The Alkaline Corner of Our Homes: Unveiling the Importance of Bases in Everyday Objects
Related Articles: The Alkaline Corner of Our Homes: Unveiling the Importance of Bases in Everyday Objects
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Alkaline Corner of Our Homes: Unveiling the Importance of Bases in Everyday Objects. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Alkaline Corner of Our Homes: Unveiling the Importance of Bases in Everyday Objects
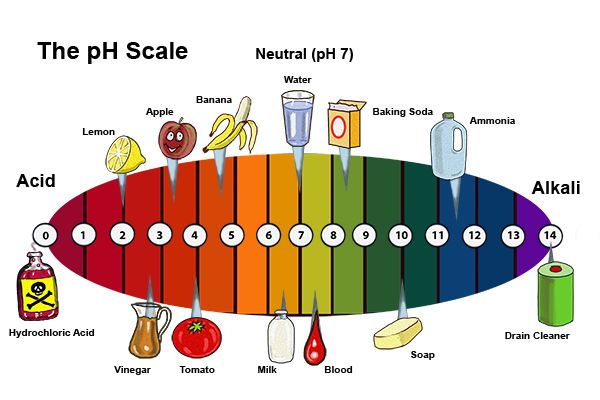
The world of chemistry, while often perceived as complex and abstract, plays a vital role in our daily lives. One key concept, often encountered in everyday objects, is that of bases. Bases, in essence, are chemical compounds that produce hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water. These ions contribute to a solution’s alkalinity, which is measured on the pH scale. While we may not always be aware of their presence, bases are essential components of numerous household items, contributing to their functionality and our overall well-being.
This article will delve into the realm of two commonly found household items that contain bases: baking soda and soap. These seemingly simple substances play crucial roles in various aspects of our lives, from cleaning and cooking to personal hygiene and even health maintenance.
Baking Soda: A Multifaceted Household Essential
Baking soda, chemically known as sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), is a white crystalline powder that has earned its place as a staple in many kitchens and households. It is a weak base, meaning it does not readily release hydroxide ions in solution. However, its ability to react with acids and release carbon dioxide gas makes it a versatile ingredient in various applications.
Culinary Uses: Baking soda is a crucial leavening agent in baking, reacting with acidic ingredients like buttermilk or lemon juice to produce carbon dioxide bubbles, resulting in light and airy baked goods. Its ability to neutralize acidity also makes it useful in reducing the bitterness of vegetables during cooking.
Cleaning and Deodorizing: Baking soda’s mild alkalinity makes it an effective cleaning agent for various surfaces. It can be used to scrub away stains, deodorize refrigerators and carpets, and even clean greasy dishes. Its ability to absorb odors makes it a popular choice for freshening up rooms and removing unpleasant smells from surfaces.
Health and Beauty: Baking soda’s mild abrasive properties make it a safe and effective ingredient in toothpastes and mouthwashes, helping to remove plaque and whiten teeth. It can also be used as a natural deodorant, absorbing moisture and neutralizing odor-causing bacteria.
Beyond the Kitchen: Baking soda’s versatility extends beyond the kitchen and bathroom. Its ability to neutralize acids makes it useful in treating insect stings and bee stings, providing temporary relief from pain and itching. It can also be used in homemade antacids to alleviate heartburn and indigestion.
Soap: Cleansing Our Way to Cleanliness
Soap, a product we encounter daily in various forms, is another household item that relies on the principles of bases. Soap is created through a process called saponification, where fats or oils are reacted with a strong base, typically sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH). This reaction breaks down the fats into fatty acid salts, which are the primary components of soap.
Cleansing Action: Soap’s cleansing power stems from its ability to interact with both water and grease. The fatty acid molecules in soap have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-fearing) tail. When soap comes into contact with water, the hydrophilic heads orient themselves towards the water molecules, while the hydrophobic tails are repelled by water.
This arrangement allows soap to form micelles, spherical structures with the hydrophobic tails pointing inwards, effectively encapsulating grease and dirt molecules. These micelles, being soluble in water, can then be easily rinsed away, leaving surfaces clean.
Beyond Cleaning: Soap’s uses extend beyond basic cleaning. It plays a crucial role in personal hygiene, removing dirt, sweat, and microorganisms from our bodies. Soap is also a key ingredient in shampoos, conditioners, and other personal care products, helping to cleanse and moisturize our hair and skin.
Understanding the Importance of Bases
The presence of bases in these everyday items highlights their vital role in our daily lives. Baking soda and soap, while seemingly simple, offer a wide range of benefits, contributing to our well-being, hygiene, and even our culinary experiences.
FAQs
Q: What are the potential risks associated with using baking soda and soap?
A: While both baking soda and soap are generally safe for household use, excessive or improper use can lead to certain risks.
Baking soda:
- Skin irritation: Direct contact with baking soda can cause irritation, dryness, or redness for individuals with sensitive skin.
- Ingestion: Ingesting large amounts of baking soda can lead to digestive issues, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Inhalation: Inhaling baking soda dust can irritate the respiratory system, especially in individuals with asthma or other respiratory conditions.
Soap:
- Skin irritation: Some individuals may experience skin irritation or allergic reactions to certain soap ingredients, such as fragrances or dyes.
- Eye irritation: Contact with soap in the eyes can cause irritation and stinging.
Q: How can I ensure safe and effective use of baking soda and soap?
A: To minimize risks and maximize benefits, follow these guidelines:
Baking soda:
- Use sparingly: Use baking soda in moderation, especially on sensitive skin.
- Dilute properly: When using baking soda for cleaning or personal care, dilute it with water to reduce its alkalinity.
- Avoid contact with eyes: Avoid getting baking soda in your eyes. If it does, rinse immediately with clean water.
Soap:
- Choose mild soaps: Select soaps formulated for sensitive skin if you have allergies or skin sensitivities.
- Rinse thoroughly: Rinse soap off your skin and hair thoroughly to avoid irritation or residue.
- Avoid contact with eyes: Avoid getting soap in your eyes. If it does, rinse immediately with clean water.
Tips
Baking soda:
- Deodorizing: Sprinkle baking soda in your refrigerator, shoes, or garbage disposal to absorb odors.
- Cleaning: Use baking soda to scrub stains from countertops, sinks, and bathtubs.
- Baking: Use baking soda in combination with acidic ingredients to create light and airy baked goods.
Soap:
- Cleaning: Use soap to wash dishes, clothes, and surfaces.
- Personal hygiene: Use soap to wash your hands, body, and hair.
- DIY cleaning solutions: Combine soap with water and other natural ingredients to create homemade cleaning solutions.
Conclusion
Understanding the presence of bases in everyday items like baking soda and soap allows us to appreciate their crucial role in our lives. From enhancing our culinary experiences to ensuring our hygiene and well-being, these seemingly simple substances play a vital role in our daily routines. By understanding their properties and using them safely and effectively, we can harness their benefits and improve our overall quality of life.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Alkaline Corner of Our Homes: Unveiling the Importance of Bases in Everyday Objects. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!