The Enduring Power of Metal: A Comprehensive Look at Metal Products in Modern Life
Related Articles: The Enduring Power of Metal: A Comprehensive Look at Metal Products in Modern Life
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Enduring Power of Metal: A Comprehensive Look at Metal Products in Modern Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enduring Power of Metal: A Comprehensive Look at Metal Products in Modern Life
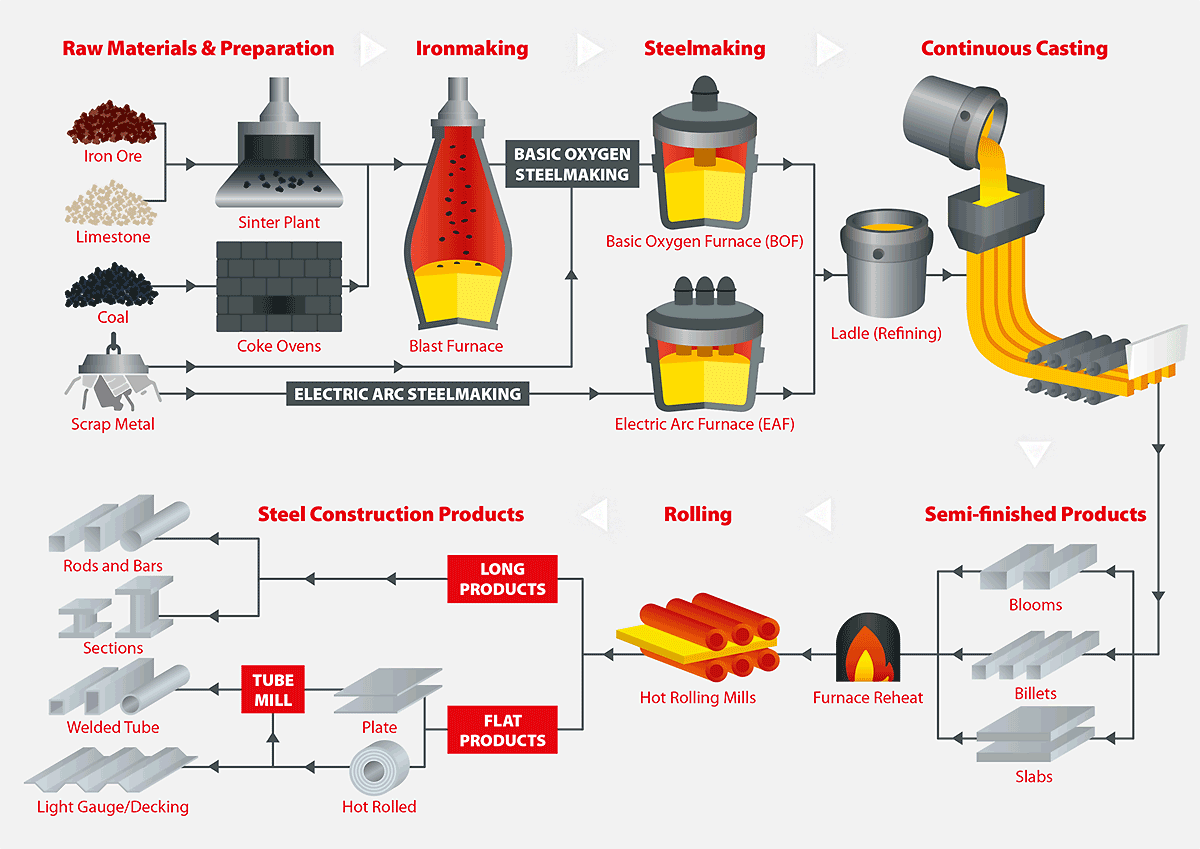
Metals, with their inherent strength, durability, and versatility, have been indispensable to human civilization for millennia. From the dawn of the Bronze Age to the modern age of advanced alloys, metal products have shaped our world, driving technological advancements and enhancing our quality of life. This article delves into the diverse applications of metals, exploring their unique properties and the myriad products they enable.
The Metal Spectrum: A Journey Through Properties and Applications
Metals, a diverse class of elements, possess a unique combination of properties that make them invaluable in various industries. Their inherent characteristics, such as malleability, ductility, and conductivity, coupled with their resistance to corrosion and high melting points, contribute to their widespread use.
1. Ferrous Metals: The Backbone of Construction and Industry
Iron, the most abundant metal on Earth, forms the foundation of the ferrous metal family. Its strength, durability, and affordability make it a cornerstone of construction and heavy industry. Steel, an alloy of iron and carbon, further enhances these properties, resulting in its ubiquitous presence in buildings, bridges, automobiles, and machinery.
a) Steel: The Workhorse of Modern Civilization
Steel, with its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio and adaptability, finds applications in an astonishing array of products. From the towering skyscrapers that define our urban landscapes to the intricate components of medical instruments, steel’s versatility knows no bounds.
-
Construction: Steel’s high tensile strength and resistance to compression make it ideal for constructing buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects. Its ability to be formed into various shapes and sizes further enhances its value in construction.
-
Automotive: Steel’s durability and ability to withstand high temperatures make it a primary material for car bodies, chassis, and engine components. Its recyclability further contributes to its sustainability in automotive manufacturing.
-
Machinery: Steel’s resilience and resistance to wear and tear make it a critical component in industrial machinery, tools, and equipment. Its ability to be hardened and tempered allows for the creation of durable and precise tools for various applications.
b) Cast Iron: The Durable and Affordable Choice
Cast iron, known for its high compressive strength and affordability, finds extensive use in various applications. Its ability to be easily cast into intricate shapes makes it ideal for producing cookware, pipes, and engine blocks.
-
Cookware: Cast iron’s excellent heat retention and distribution make it a preferred material for cooking pots, pans, and skillets. Its durability and ability to develop a natural patina with use enhance its value for cooking enthusiasts.
-
Pipes and Fittings: Cast iron’s resistance to corrosion and pressure makes it a reliable material for water and gas pipes, as well as fittings and valves. Its durability ensures long-term performance and reduces the need for frequent replacements.
-
Engine Blocks: Cast iron’s ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures makes it a suitable material for engine blocks, providing structural integrity and durability.
2. Non-Ferrous Metals: A Spectrum of Properties and Applications
Non-ferrous metals, encompassing a wide range of elements, exhibit unique properties that make them valuable in various applications. Their resistance to corrosion, excellent conductivity, and malleability contribute to their importance in electronics, aerospace, and medical industries.
a) Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Aluminum, known for its lightweight and excellent corrosion resistance, has become a ubiquitous material in various industries. Its ability to be easily formed and recycled makes it a sustainable and versatile choice.
-
Aerospace: Aluminum’s high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to fatigue make it a critical component in aircraft construction, contributing to fuel efficiency and overall performance.
-
Packaging: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance and ability to be easily molded make it a preferred material for beverage cans, food containers, and other packaging applications. Its recyclability further contributes to its environmental sustainability.
-
Building Materials: Aluminum’s lightweight and corrosion resistance make it ideal for window frames, siding, and other building materials, contributing to energy efficiency and aesthetic appeal.
b) Copper: The Conductor of Electricity and Heat
Copper, renowned for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, plays a crucial role in various applications, from electrical wiring to plumbing. Its resistance to corrosion and malleability further enhance its value.
-
Electrical Wiring: Copper’s high electrical conductivity makes it the preferred material for electrical wiring, ensuring efficient and reliable energy transmission. Its durability and resistance to corrosion ensure long-term performance.
-
Plumbing: Copper’s resistance to corrosion and its ability to withstand high temperatures make it a reliable material for plumbing pipes, fittings, and valves. Its durability and longevity contribute to its value in plumbing systems.
-
Industrial Applications: Copper’s excellent thermal conductivity makes it valuable in heat exchangers, radiators, and other industrial applications where efficient heat transfer is crucial.
c) Gold: The Precious Metal with Diverse Applications
Gold, a highly valuable and inert metal, has been prized for its beauty and durability for centuries. Its resistance to corrosion and its ability to be easily worked into intricate designs make it a valuable material in jewelry, electronics, and dentistry.
-
Jewelry: Gold’s lustrous appearance and resistance to tarnishing make it a timeless and treasured material for jewelry, from rings and necklaces to intricate ornaments. Its durability ensures that gold jewelry can be passed down through generations.
-
Electronics: Gold’s excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion make it a valuable material in electronic components, such as connectors, contacts, and integrated circuits. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and currents ensures reliable performance.
-
Dentistry: Gold’s biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion make it a valuable material for dental fillings, crowns, and other dental applications. Its durability and aesthetic appeal contribute to its value in dentistry.
d) Silver: The Reflective and Conductive Metal
Silver, known for its high reflectivity and electrical conductivity, finds applications in various industries, from photography to electronics. Its resistance to corrosion and its ability to be easily worked into intricate shapes further enhance its value.
-
Photography: Silver’s sensitivity to light makes it a crucial component in photographic film and printing processes, capturing images and creating lasting memories. Its ability to react with light allows for the creation of photographic images.
-
Electronics: Silver’s high electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion make it a valuable material in electronic components, such as contacts, connectors, and integrated circuits. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and currents ensures reliable performance.
-
Mirrors: Silver’s high reflectivity makes it an ideal material for mirrors, reflecting light and creating images. Its durability and resistance to tarnishing ensure long-lasting performance.
3. Specialty Metals: Tailored for Performance and Precision
Specialty metals, often alloys with unique compositions, are designed for specific applications where demanding performance requirements are paramount. Their exceptional properties, such as high strength, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance, make them essential in aerospace, medical, and energy industries.
a) Titanium: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Titanium, a lightweight and corrosion-resistant metal, is prized for its high strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility. It finds applications in aerospace, medical implants, and industrial equipment.
-
Aerospace: Titanium’s high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to fatigue make it a critical component in aircraft construction, contributing to fuel efficiency and overall performance. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures makes it ideal for jet engines and other high-stress components.
-
Medical Implants: Titanium’s biocompatibility and resistance to corrosion make it a suitable material for medical implants, such as artificial joints, dental implants, and surgical instruments. Its durability and ability to integrate with bone tissue contribute to its value in medical applications.
-
Industrial Equipment: Titanium’s resistance to corrosion and its ability to withstand extreme temperatures make it valuable in industrial equipment, such as chemical processing plants, power generation facilities, and oil and gas exploration.
b) Nickel: The Versatile and Corrosion-Resistant Alloy
Nickel, a highly corrosion-resistant metal, is often used in alloys to enhance their properties. Its resistance to corrosion, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures make it valuable in various industries.
-
Stainless Steel: Nickel is a key component in stainless steel alloys, contributing to their corrosion resistance, strength, and durability. Stainless steel’s versatility makes it ideal for applications ranging from kitchen sinks and cutlery to medical instruments and industrial equipment.
-
Superalloys: Nickel-based superalloys are known for their exceptional strength, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance. They are used in high-performance applications, such as jet engine components, gas turbines, and nuclear reactors.
-
Coinage: Nickel is often used in coinage alloys, contributing to their durability and resistance to wear and tear. Its affordability and resistance to corrosion make it a suitable material for coins.
c) Tungsten: The Dense and Heat-Resistant Metal
Tungsten, a dense and heat-resistant metal, is known for its high melting point and exceptional strength. Its unique properties make it valuable in various industries, from lighting to aerospace.
-
Lighting: Tungsten’s high melting point and ability to emit light make it a critical component in incandescent light bulbs. Its durability and resistance to high temperatures ensure long-lasting performance.
-
Aerospace: Tungsten’s high density and strength make it a valuable material for counterweights, radiation shielding, and other aerospace applications. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures makes it ideal for high-performance applications.
-
Industrial Applications: Tungsten’s high melting point and hardness make it valuable in tools, dies, and other industrial applications where resistance to wear and tear is crucial.
4. The Future of Metal: Advanced Alloys and Emerging Applications
As technology advances, the demand for metals with unique properties continues to grow. Research and development efforts focus on creating advanced alloys with tailored properties for specific applications.
-
High-Entropy Alloys: These alloys, composed of multiple elements in near-equal proportions, exhibit exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance. They hold promise for applications in aerospace, automotive, and energy industries.
-
Metallic Glasses: These amorphous alloys, with their unique atomic structure, exhibit exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. They have potential applications in medical implants, electronics, and aerospace.
-
Shape Memory Alloys: These alloys, capable of returning to their original shape after deformation, find applications in actuators, sensors, and medical devices. Their ability to respond to temperature changes makes them valuable in various applications.
FAQs about Metal Products
Q: What are the benefits of using metal products?
A: Metal products offer numerous benefits, including:
-
Strength and Durability: Metals are known for their high strength and durability, making them suitable for structural applications and resisting wear and tear.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Many metals are resistant to corrosion, ensuring long-term performance and reducing maintenance costs.
-
Conductivity: Metals are excellent conductors of heat and electricity, making them valuable in electrical wiring, heating systems, and other applications.
-
Malleability and Ductility: Many metals can be easily formed and shaped, allowing for the creation of intricate designs and complex products.
-
Recyclability: Metals are highly recyclable, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Q: What are some common metal products used in everyday life?
A: Metal products are ubiquitous in our daily lives, ranging from:
-
Construction: Buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure rely heavily on steel and other metals.
-
Transportation: Automobiles, airplanes, and ships utilize metals extensively for their structural integrity and durability.
-
Electronics: Computers, smartphones, and other electronic devices contain various metals for their electrical conductivity and heat dissipation.
-
Household Appliances: Refrigerators, washing machines, and other appliances often utilize metals for their durability and resistance to corrosion.
-
Cookware: Pots, pans, and other cookware are frequently made from metals like stainless steel, cast iron, and aluminum for their heat conductivity and durability.
Q: What are some of the environmental considerations associated with metal production?
A: Metal production can have environmental impacts, including:
-
Mining: Mining for metal ores can result in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution.
-
Energy Consumption: Metal production requires significant energy consumption, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Waste Generation: Metal production can generate waste, including slag, dust, and hazardous materials.
Tips for Choosing Metal Products
-
Consider the Application: Choose metals with properties suitable for the specific application, considering strength, corrosion resistance, conductivity, and other factors.
-
Evaluate Sustainability: Opt for metals with high recyclability and low environmental impact.
-
Seek Certifications: Look for certifications, such as LEED or Cradle to Cradle, indicating sustainable practices in metal production.
-
Support Responsible Sourcing: Choose products made from metals sourced from responsible and ethical mining operations.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Metal
Metals, with their inherent strength, versatility, and durability, continue to play a crucial role in modern life. Their applications range from the towering skyscrapers that define our cities to the intricate components of medical devices that improve our health. As technology advances, the demand for metals with unique properties continues to grow, driving innovation in alloy development and expanding the possibilities of metal applications. By understanding the properties and applications of metals, we can make informed choices about the products we use, ensuring their performance, sustainability, and impact on our world.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enduring Power of Metal: A Comprehensive Look at Metal Products in Modern Life. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!