The Powerhouse Within: Unveiling the Crucial Role of Mitochondria in Everyday Life
Related Articles: The Powerhouse Within: Unveiling the Crucial Role of Mitochondria in Everyday Life
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Powerhouse Within: Unveiling the Crucial Role of Mitochondria in Everyday Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Powerhouse Within: Unveiling the Crucial Role of Mitochondria in Everyday Life
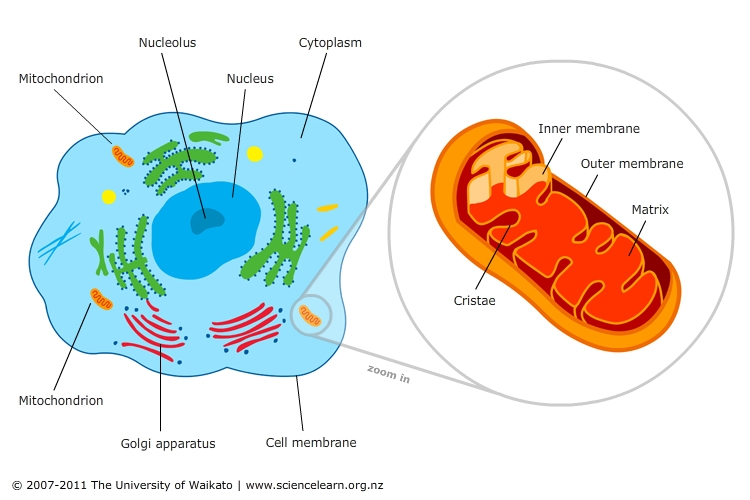
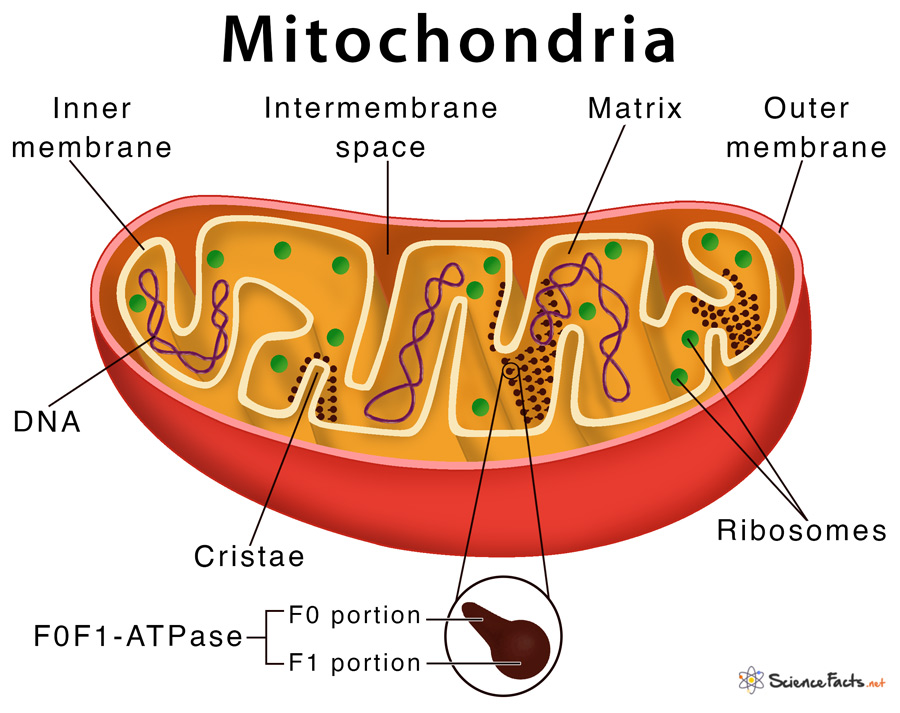
The human body is a marvel of intricate machinery, a symphony of coordinated processes that sustain life. At the heart of this intricate system lies a tiny organelle, often referred to as the "powerhouse of the cell": the mitochondrion. While invisible to the naked eye, these minuscule structures play a crucial role in our daily lives, influencing everything from the energy that fuels our muscles to the intricate processes that govern our thoughts and emotions.
Mitochondria: The Energy Factories of the Cell
Mitochondria are the primary energy producers in our cells, responsible for converting nutrients into usable energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This process, known as cellular respiration, involves a series of chemical reactions that extract energy from glucose and other fuel sources, ultimately powering the multitude of functions that keep us alive.
Beyond Energy: The Diverse Roles of Mitochondria
While their energy-generating role is paramount, mitochondria perform a range of other essential functions within the cell:
-
Calcium Signaling: Mitochondria act as crucial calcium storage and release sites, contributing to the precise regulation of calcium signaling within the cell. This intricate interplay of calcium ions is vital for processes such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and hormone secretion.
-
Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death): Mitochondria play a critical role in the programmed death of cells, a process known as apoptosis. This carefully controlled process eliminates damaged or unwanted cells, ensuring the proper development and maintenance of tissues.
-
Cellular Metabolism: Mitochondria are involved in a multitude of metabolic pathways, including the synthesis of amino acids, heme, and steroids. These metabolic activities are essential for growth, repair, and the production of vital molecules.
-
Heat Production: Mitochondria contribute to the generation of heat, particularly in brown adipose tissue, a specialized type of fat that plays a significant role in regulating body temperature.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production: Mitochondria are also a major source of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage cellular components if not properly controlled. However, ROS also play important roles in signaling and cellular defense.
Mitochondria and Human Health: A Complex Relationship
The intricate functions of mitochondria make them central to maintaining human health. Dysfunctional mitochondria can lead to a range of debilitating conditions, underscoring the importance of these tiny organelles.
Mitochondrial Diseases: A spectrum of genetic and acquired disorders can affect mitochondrial function, leading to a variety of symptoms. These conditions often involve the energy-producing capacity of mitochondria, resulting in fatigue, muscle weakness, and other debilitating problems.
Aging and Mitochondrial Function: As we age, the efficiency of mitochondrial function gradually declines, contributing to the overall aging process. This decline can lead to a range of age-related diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Disease: Mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated in a wide range of chronic diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
The Importance of Mitochondrial Health
Maintaining mitochondrial health is essential for overall well-being. Several lifestyle factors can positively influence mitochondrial function:
-
Diet: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients can support mitochondrial health.
-
Exercise: Regular physical activity promotes mitochondrial biogenesis, increasing the number and efficiency of mitochondria within cells.
-
Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact mitochondrial function. Techniques for stress management, such as meditation and yoga, can help maintain mitochondrial health.
-
Sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for mitochondrial repair and function.
Mitochondria: A Window into Our Evolutionary Past
Mitochondria hold a fascinating story of our evolutionary past. They are believed to have originated from free-living bacteria that were engulfed by ancient eukaryotic cells, eventually becoming an integral part of the cell. This endosymbiotic relationship, where both the host cell and the engulfed bacteria benefited, led to the evolution of complex eukaryotic cells, including those that make up the human body.
Mitochondrial DNA: A Unique Genetic Legacy
Mitochondria possess their own unique DNA, separate from the nuclear DNA found in the cell’s nucleus. This mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is inherited solely from the mother and can be traced back through generations, providing insights into human ancestry and evolution.
Mitochondria in Research: Unlocking New Possibilities
Mitochondria are a subject of intense scientific investigation, with researchers constantly uncovering new insights into their intricate functions and their role in health and disease.
-
Mitochondrial Therapy: Researchers are exploring novel therapies aimed at restoring mitochondrial function in individuals with mitochondrial diseases.
-
Mitochondrial Biomarkers: Scientists are developing biomarkers based on mitochondrial function to diagnose and monitor various diseases.
-
Mitochondrial Reprogramming: Research is exploring ways to reprogram mitochondria to improve cellular function and combat age-related decline.
FAQs about Mitochondria
Q: What is the role of mitochondria in energy production?
A: Mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration, the process of converting nutrients into ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell. This process involves a series of chemical reactions that extract energy from glucose and other fuel sources.
Q: How do mitochondria contribute to human health?
A: Mitochondria are essential for a range of cellular functions, including energy production, calcium signaling, apoptosis, and cellular metabolism. Dysfunctional mitochondria can lead to a variety of health problems, including mitochondrial diseases, age-related decline, and chronic diseases.
Q: What are some lifestyle factors that can influence mitochondrial health?
A: Maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep can all positively influence mitochondrial function.
Q: What are some potential future applications of mitochondrial research?
A: Researchers are exploring novel therapies to restore mitochondrial function in individuals with mitochondrial diseases, developing biomarkers to diagnose and monitor various diseases, and investigating ways to reprogram mitochondria to improve cellular function and combat age-related decline.
Tips for Maintaining Mitochondrial Health
- Adopt a balanced diet: Prioritize whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Manage stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Prioritize sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Consider supplements: Consult with a healthcare professional about potential benefits of supplements like CoQ10, alpha-lipoic acid, and resveratrol.
Conclusion
The unassuming mitochondrion, a tiny organelle residing within our cells, plays a pivotal role in our lives. Its energy-producing capacity fuels our every move, while its diverse functions contribute to the intricate processes that govern our health and well-being. From the energy that powers our muscles to the precise regulation of calcium signaling, mitochondria are indispensable for life as we know it. Understanding the importance of these tiny powerhouses and adopting lifestyle choices that support their health is crucial for maintaining overall well-being and preventing disease. As research into mitochondria continues to advance, we can expect further breakthroughs that unlock new possibilities for enhancing human health and longevity.
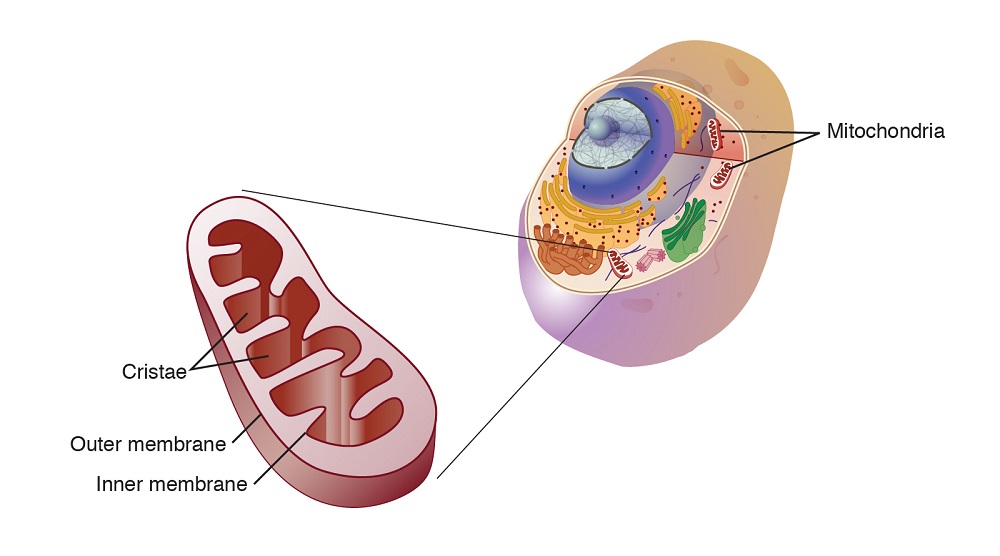

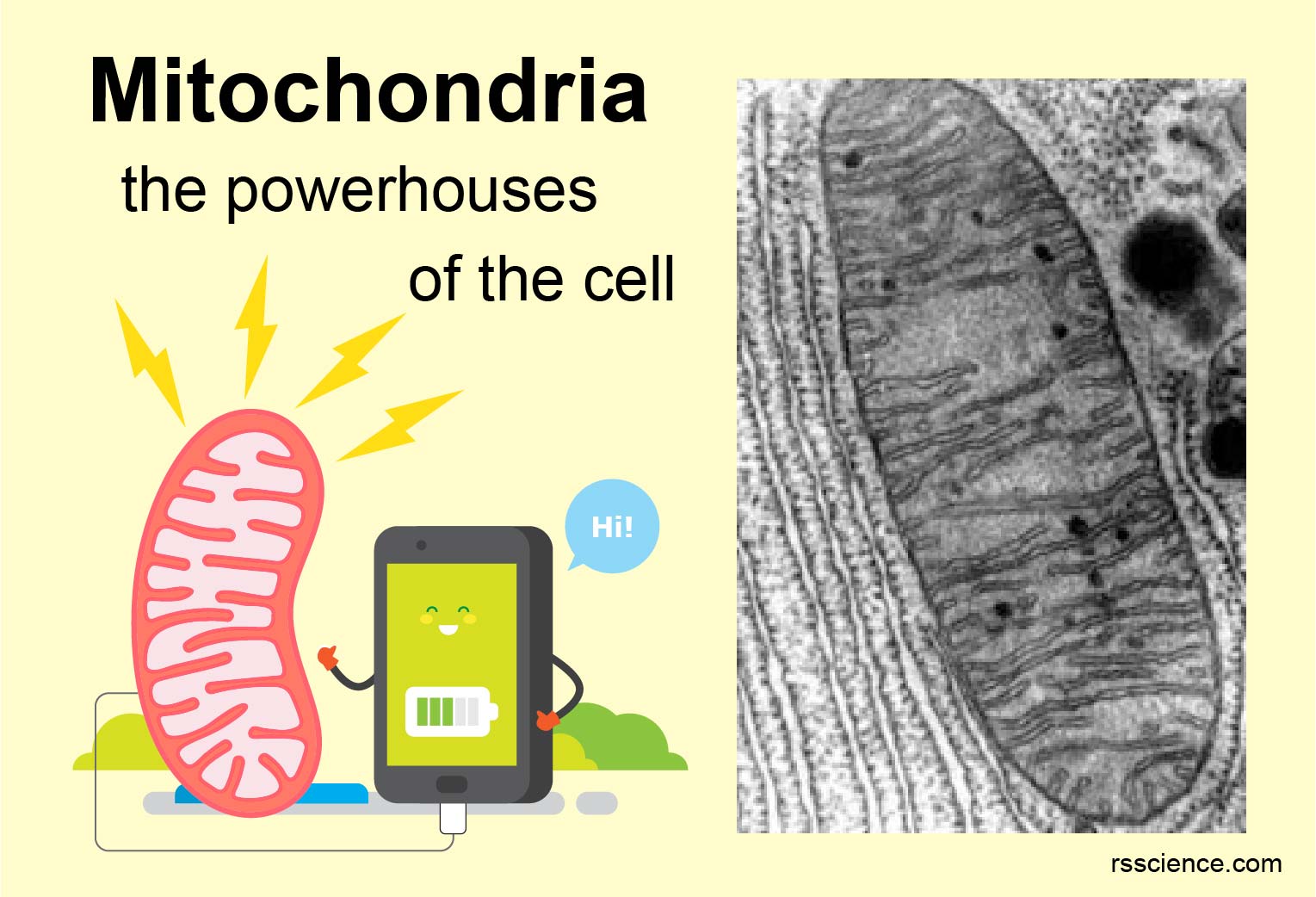



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Powerhouse Within: Unveiling the Crucial Role of Mitochondria in Everyday Life. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!