The Enigma of Shift Letters by Number: A Comprehensive Exploration of Cryptographic Substitution
Related Articles: The Enigma of Shift Letters by Number: A Comprehensive Exploration of Cryptographic Substitution
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Enigma of Shift Letters by Number: A Comprehensive Exploration of Cryptographic Substitution. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Enigma of Shift Letters by Number: A Comprehensive Exploration of Cryptographic Substitution
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Enigma of Shift Letters by Number: A Comprehensive Exploration of Cryptographic Substitution
- 3.1 Understanding the Basics: A Shift in Perspective
- 3.2 The Caesar Cipher: A Historical Precedent
- 3.3 Beyond the Caesar Cipher: Exploring Variations
- 3.4 The Enduring Legacy: From Ancient Times to Modern Cryptography
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Implementation
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Foundational Step in the Evolution of Cryptography
- 4 Closure
The Enigma of Shift Letters by Number: A Comprehensive Exploration of Cryptographic Substitution
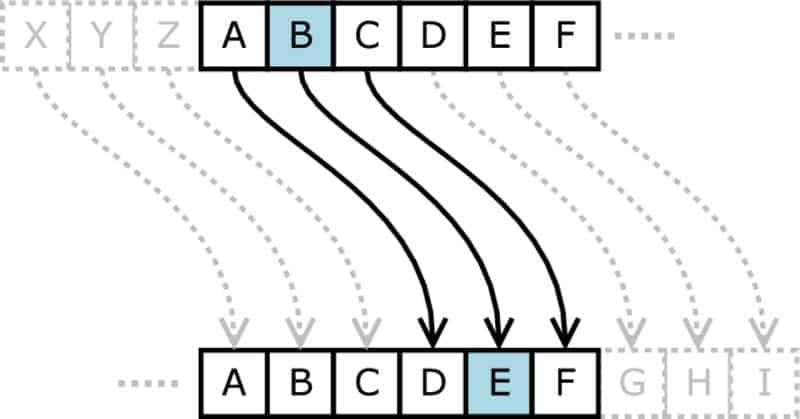
The realm of cryptography, the art and science of secure communication, is replete with fascinating techniques that have been employed throughout history to protect sensitive information. Among these, the concept of "shift letters by number" stands out as a fundamental and versatile method of substitution, laying the groundwork for more complex encryption algorithms. This exploration delves into the core principles of shift letters by number, unraveling its mechanics, applications, and historical significance, while illuminating its enduring influence on modern cryptography.
Understanding the Basics: A Shift in Perspective
At its essence, "shift letters by number" involves systematically shifting the letters of a message according to a predetermined numerical value. This numerical value, known as the "key," dictates the magnitude of the shift, determining how many positions each letter is moved within the alphabet. For instance, a key of 3 would shift "A" to "D", "B" to "E", and so on, creating a simple yet effective substitution cipher.
To illustrate, let’s consider the phrase "HELLO WORLD" and apply a key of 3:
- Original: HELLO WORLD
- Shifted: KHOOR ZRUOG
This seemingly straightforward process of letter shifting forms the bedrock of several cryptographic techniques, including the renowned Caesar cipher, which employs a fixed key of 3.
The Caesar Cipher: A Historical Precedent
The Caesar cipher, named after the Roman emperor Gaius Julius Caesar, is perhaps the most famous example of shift letters by number. Used for military communication during Caesar’s time, this cipher relied on a simple shift of three positions, effectively substituting "A" with "D", "B" with "E", and so on. While rudimentary by modern standards, the Caesar cipher offered a degree of secrecy in an era devoid of sophisticated encryption methods.
The simplicity of the Caesar cipher, however, also makes it vulnerable to cryptanalysis. By analyzing the frequency of letter occurrences in the ciphertext, one can easily deduce the key and decipher the original message. This inherent weakness prompted the development of more robust substitution ciphers, where the key is not fixed but rather varies throughout the message.
Beyond the Caesar Cipher: Exploring Variations
Shift letters by number, however, extends beyond the confines of the Caesar cipher. Variations on this fundamental concept have been devised throughout history, enhancing its complexity and cryptographic strength.
One notable variation is the affine cipher, which introduces a mathematical function to the shifting process. Instead of simply shifting letters by a fixed number, the affine cipher uses a combination of multiplication and addition, further obscuring the relationship between plaintext and ciphertext. This enhanced complexity makes the affine cipher more resistant to brute-force attacks, requiring a more sophisticated approach to cryptanalysis.
Another variation involves the use of a polyalphabetic cipher, where multiple keys are employed throughout the message. This technique, exemplified by the Vigenère cipher, introduces a level of unpredictability, making it significantly more challenging to decipher. Instead of using a single key, the Vigenère cipher employs a keyword, where each letter in the keyword corresponds to a different shift value, creating a dynamic and complex substitution pattern.
The Enduring Legacy: From Ancient Times to Modern Cryptography
The concept of shift letters by number, despite its apparent simplicity, has left an indelible mark on the evolution of cryptography. It provided the foundational principles for more intricate ciphers, paving the way for the development of modern encryption algorithms.
Modern cryptographic techniques, like the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), while significantly more complex, still draw inspiration from the fundamental principles of substitution. AES, a widely used encryption standard, operates on a block of data, applying a series of complex transformations, including substitution, to scramble the information. This intricate process, while vastly different from the simple letter shifts of the Caesar cipher, underscores the enduring legacy of this foundational cryptographic concept.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
1. Can shift letters by number be used for secure communication today?
While shift letters by number served as a rudimentary form of encryption in the past, its simplicity makes it easily breakable by modern cryptanalytic techniques. Therefore, it is not recommended for secure communication in contemporary environments.
2. How can I decipher a message encrypted with shift letters by number?
Deciphering a message encrypted using shift letters by number involves identifying the key used for the shift. This can be achieved through various methods, including frequency analysis, brute-force attacks, and pattern recognition.
3. Are there any practical applications for shift letters by number in the modern world?
While not suitable for secure communication, shift letters by number can be used for educational purposes, teaching basic cryptographic principles and demonstrating the evolution of encryption techniques. Additionally, its simplicity makes it a useful tool for creating puzzles and games, enhancing logic and problem-solving skills.
Tips for Effective Implementation
1. Utilize variable keys: To enhance security, avoid using a fixed key for all messages. Vary the key for each communication, introducing unpredictability and making cryptanalysis more challenging.
2. Employ multiple layers of encryption: Combine shift letters by number with other cryptographic techniques, such as transposition ciphers, to create a more robust encryption scheme.
3. Limit the length of messages: Shorter messages are less susceptible to cryptanalysis, as they provide less data for attackers to analyze.
4. Understand the limitations: Recognize that shift letters by number is a rudimentary technique and should not be relied upon for sensitive communication in modern environments.
Conclusion: A Foundational Step in the Evolution of Cryptography
The concept of shift letters by number, though seemingly simple, holds profound significance in the history of cryptography. It served as a stepping stone, laying the groundwork for more sophisticated techniques that have transformed the way we communicate securely in the digital age. While its limitations are evident in the modern context, its contribution to the development of modern encryption algorithms is undeniable. Understanding the principles of shift letters by number provides a valuable foundation for appreciating the complexities and advancements in cryptography, a field that continues to evolve and adapt to the ever-changing landscape of information security.





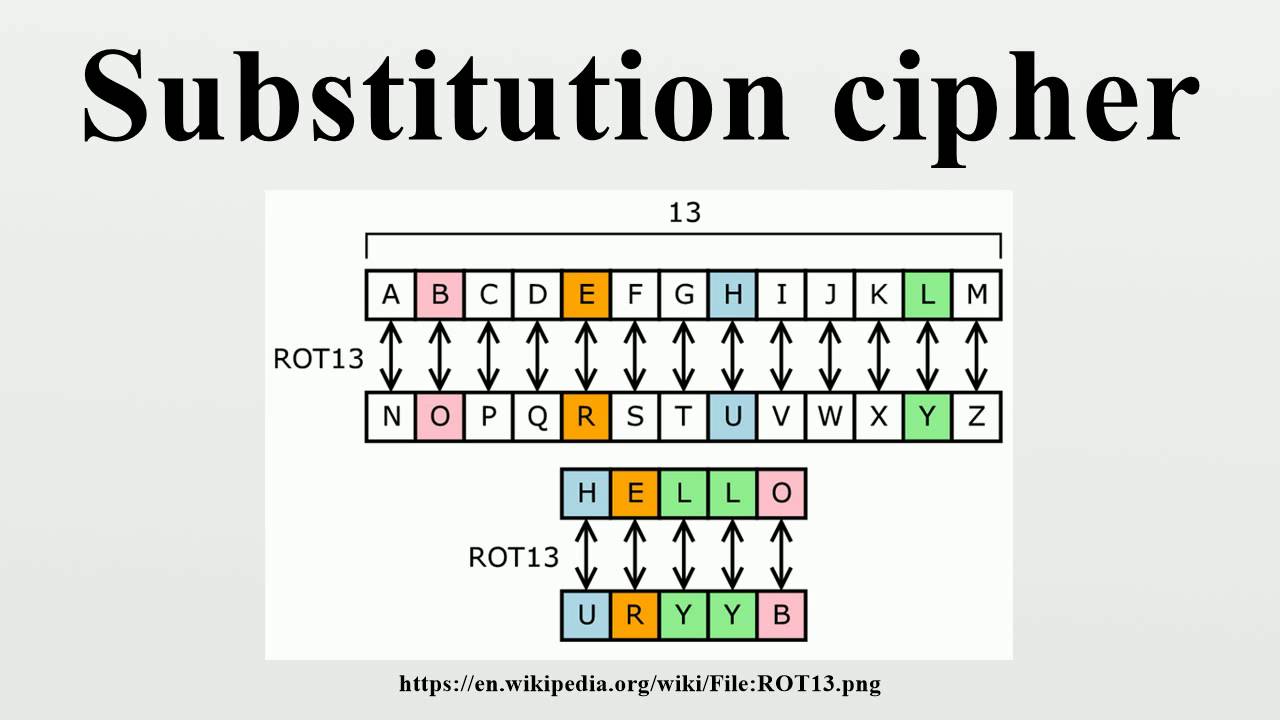
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enigma of Shift Letters by Number: A Comprehensive Exploration of Cryptographic Substitution. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!