The Powerhouse Within: Mitochondria and Their Vital Role in Life
Related Articles: The Powerhouse Within: Mitochondria and Their Vital Role in Life
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Powerhouse Within: Mitochondria and Their Vital Role in Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Powerhouse Within: Mitochondria and Their Vital Role in Life

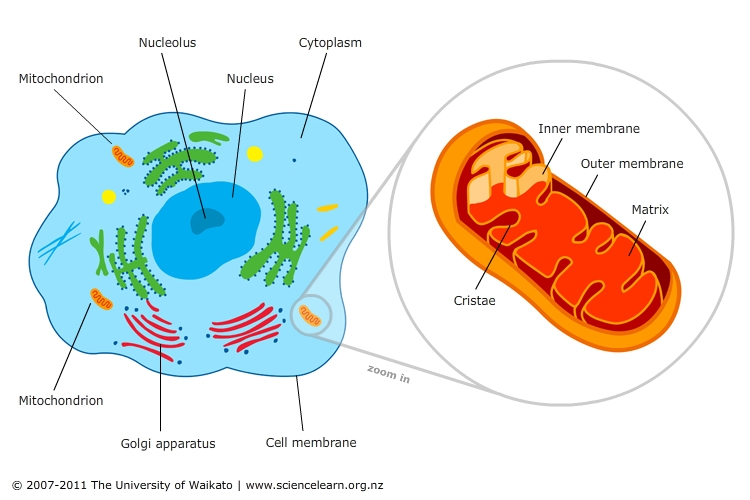
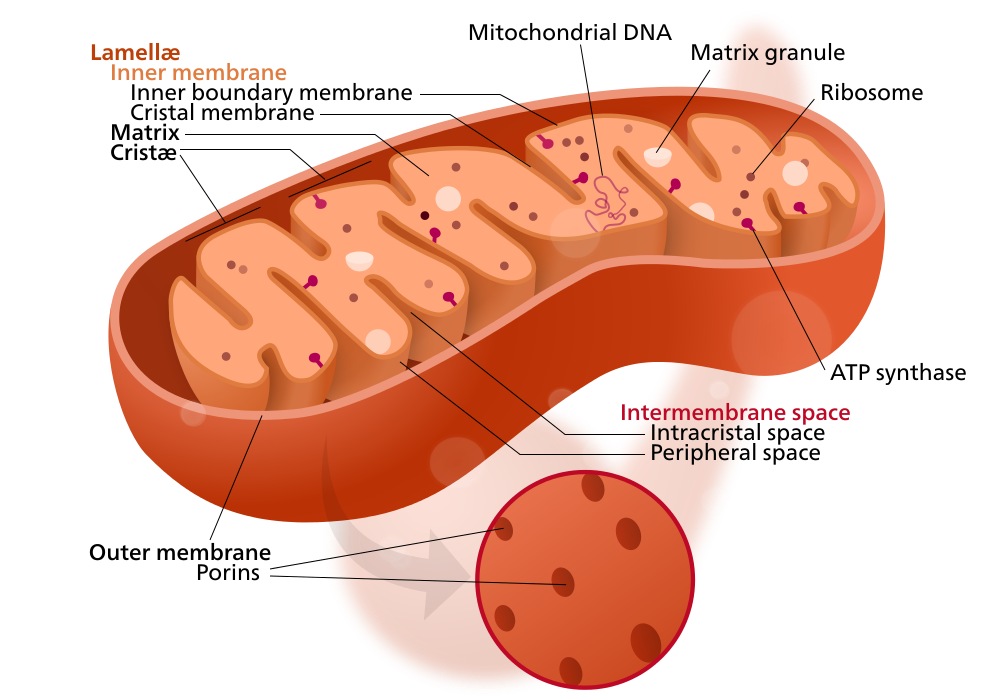
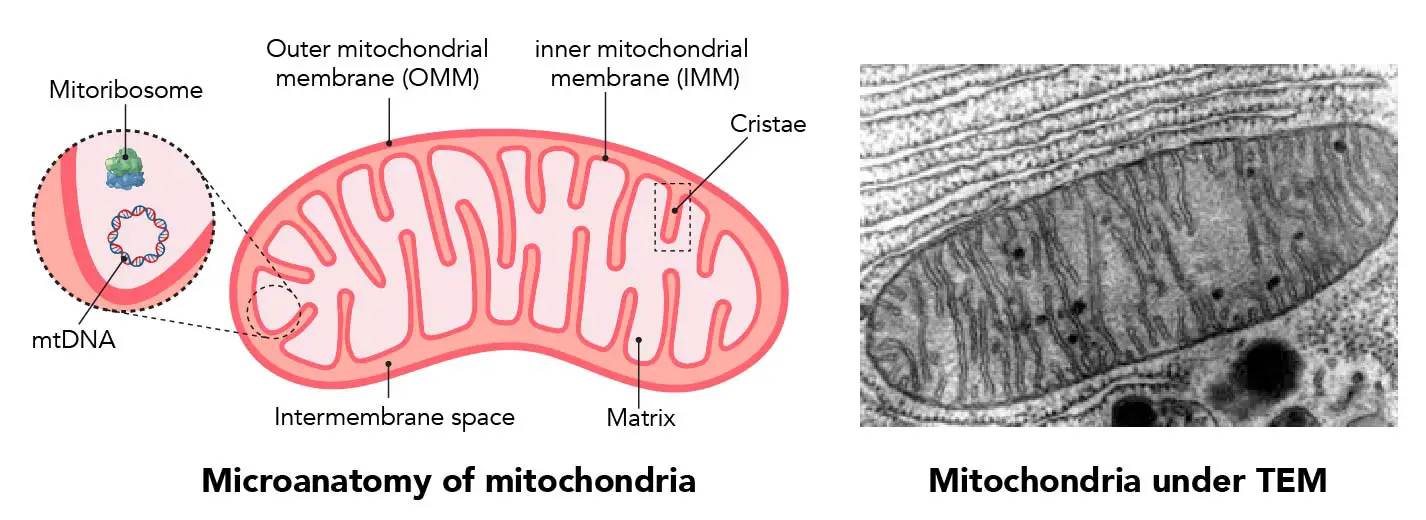
The human body is a marvel of intricate machinery, a complex system of interconnected parts working in harmony to sustain life. At the heart of this intricate system lies a tiny, yet powerful organelle known as the mitochondrion. Often referred to as the "powerhouse of the cell," mitochondria play a crucial role in cellular energy production, influencing a vast array of bodily functions.
Mitochondria: The Energy Generators of Life
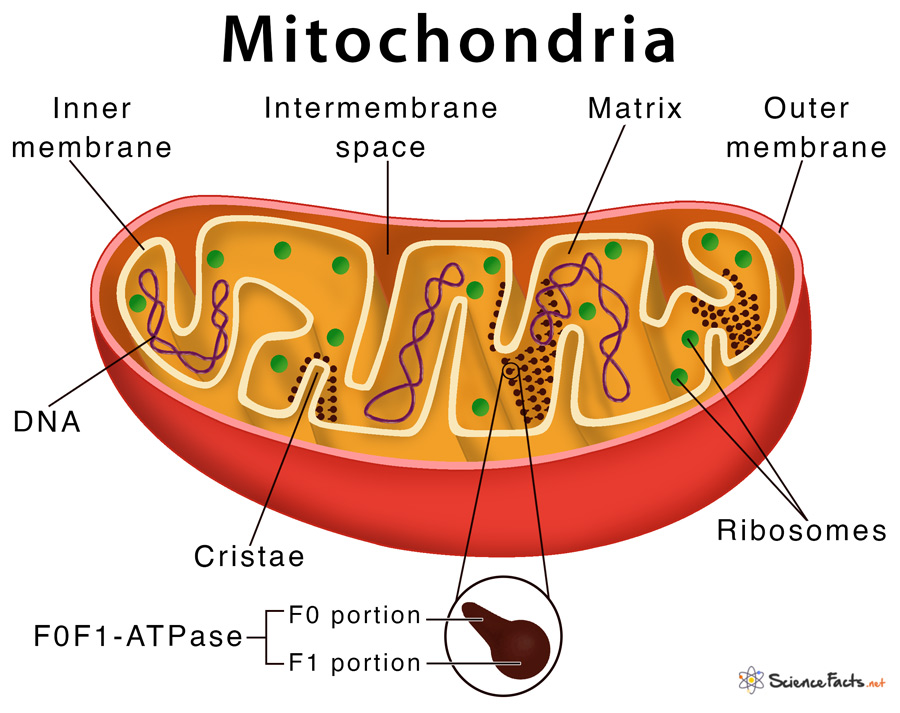
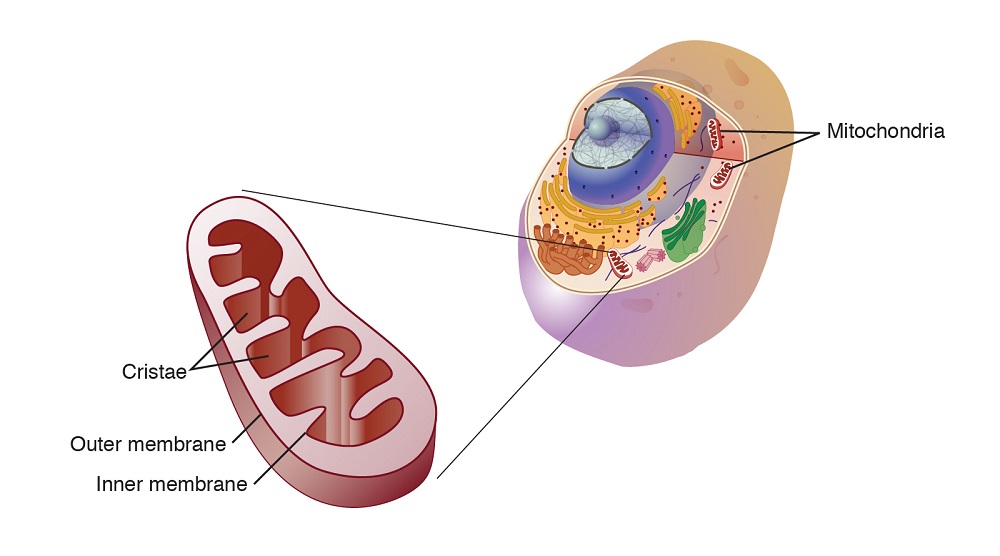
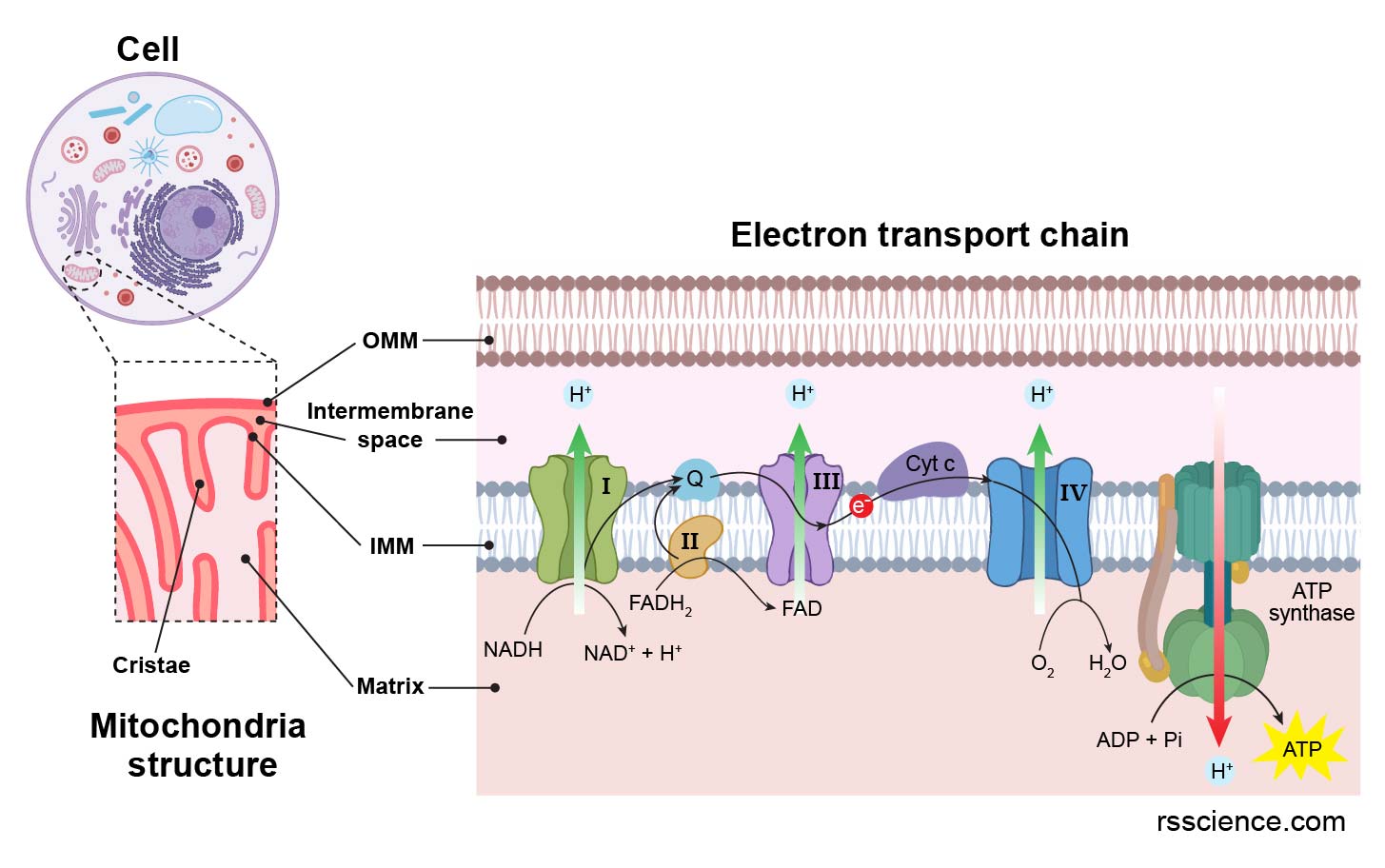
Mitochondria are ubiquitous in eukaryotic cells, the cells that form the basis of all complex organisms, including humans, animals, plants, and fungi. These tiny, bean-shaped structures are responsible for the majority of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, the primary energy currency of cells. Through a complex process known as oxidative phosphorylation, mitochondria break down nutrients, primarily glucose and fatty acids, to generate ATP, the fuel that powers cellular processes.
Beyond Energy Production: A Multifaceted Role
While their energy production role is paramount, mitochondria play a much broader role in cellular function. They are involved in:
- Cellular Signaling: Mitochondria communicate with other cellular components, influencing processes like cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis (programmed cell death).
- Calcium Homeostasis: They play a critical role in regulating intracellular calcium levels, essential for various cellular functions, including muscle contraction and neurotransmitter release.
- Cellular Defense: Mitochondria participate in cellular defense mechanisms, producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can fight off invading pathogens.
- Apoptosis: They are involved in the regulated death of cells, a crucial process for maintaining tissue health and preventing uncontrolled growth.
- Hormone Synthesis: Mitochondria contribute to the production of hormones like steroid hormones, vital for regulating various bodily functions.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Human Health
The vital role of mitochondria in cellular function makes them central to human health. Mitochondrial dysfunction, resulting from genetic mutations, environmental factors, or aging, can lead to a range of diseases and disorders.
- Mitochondrial Diseases: These are a group of inherited or acquired disorders affecting mitochondrial function. Symptoms can vary widely, ranging from muscle weakness and fatigue to severe neurological problems and developmental delays.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Mitochondrial dysfunction is implicated in the development of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, where neuronal death and dysfunction contribute to disease progression.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Mitochondrial dysfunction can affect heart function, contributing to heart failure and other cardiovascular problems.
- Cancer: Abnormal mitochondrial function can promote tumor growth and resistance to cancer therapies.
- Aging: Mitochondrial decline is a hallmark of aging, contributing to age-related decline in various tissues and organs.
Mitochondria and the Quest for Longevity
The link between mitochondrial function and health has sparked intense research into strategies to maintain mitochondrial health and prevent age-related decline. This research focuses on:
- Lifestyle Interventions: Exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management can promote mitochondrial function and improve overall health.
- Nutritional Supplements: Certain nutrients, like coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), have shown potential benefits in supporting mitochondrial function and preventing age-related decline.
- Pharmacological Approaches: Research is exploring drugs and therapies that target mitochondrial function to treat various diseases and promote healthy aging.
Mitochondria: A Symphony of Life
Mitochondria are not merely energy factories; they are intricate cellular components that orchestrate a symphony of life processes. Their vital role in energy production, cellular signaling, and defense makes them central to human health and longevity. Understanding the intricate workings of mitochondria holds immense potential for developing new therapies and interventions to combat diseases and promote healthy aging.
FAQs by Mitochondria Example in Real Life
Q1: What are the most common mitochondrial diseases?
A: There are many types of mitochondrial diseases, each with its own unique set of symptoms. Some of the most common include:
- Leigh Syndrome: A severe neurological disorder affecting the brain and central nervous system, often leading to developmental delays and death.
- Kearns-Sayre Syndrome: A rare disorder characterized by progressive muscle weakness, vision problems, and heart conduction defects.
- MELAS (Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic Acidosis, and Stroke-like Episodes): A disorder characterized by recurrent stroke-like episodes, muscle weakness, and lactic acidosis.
Q2: Can mitochondrial dysfunction be reversed?
A: While complete reversal of mitochondrial dysfunction may not always be possible, there are strategies that can improve mitochondrial function and mitigate its effects. These include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management can improve mitochondrial function.
- Nutritional Supplements: Certain nutrients, like CoQ10, have shown potential benefits in supporting mitochondrial health.
- Pharmacological Therapies: Research is exploring drugs that can target mitochondrial function and improve cellular energy production.
Q3: How can I protect my mitochondria from damage?
A: Protecting your mitochondria from damage involves adopting a healthy lifestyle:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis, increasing the number of mitochondria in cells.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients for mitochondrial function.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact mitochondrial function. Practicing stress reduction techniques like yoga or meditation can be beneficial.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: These habits can damage mitochondria and contribute to cellular dysfunction.
Tips by Mitochondria Example in Real Life
- Understand your family history: If you have a family history of mitochondrial diseases, it’s important to consult a genetic counselor to assess your risk.
- Seek medical attention for unexplained symptoms: If you experience unexplained fatigue, muscle weakness, or other symptoms, consult a doctor to rule out potential mitochondrial disorders.
- Embrace a healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can help protect your mitochondria and promote overall health.
- Stay informed: Keep up to date with the latest research on mitochondria and their role in health and disease.
Conclusion by Mitochondria Example in Real Life
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of our cells, playing a vital role in energy production, cellular signaling, and defense. Their dysfunction can lead to a range of diseases and disorders, highlighting the importance of maintaining mitochondrial health. By understanding the intricate workings of these tiny organelles and adopting healthy lifestyle choices, we can empower our cells and promote a life of vitality and well-being.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Powerhouse Within: Mitochondria and Their Vital Role in Life. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!