The Second Life of Things: A Comprehensive Guide to Recycling Household Items
Related Articles: The Second Life of Things: A Comprehensive Guide to Recycling Household Items
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Second Life of Things: A Comprehensive Guide to Recycling Household Items. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Second Life of Things: A Comprehensive Guide to Recycling Household Items

Our homes are a constant source of discarded materials, from food packaging to worn-out clothes. While many of these items end up in landfills, a significant portion can be given a second life through recycling. This practice not only reduces waste but also conserves resources and minimizes environmental impact. This article explores the vast world of household recycling, delving into the various materials, benefits, and practical tips for maximizing this essential practice.
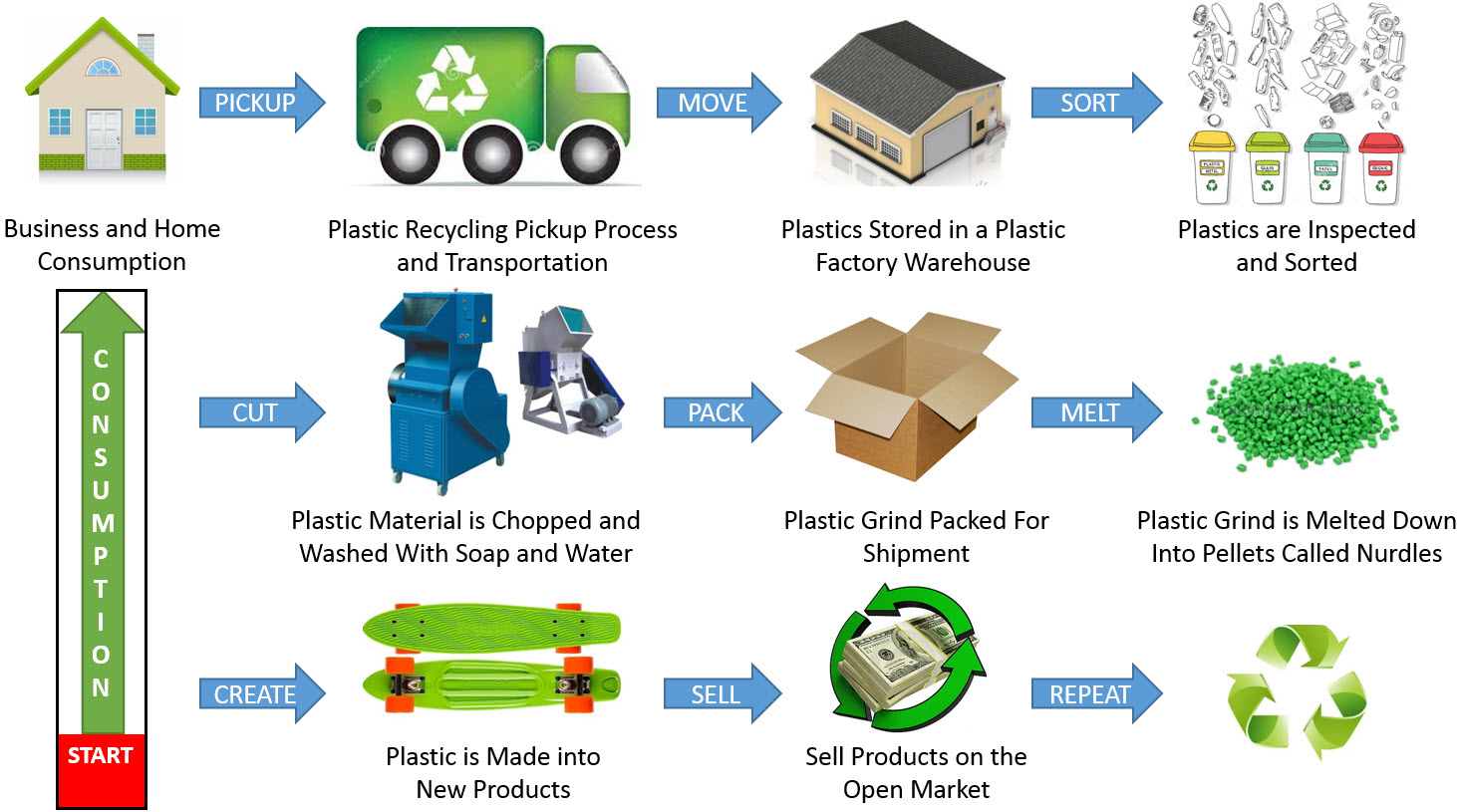
Understanding the Recycling Process:
Recycling involves transforming used materials into new products, effectively diverting them from landfills and reducing the demand for virgin resources. This process typically involves several stages:
- Collection: Household items are gathered through curbside pick-up, drop-off centers, or specialized collection programs.
- Sorting: Collected materials are sorted based on type, separating paper, plastic, metal, glass, and other recyclables.
- Processing: Sorted materials undergo various treatments, such as cleaning, shredding, or melting, depending on their composition.
- Manufacturing: Processed materials are transformed into new products, ranging from packaging and furniture to construction materials and clothing.
The Benefits of Recycling Household Items:
Recycling offers a plethora of environmental and economic advantages, contributing to a more sustainable future:
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Recycling reduces the need to extract raw materials from the earth, minimizing the environmental damage associated with mining and logging.
- Energy Savings: Manufacturing products from recycled materials often requires less energy than creating them from virgin resources, leading to lower carbon emissions.
- Reduced Landfill Space: Recycling diverts waste from landfills, extending their lifespan and mitigating the risk of environmental contamination.
- Pollution Reduction: By reducing the demand for new materials, recycling contributes to lower air and water pollution associated with manufacturing processes.
- Economic Growth: Recycling fosters a circular economy, creating jobs and stimulating innovation in recycling technologies and product design.
Common Household Items and Their Recycling Potential:
Numerous everyday items can be recycled, contributing to a greener lifestyle:
- Paper and Cardboard: Newspapers, magazines, junk mail, cardboard boxes, and paper packaging can be recycled into new paper products.
- Plastic: Bottles, containers, bags, and other plastic items can be recycled into various products, including clothing, furniture, and building materials.
- Metal: Aluminum cans, tin cans, and other metal items can be recycled into new cans, building materials, and other products.
- Glass: Bottles, jars, and other glass items can be recycled into new glass containers, insulation, and construction materials.
- Textiles: Old clothing, towels, and linens can be recycled into new clothing, insulation, and other products.
- Electronics: Old computers, phones, and other electronic devices can be recycled to recover valuable metals and reduce electronic waste.
Recycling Challenges and Considerations:
While recycling offers substantial benefits, certain challenges and considerations must be addressed:
- Contamination: Recycling processes can be compromised by contamination, such as food residue in containers or non-recyclable items mixed with recyclables.
- Market Fluctuations: The market for recycled materials can fluctuate, affecting the economic viability of recycling programs.
- Recycling Infrastructure: Access to recycling facilities and collection programs can vary depending on location and infrastructure development.
- Public Awareness and Education: Effective recycling requires public awareness and education to ensure proper sorting and disposal practices.
FAQs about Recycling Household Items:
Q: What materials can be recycled?
A: The specific materials accepted for recycling vary depending on local programs. However, common recyclable items include paper, cardboard, plastic, metal, glass, and textiles.
Q: How do I prepare my recyclable items?
A: Rinse containers, remove lids, and flatten cardboard boxes. Avoid mixing different materials, such as paper and plastic. Consult your local recycling guidelines for specific instructions.
Q: What happens to my recyclables after I put them out for collection?
A: Collected recyclables are transported to sorting facilities, where they are separated by type and processed for reuse.
Q: Why is it important to recycle?
A: Recycling conserves natural resources, reduces pollution, saves energy, and helps create a more sustainable future.
Q: What are some tips for reducing waste and maximizing recycling?
A: Choose products with minimal packaging, buy reusable items, and compost food scraps.
Tips for Maximizing Recycling Efforts:
- Check Local Guidelines: Consult your local recycling program for specific guidelines and accepted materials.
- Sort and Clean: Properly sort and clean recyclable items to avoid contamination.
- Flatten and Compact: Flatten cardboard boxes and compact plastic containers to save space.
- Avoid Contamination: Keep food residue out of containers and avoid mixing different materials.
- Support Local Recycling Programs: Participate in local recycling programs and support initiatives that promote sustainability.
- Educate Others: Share your knowledge about recycling with friends, family, and community members.
Conclusion:
Recycling household items is a crucial step towards a more sustainable future. By understanding the process, benefits, and challenges associated with recycling, individuals can actively contribute to environmental conservation, resource preservation, and economic growth. By embracing responsible disposal practices and supporting local recycling initiatives, we can collectively minimize our environmental footprint and create a cleaner, healthier planet for generations to come.






![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Second Life of Things: A Comprehensive Guide to Recycling Household Items. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!