insulate the hot water tank, adjust the thermostat to a lower temperature, and use low-flow showerheads.
7. Lighting:
- Average Power Consumption: 5-15 watts (LED bulbs), 40-100 watts (incandescent bulbs)
- Energy Consumption per Year: 10-50 kWh (LED bulbs), 50-200 kWh (incandescent bulbs)
- Factors Influencing Consumption: Bulb type, wattage, and usage hours.
- Tips for Efficient Use: Replace incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs, use dimmers to adjust brightness, and turn off lights when not in use.
8. Televisions:
- Average Power Consumption: 50-200 watts
- Energy Consumption per Year: 100-400 kWh
- Factors Influencing Consumption: Screen size, resolution, and usage patterns.
- Tips for Efficient Use: Choose energy-efficient models, use the eco mode, and turn off the television when not in use.
9. Computers and Laptops:
- Average Power Consumption: 50-200 watts
- Energy Consumption per Year: 100-400 kWh
- Factors Influencing Consumption: Processor speed, memory, and usage patterns.
- Tips for Efficient Use: Choose energy-efficient models, enable sleep mode, and unplug devices when not in use.
10. Air Conditioners:
- Average Power Consumption: 1000-2000 watts
- Energy Consumption per Year: 1000-2500 kWh
- Factors Influencing Consumption: Unit size, efficiency rating, and usage patterns.
- Tips for Efficient Use: Choose an appropriately sized unit, clean filters regularly, install window shades, and use fans to circulate air.
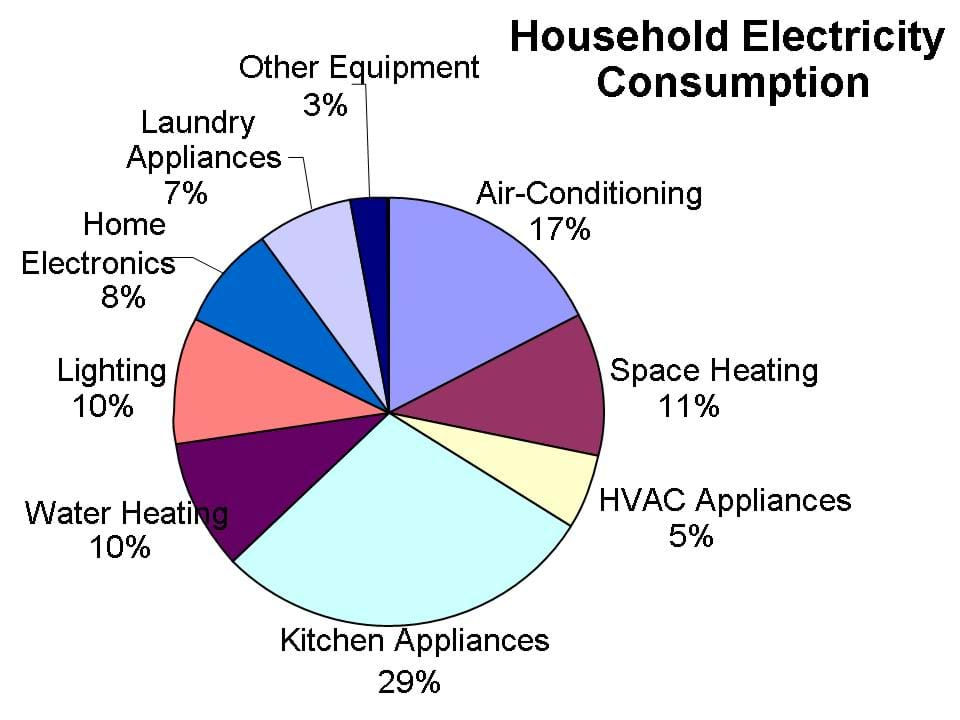
Importance of Understanding Appliance Power Consumption
- Reduced Energy Bills: Understanding appliance energy consumption allows homeowners to make informed choices about usage and optimize energy savings.
- Environmental Sustainability: Reducing energy consumption from household appliances contributes to a lower carbon footprint and helps mitigate climate change.
- Informed Purchasing Decisions: Knowing the power consumption of different appliance models empowers consumers to select energy-efficient options.
- Enhanced Energy Management: By analyzing energy usage patterns, homeowners can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to reduce overall energy consumption.
FAQs: Power Consumption and Household Appliances
1. How can I determine the power consumption of my appliances?
- Check the appliance’s energy label or user manual for its wattage rating.
- Use a power meter to measure the actual power consumption of an appliance in real-time.
2. What is a kilowatt-hour (kWh)?
- A kilowatt-hour is the amount of energy consumed by a 1-kilowatt appliance operating for one hour.
3. How can I calculate my appliance energy consumption?
- Multiply the appliance’s wattage by the number of hours it operates daily, then divide by 1000 to convert watts to kilowatts. Finally, multiply the result by the number of days in a year to get the annual energy consumption in kWh.
4. What is the best way to reduce my electricity bill?
- Use energy-efficient appliances, optimize appliance usage, and adopt energy-saving habits like turning off lights when not in use.
5. How can I tell if an appliance is energy-efficient?
- Look for the Energy Star label, which indicates that an appliance meets specific energy efficiency standards.
Tips for Reducing Appliance Power Consumption
- Use Energy-Efficient Appliances: Choose models with high energy efficiency ratings, such as those bearing the Energy Star label.
- Optimize Appliance Usage: Wash full loads in washing machines and dishwashers, use cold water whenever possible, and avoid pre-washing dishes.
- Reduce Standby Power Consumption: Unplug devices when not in use, use power strips with on/off switches, and consider using smart plugs to automate power management.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean appliance filters, coils, and lint traps regularly to ensure optimal performance and reduce energy consumption.
- Adjust Thermostat Settings: Set the thermostat to a comfortable temperature for heating and cooling, and consider using programmable thermostats for automated temperature control.
- Utilize Alternative Cooking Methods: Explore alternative cooking methods like microwaving, slow cooking, or using a pressure cooker to reduce energy consumption compared to traditional ovens.
- Adopt Energy-Saving Habits: Turn off lights when leaving a room, use natural light whenever possible, and unplug appliances when not in use.
Conclusion
Understanding the power consumption of household appliances is essential for managing energy bills, reducing environmental impact, and making informed purchasing decisions. By implementing energy-efficient practices and utilizing energy-saving appliances, homeowners can significantly reduce their energy consumption, contributing to a more sustainable future. As technology continues to evolve, advancements in appliance efficiency and smart home integration will further enhance energy management capabilities, empowering individuals to make responsible choices that benefit both their wallets and the planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Household Appliance Power Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!