The Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS) Dilemma: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS) Dilemma: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS) Dilemma: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS) Dilemma: A Comprehensive Overview
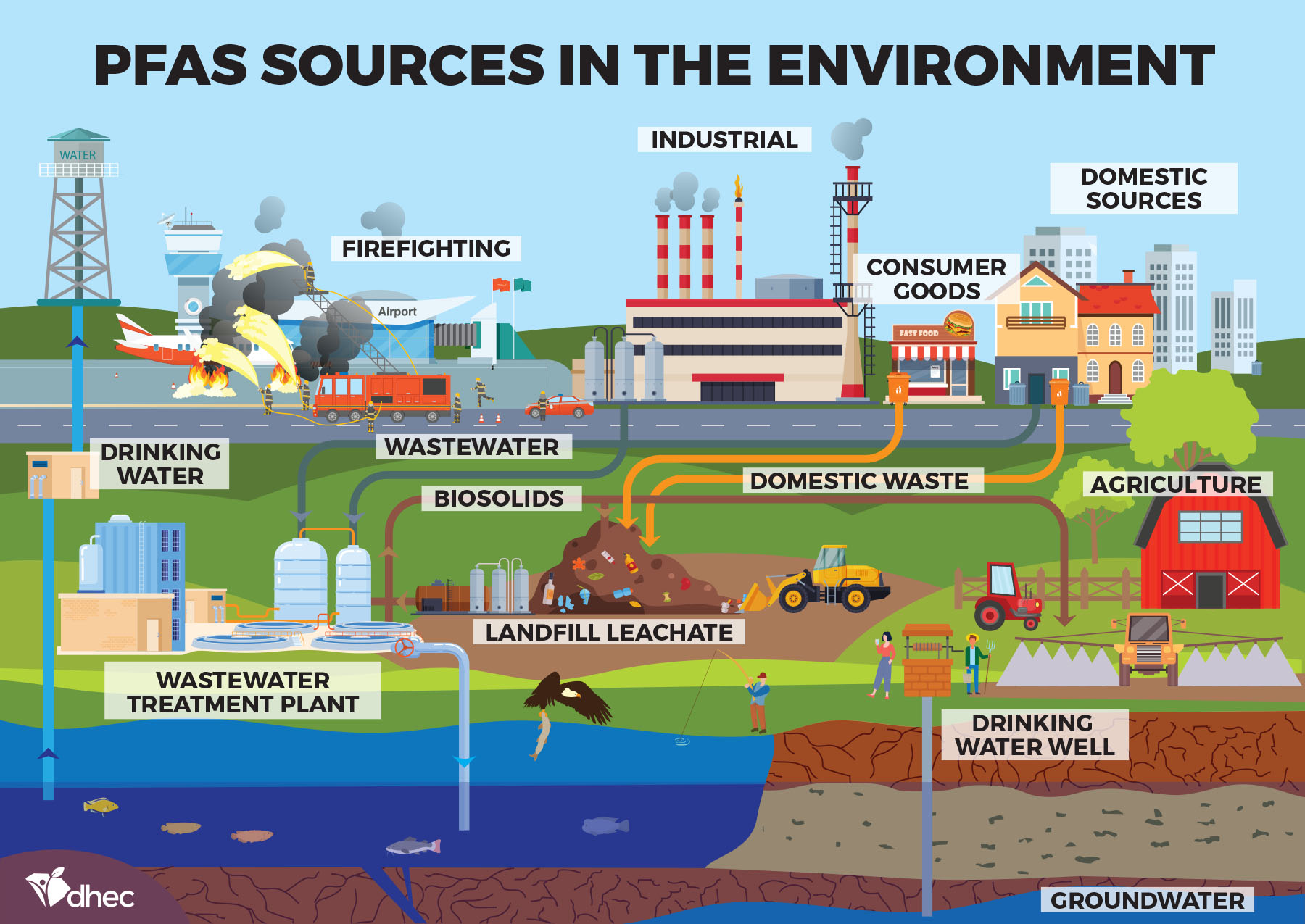
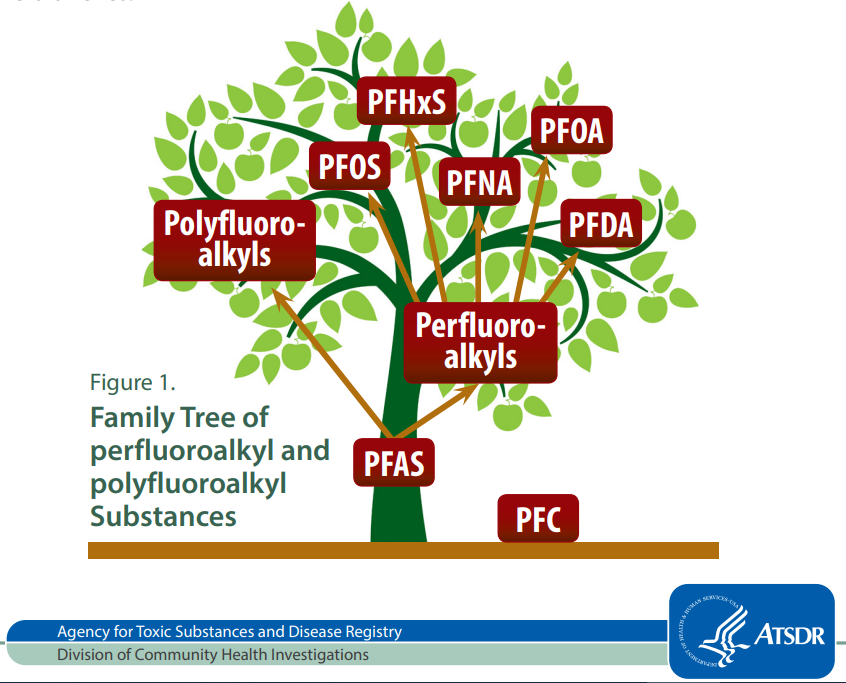
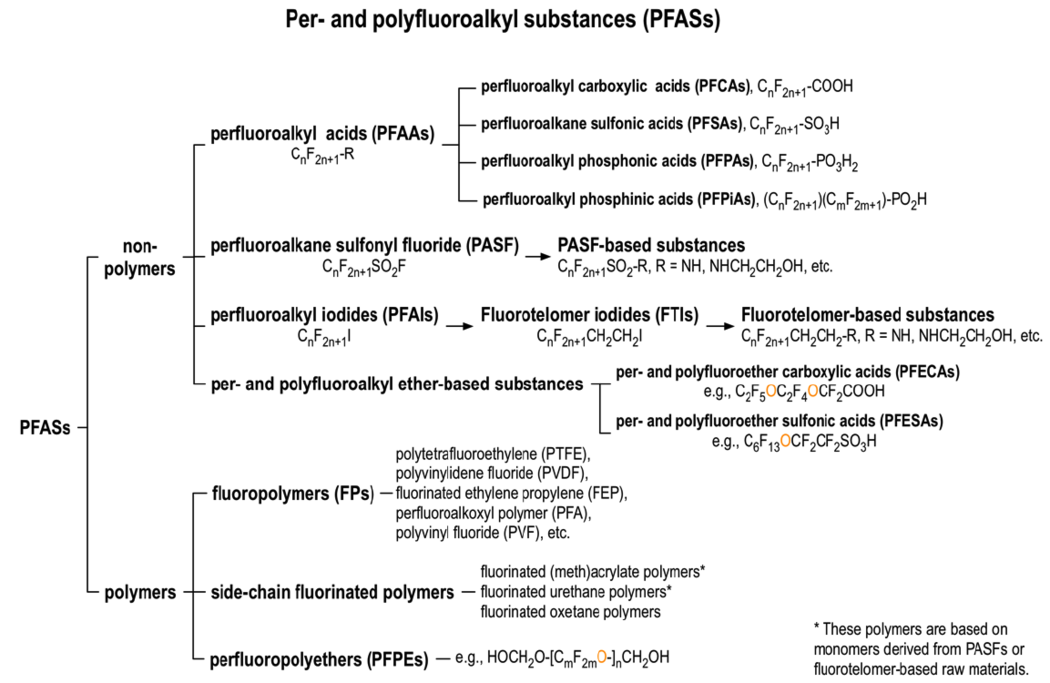
Perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of synthetic chemicals characterized by a unique carbon-fluorine bond that renders them incredibly stable and resistant to degradation. This very property, once hailed for its remarkable qualities, has now become the source of significant environmental and health concerns.
PFAS, also known as "forever chemicals," have been widely used in various industrial and consumer products due to their exceptional properties:
- Water and oil repellency: PFAS’s ability to repel both water and oil makes them ideal for applications like non-stick cookware, stain-resistant fabrics, and fire-fighting foams.
- Heat resistance: Their exceptional heat resistance makes them suitable for applications like food packaging, electrical insulation, and high-temperature lubricants.
- Chemical inertness: PFAS’s resistance to chemical reactions makes them useful in a wide range of applications, including paints, coatings, and medical devices.
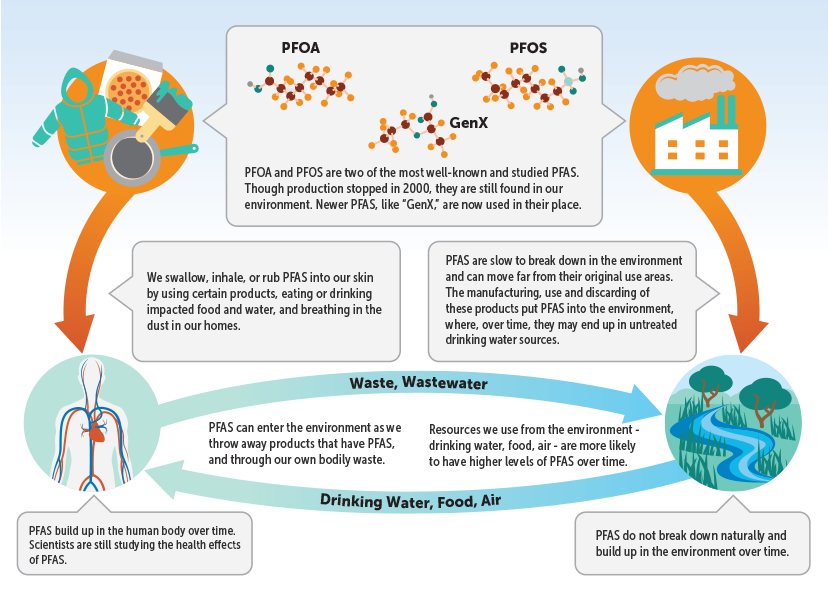
However, the very properties that make PFAS so desirable also make them a persistent environmental threat. Their non-degradable nature means they can accumulate in the environment, potentially contaminating water sources, soil, and even the food chain.
The Growing Concerns about PFAS
The ubiquitous presence of PFAS in various products has raised serious concerns about their potential health and environmental impacts.
Health Risks:
- Immune system suppression: Studies have linked PFAS exposure to weakened immune responses, potentially increasing susceptibility to infections and diseases.
- Hormonal disruption: Some PFAS have been shown to interfere with hormone regulation, potentially affecting reproductive health, thyroid function, and development.
- Liver and kidney problems: Long-term exposure to PFAS has been associated with liver damage, kidney dysfunction, and increased risk of certain cancers.
- Developmental effects: PFAS exposure during pregnancy has been linked to developmental problems in children, including low birth weight and developmental delays.
Environmental Impacts:
- Water contamination: PFAS can leach into water sources from industrial discharges, landfill leachates, and even household products.
- Soil contamination: PFAS can accumulate in soil, posing risks to plant growth and potentially contaminating groundwater.
- Bioaccumulation: PFAS can accumulate in the food chain, reaching high concentrations in animals and posing risks to human health through consumption.
The Quest for Alternatives
Recognizing the growing concerns, research and development efforts are underway to identify and implement safer alternatives to PFAS. These efforts focus on:
- Developing new chemistries: Scientists are actively exploring new compounds with similar functionalities to PFAS but without the environmental and health risks.
- Utilizing existing technologies: Existing technologies like silica-based coatings and fluoropolymer-free non-stick coatings are being investigated and refined for broader applications.
- Promoting sustainable practices: Initiatives are underway to minimize the use of PFAS in products and promote responsible disposal and recycling of PFAS-containing materials.
Understanding PFAS in Products
While the use of PFAS is widespread, it is crucial to understand where they are present in our daily lives. Here’s a breakdown of common product categories containing PFAS:
1. Food Packaging:
- Microwave popcorn bags: The "grease-resistant" properties of PFAS make them suitable for microwave popcorn bags, preventing the bag from becoming soggy.
- Fast food wrappers: Similar to popcorn bags, PFAS are used in fast food wrappers to prevent grease and oil from soaking through.
- Food containers: Some food containers, especially those designed for microwave use, may contain PFAS to enhance their durability and prevent food from sticking.
- Parchment paper: While not all parchment paper contains PFAS, some brands use it to enhance its non-stick properties.
2. Consumer Products:
- Non-stick cookware: The "Teflon" coating on non-stick cookware is a type of PFAS that allows for easy food release and cleaning.
- Stain-resistant carpets and fabrics: PFAS are incorporated into fabrics to make them stain-resistant and water-repellent, commonly found in carpets, upholstery, and clothing.
- Fire-fighting foams: PFAS are used in fire-fighting foams due to their ability to suppress flammable liquids and create a barrier between the fire and the fuel.
- Personal care products: Some cosmetics, shampoos, and lotions may contain PFAS to enhance their texture, water resistance, or stability.
3. Industrial Applications:
- Electronics: PFAS are used in electronics manufacturing for various purposes, including creating protective coatings, insulators, and lubricants.
- Aerospace: PFAS are used in aerospace applications due to their heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and low friction properties.
- Textile manufacturing: PFAS are used in textile manufacturing to create water-resistant and stain-resistant fabrics, including clothing, carpets, and upholstery.
- Construction: PFAS are used in construction materials like paints, coatings, and sealants for their water-repellent and weather-resistant properties.
FAQs about PFAS
Q: Are all PFAS harmful?
A: While some PFAS have been identified as posing potential health and environmental risks, others are considered safer. However, the overall consensus is that PFAS, as a group, require careful monitoring and management due to their persistence and potential for bioaccumulation.
Q: How can I reduce my exposure to PFAS?
A: There are several steps you can take to minimize your exposure to PFAS:
- Choose PFAS-free products: Look for products labeled as "PFAS-free" or "PFOA-free."
- Avoid using non-stick cookware at high temperatures: High heat can cause PFAS to leach from non-stick cookware.
- Wash food containers thoroughly: Wash food containers, especially those made of plastic, before using them to reduce the risk of PFAS leaching into food.
- Choose organic food: Organic food is less likely to be contaminated with PFAS from agricultural practices.
- Avoid using fire-fighting foams: If you come into contact with fire-fighting foam, wash your skin and clothing thoroughly.
Q: What are the current regulations on PFAS?
A: Regulations on PFAS are evolving globally. Many countries, including the United States and European Union, are implementing restrictions and monitoring programs to address PFAS contamination. These regulations focus on:
- Restricting the use of certain PFAS: Some countries have banned or restricted the use of specific PFAS in certain products.
- Setting limits for PFAS in drinking water: Many countries have established maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) for PFAS in drinking water.
- Promoting research and development of PFAS alternatives: Governments are investing in research and development efforts to identify and implement safer alternatives to PFAS.
Tips for Reducing PFAS Exposure
- Choose cookware with ceramic or stainless steel coatings: Opt for cookware with non-stick coatings that do not contain PFAS.
- Wash fabrics thoroughly before first use: Wash new carpets, upholstery, and clothing before using them to remove any PFAS residues.
- Use reusable water bottles and food containers: Avoid using single-use plastic water bottles and food containers, which may contain PFAS.
- Support legislation and regulations: Advocate for stricter regulations on PFAS to protect public health and the environment.
- Educate yourself and others: Spread awareness about the potential risks of PFAS and encourage others to take steps to reduce their exposure.
Conclusion
PFAS, despite their remarkable properties, pose significant environmental and health concerns. Their persistence and potential for bioaccumulation necessitate a proactive approach to minimize their use and mitigate their impacts. Ongoing research and development efforts are crucial to identify and implement safe alternatives to PFAS, while regulatory measures and consumer awareness play a vital role in safeguarding public health and the environment. By understanding the risks associated with PFAS, making informed choices about the products we use, and advocating for responsible policies, we can collectively work towards a future where these "forever chemicals" are no longer a threat to our well-being and the planet.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS) Dilemma: A Comprehensive Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!