The Invisible Threat: Unraveling the Sources of Carbon Monoxide
Related Articles: The Invisible Threat: Unraveling the Sources of Carbon Monoxide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Invisible Threat: Unraveling the Sources of Carbon Monoxide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Invisible Threat: Unraveling the Sources of Carbon Monoxide

Carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas, poses a significant threat to human health and the environment. While often associated with accidental poisoning, CO’s sources are diverse and pervasive, extending beyond the confines of our homes and workplaces. Understanding the origins of this insidious gas is crucial for mitigating its harmful effects and ensuring public safety.
Natural Sources: A Constant Presence
Nature itself contributes to the global carbon monoxide pool. Volcanic eruptions, wildfires, and the decomposition of organic matter release substantial amounts of CO into the atmosphere. These natural processes, while contributing to the overall CO burden, are often less controllable than anthropogenic sources.
Human Activities: The Dominant Factor
Human activities, particularly those related to energy production and transportation, are the primary contributors to CO emissions. These sources, while often preventable, are responsible for the majority of CO exposure and its associated health risks.
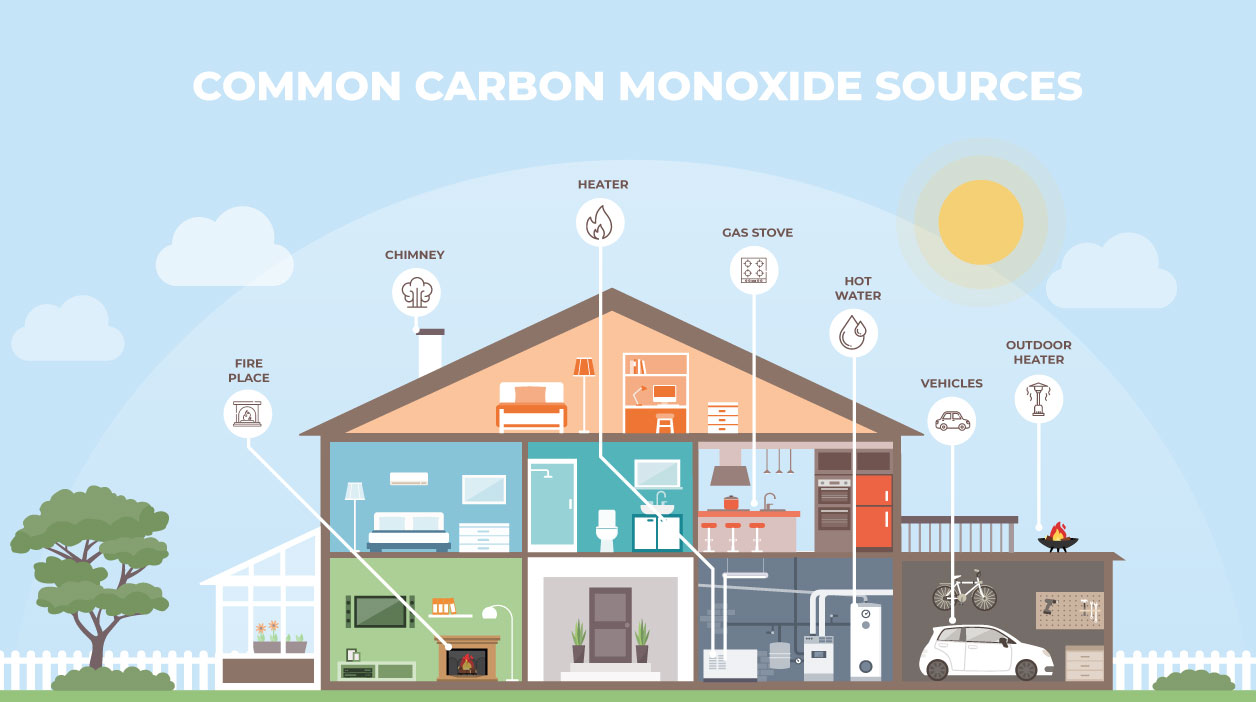
1. Combustion: The Heart of CO Production
Combustion, the process of burning fuel to release energy, is the most significant source of CO. This occurs in various settings, each contributing to the overall CO burden:
- Fossil Fuel Power Plants: These facilities rely on burning coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity, releasing substantial amounts of CO as a byproduct.
- Internal Combustion Engines: Vehicles powered by gasoline or diesel engines are major CO emitters. Incomplete combustion within these engines leads to the release of CO into the exhaust.
- Industrial Processes: Many industries, including manufacturing, metal production, and chemical processing, involve combustion processes that release CO.
- Residential Heating and Cooking: Burning fuels like wood, propane, and natural gas for heating and cooking in homes and businesses also contributes to CO emissions.
2. Transportation: A Mobile Source of CO
The transportation sector plays a crucial role in CO emissions, with road vehicles being the primary contributor. The incomplete combustion of fuel in internal combustion engines, especially in older or poorly maintained vehicles, leads to significant CO release. Other transportation sources, including ships, airplanes, and trains, also contribute to the global CO pool.
3. Agriculture: A Complex Source
Agricultural activities, while often associated with greenhouse gas emissions, also contribute to CO production. The burning of agricultural waste, livestock manure, and crop residues, along with the use of fertilizers, release CO into the atmosphere.
4. Waste Management: A Hidden Source
Waste management practices, particularly the burning of municipal solid waste and the decomposition of organic matter in landfills, contribute to CO emissions. These processes release CO as a byproduct, adding to the overall burden.
Understanding the Importance of CO Reduction
Carbon monoxide, while often overlooked, poses a significant threat to human health and the environment. Exposure to CO can lead to a range of adverse health effects, including:
- Cardiovascular Issues: CO reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, leading to heart strain and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Respiratory Problems: CO exposure can exacerbate respiratory conditions like asthma and emphysema, leading to shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
- Neurological Damage: CO can affect the brain, leading to headaches, dizziness, confusion, and even coma in severe cases.
- Developmental Effects: Exposure to CO during pregnancy can have detrimental effects on fetal development, leading to low birth weight and other health problems.
Beyond Human Health: Environmental Impacts
The impact of CO extends beyond human health, affecting the environment in several ways:
- Climate Change: While CO’s atmospheric lifetime is relatively short compared to other greenhouse gases, it contributes to global warming by absorbing infrared radiation, trapping heat in the atmosphere.
- Air Pollution: CO is a major component of smog, contributing to poor air quality and respiratory problems in urban areas.
- Ozone Formation: CO reacts with other pollutants in the atmosphere to form ozone, a harmful air pollutant that damages human lungs and vegetation.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: What are the symptoms of CO poisoning?
A: Symptoms of CO poisoning vary depending on the severity of exposure. Mild symptoms include headache, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. Severe exposure can lead to confusion, disorientation, loss of consciousness, and even death.
Q: How can I prevent CO poisoning in my home?
A: To prevent CO poisoning, ensure proper ventilation when using fuel-burning appliances, have your appliances inspected regularly, and install CO detectors in your home.
Q: What are the most effective ways to reduce CO emissions?
A: Reducing CO emissions requires a multifaceted approach, including promoting energy efficiency, transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving vehicle fuel economy, and implementing stricter emission standards for industries.
Tips: Reducing Your Exposure to CO
- Maintain Appliances: Regularly inspect and maintain fuel-burning appliances like furnaces, water heaters, and stoves to ensure proper operation and prevent CO leaks.
- Ventilate Properly: Ensure adequate ventilation when using fuel-burning appliances, opening windows or using exhaust fans.
- Install CO Detectors: Install CO detectors in your home and test them regularly.
- Choose Low-Emission Vehicles: Consider purchasing fuel-efficient vehicles or electric vehicles to reduce CO emissions from transportation.
- Support Renewable Energy: Advocate for the development and deployment of renewable energy sources to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Conclusion: A Collective Responsibility
Reducing carbon monoxide emissions requires a collaborative effort from individuals, businesses, and governments. By understanding the sources of CO, implementing preventive measures, and promoting sustainable practices, we can mitigate the risks posed by this invisible threat and create a healthier and safer environment for all. The fight against CO is not just about reducing its harmful effects; it’s about protecting our health, preserving our environment, and ensuring a sustainable future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Invisible Threat: Unraveling the Sources of Carbon Monoxide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!