The Palm Oil Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Products Derived from the Oil Palm
Related Articles: The Palm Oil Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Products Derived from the Oil Palm
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Palm Oil Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Products Derived from the Oil Palm. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Palm Oil Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Products Derived from the Oil Palm

The oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) stands as a remarkable botanical marvel, its fruit yielding a versatile oil that has woven itself into the fabric of countless products we use daily. This article delves into the diverse world of palm oil byproducts, exploring their applications, benefits, and the multifaceted role they play in our modern world.
A Versatile Oil: Unpacking the Properties of Palm Oil
Palm oil, extracted from the fleshy mesocarp of the oil palm fruit, is a unique oil characterized by its high content of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. This composition grants it a distinctive profile:
- High Stability: Palm oil’s unique fatty acid composition renders it highly resistant to oxidation, making it ideal for frying and other high-heat cooking applications. Its extended shelf life also minimizes spoilage, making it a favored ingredient in processed foods.
- Rich in Carotenoids: Palm oil is naturally rich in carotenoids, particularly beta-carotene, a precursor to Vitamin A. This attribute contributes to its vibrant orange hue and enhances its nutritional value.
- Versatile Texture: Palm oil’s unique melting point allows it to solidify at room temperature, offering a creamy texture that makes it suitable for various cosmetic and industrial applications.
Beyond the Oil: A Spectrum of Palm Oil Byproducts
While palm oil itself holds immense value, the oil palm offers a treasure trove of additional byproducts, each with its own unique applications and benefits. These byproducts transform the oil palm into a highly sustainable and economically valuable resource.
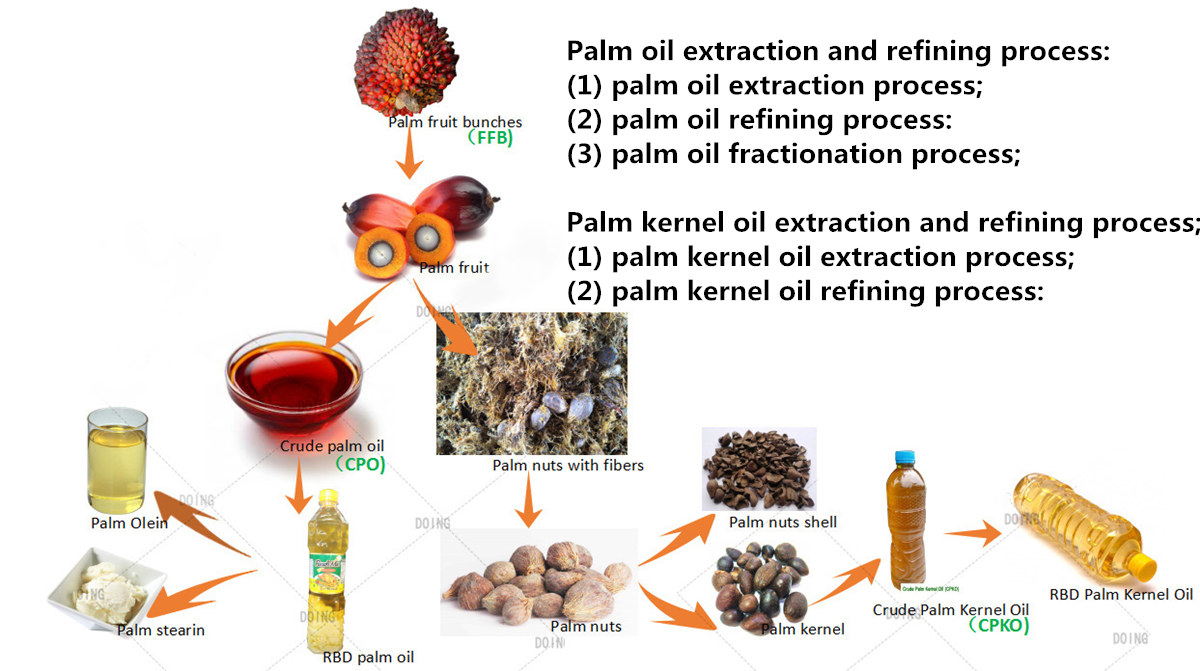
1. Palm Kernel Oil:
- Extraction: Palm kernel oil is extracted from the hard kernel within the oil palm fruit.
- Properties: This oil boasts a high lauric acid content, making it similar in composition to coconut oil. It possesses a mild flavor and a high smoke point, making it suitable for cooking and baking.
- Applications: Palm kernel oil finds use in various food applications, including margarine, shortening, and cooking oils. Its high lauric acid content also makes it ideal for personal care products like soaps, shampoos, and lotions.
2. Palm Kernel Cake:
- Source: The residue remaining after oil extraction from palm kernels is known as palm kernel cake.
- Composition: Palm kernel cake is rich in protein, fiber, and other nutrients, making it a valuable feed ingredient for livestock.
- Applications: It serves as a valuable source of protein and energy for cattle, pigs, poultry, and fish. Its high fiber content also contributes to improved digestion and overall animal health.
3. Palm Fiber:
- Origin: Palm fiber is extracted from the outer husk of the oil palm fruit.
- Properties: This fiber is strong, durable, and naturally resistant to moisture and pests.
- Applications: Palm fiber finds use in various industries. It serves as a reinforcement material in composites, providing strength and durability. It also finds application in packaging materials, rope production, and even as a sustainable alternative to synthetic fibers in textiles.
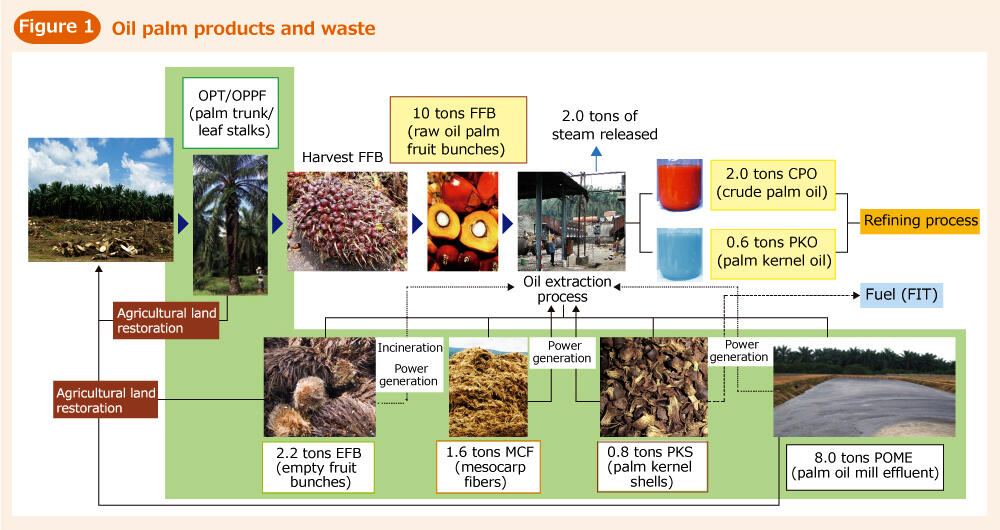
4. Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME):
- Source: POME is a liquid waste generated during palm oil extraction.
- Composition: POME is rich in organic matter, nutrients, and water.
- Applications: POME can be treated and utilized as a valuable fertilizer in agriculture. It also finds application in biogas production, providing a renewable energy source.
5. Palm Fronds:
- Source: The leaves of the oil palm are known as palm fronds.
- Uses: Palm fronds are traditionally used as roofing materials and for crafting baskets and other household items. They also find use as animal feed and in the production of biofuel.
6. Palm Shell:
- Source: The hard outer shell of the oil palm fruit is known as the palm shell.
- Applications: Palm shells are a valuable source of biochar, a charcoal-like material that enhances soil fertility and can be used as a sustainable fuel source. They also find application in the production of activated carbon, used in various industrial processes.
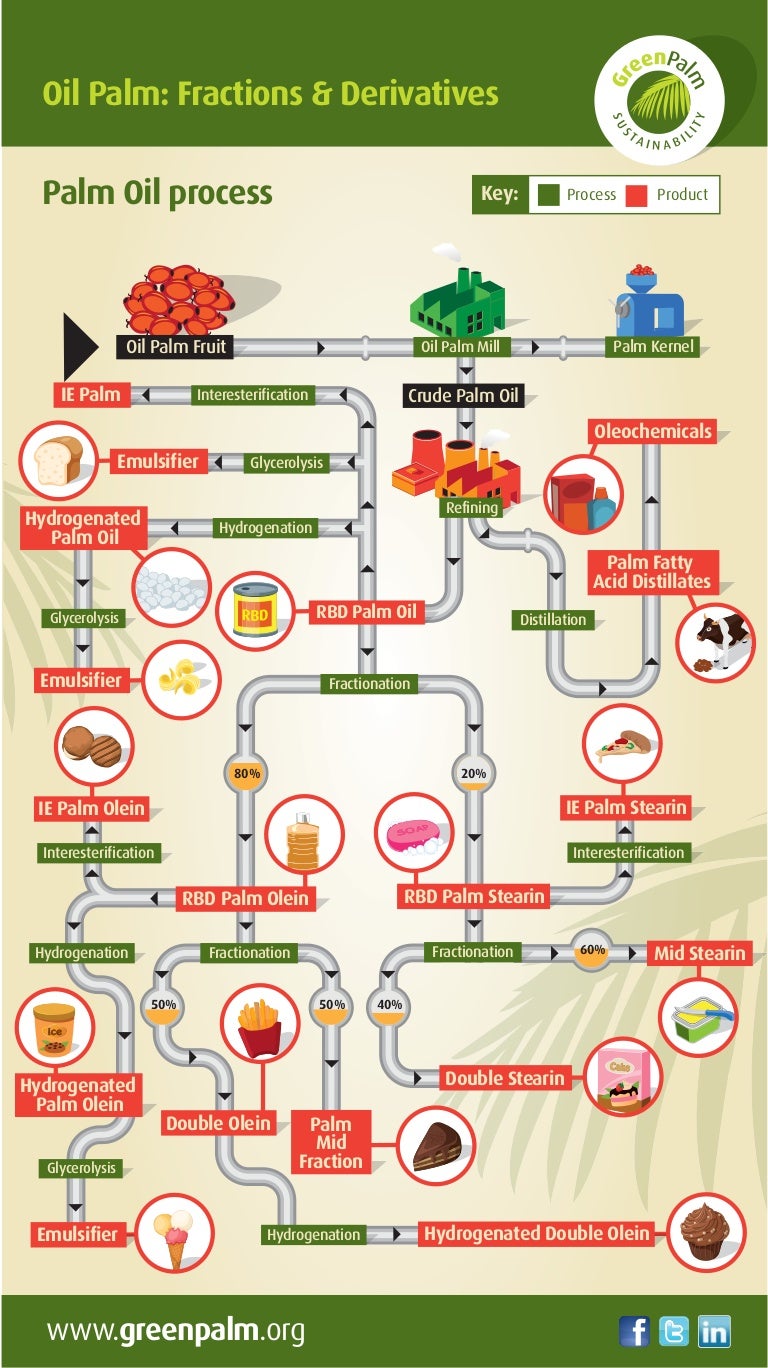
7. Palm Oil Glycerin:
- Source: Palm oil glycerin is a byproduct of the palm oil refining process.
- Properties: It is a humectant, meaning it attracts and retains moisture, making it valuable in cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications.
- Applications: Palm oil glycerin is commonly used in moisturizers, soaps, lotions, and other personal care products. It also finds use in food products as a humectant and sweetener.
8. Palm Oil Fatty Acids:
- Source: Palm oil fatty acids are derived from the hydrolysis of palm oil.
- Applications: These fatty acids are used in a wide range of industrial applications, including the production of soaps, detergents, and biolubricants.
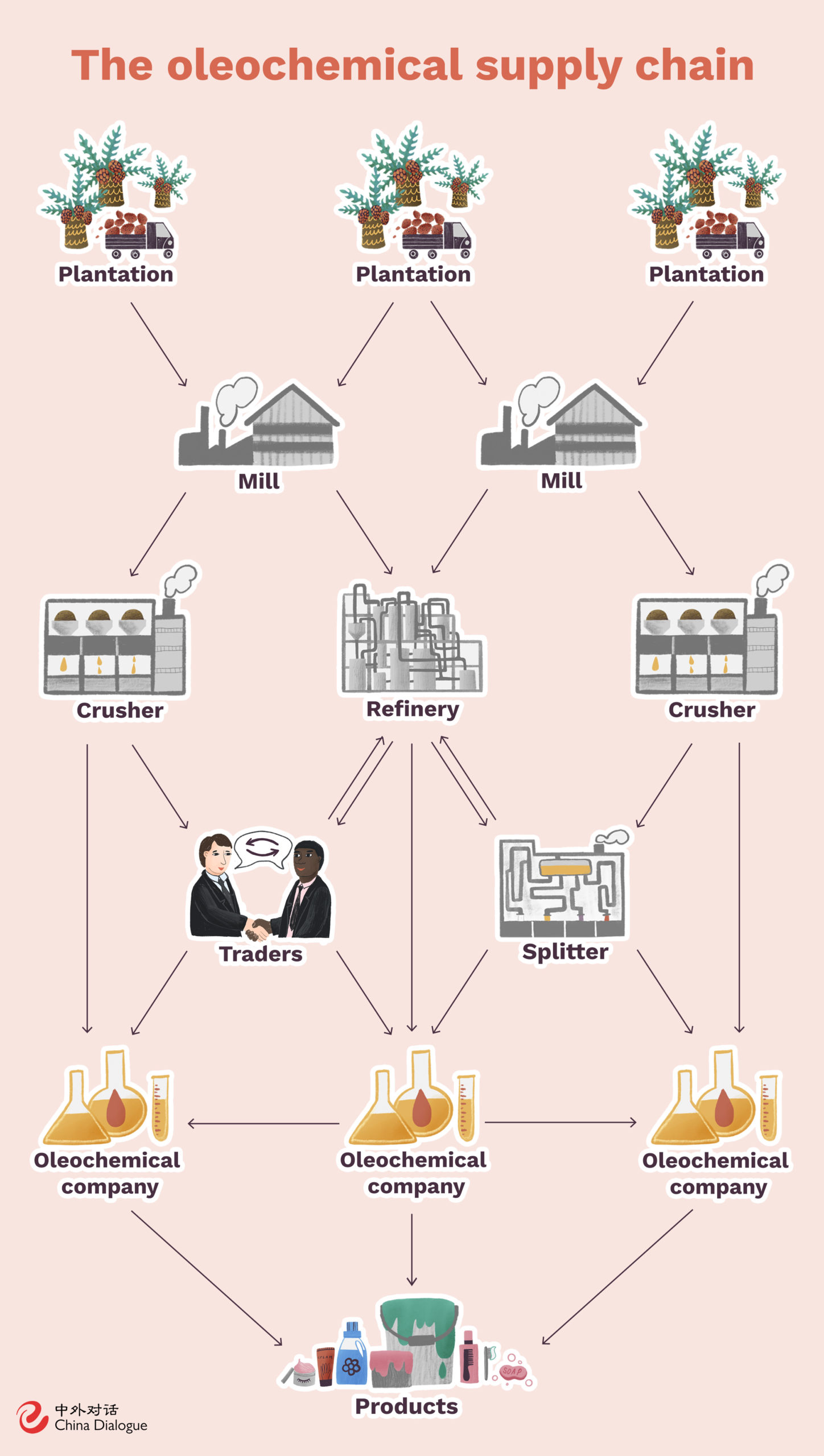
The Importance of Sustainable Palm Oil Production
The growing demand for palm oil and its byproducts has raised concerns about environmental sustainability. Unsustainable practices, such as deforestation and habitat destruction, can have devastating impacts on biodiversity and climate change.
Addressing Sustainability Challenges:
- Certification Schemes: Organizations like the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) have established certification schemes to promote sustainable palm oil production. These schemes require adherence to strict environmental and social standards, ensuring responsible sourcing and minimizing negative impacts.
- Sustainable Practices: Sustainable palm oil production involves practices like agroforestry, which integrates trees with crops, promoting biodiversity and soil health. Implementing responsible land management practices, such as minimizing deforestation and adopting sustainable harvesting methods, is crucial.
- Research and Innovation: Ongoing research and development are essential to identify and implement more sustainable palm oil production methods. This includes exploring alternative oil sources, developing new technologies for efficient oil extraction, and optimizing byproducts utilization.
FAQs about Palm Oil Byproducts:
1. Is palm oil bad for your health?
Palm oil, when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet, is not inherently bad for your health. However, excessive consumption of any type of oil, including palm oil, can contribute to weight gain and other health issues.
2. Is palm oil sustainable?
The sustainability of palm oil production depends heavily on the practices employed. Sustainable palm oil production adheres to strict environmental and social standards, minimizing negative impacts on biodiversity and the environment.
3. What are the alternatives to palm oil?
Alternatives to palm oil include other vegetable oils like soybean oil, sunflower oil, and rapeseed oil. However, each oil has its own unique properties and environmental impacts, making it essential to consider the entire supply chain and sustainability aspects.
4. What are the benefits of using palm oil byproducts?
Palm oil byproducts offer numerous benefits, including providing valuable feed for livestock, serving as raw materials for various industries, and contributing to renewable energy production.
5. How can I ensure that the palm oil products I buy are sustainable?
Look for products certified by organizations like the RSPO, which guarantee that the palm oil used is sourced sustainably and meets strict environmental and social standards.
Tips for Consumers:
- Choose certified sustainable palm oil products: Look for products bearing the RSPO or other reputable sustainability certifications.
- Consider alternatives: Explore alternative oils and ingredients that may be more sustainable or better suited for your needs.
- Support sustainable practices: Choose brands that prioritize sustainable palm oil production and responsible sourcing.
- Educate yourself: Stay informed about the environmental and social impacts of palm oil production and advocate for sustainable practices.
Conclusion:
The oil palm, with its diverse range of byproducts, presents a remarkable opportunity for sustainable development. By embracing responsible production practices and promoting the use of palm oil byproducts, we can unlock the full potential of this valuable resource while minimizing negative environmental and social impacts. As we navigate the complex landscape of palm oil production and consumption, prioritizing sustainability and informed choices will be crucial in ensuring a future where the benefits of this versatile resource are enjoyed by all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Palm Oil Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Products Derived from the Oil Palm. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!