Shielding from the Invisible Threat: Understanding and Mitigating Alpha Particle Radiation
Related Articles: Shielding from the Invisible Threat: Understanding and Mitigating Alpha Particle Radiation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Shielding from the Invisible Threat: Understanding and Mitigating Alpha Particle Radiation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shielding from the Invisible Threat: Understanding and Mitigating Alpha Particle Radiation
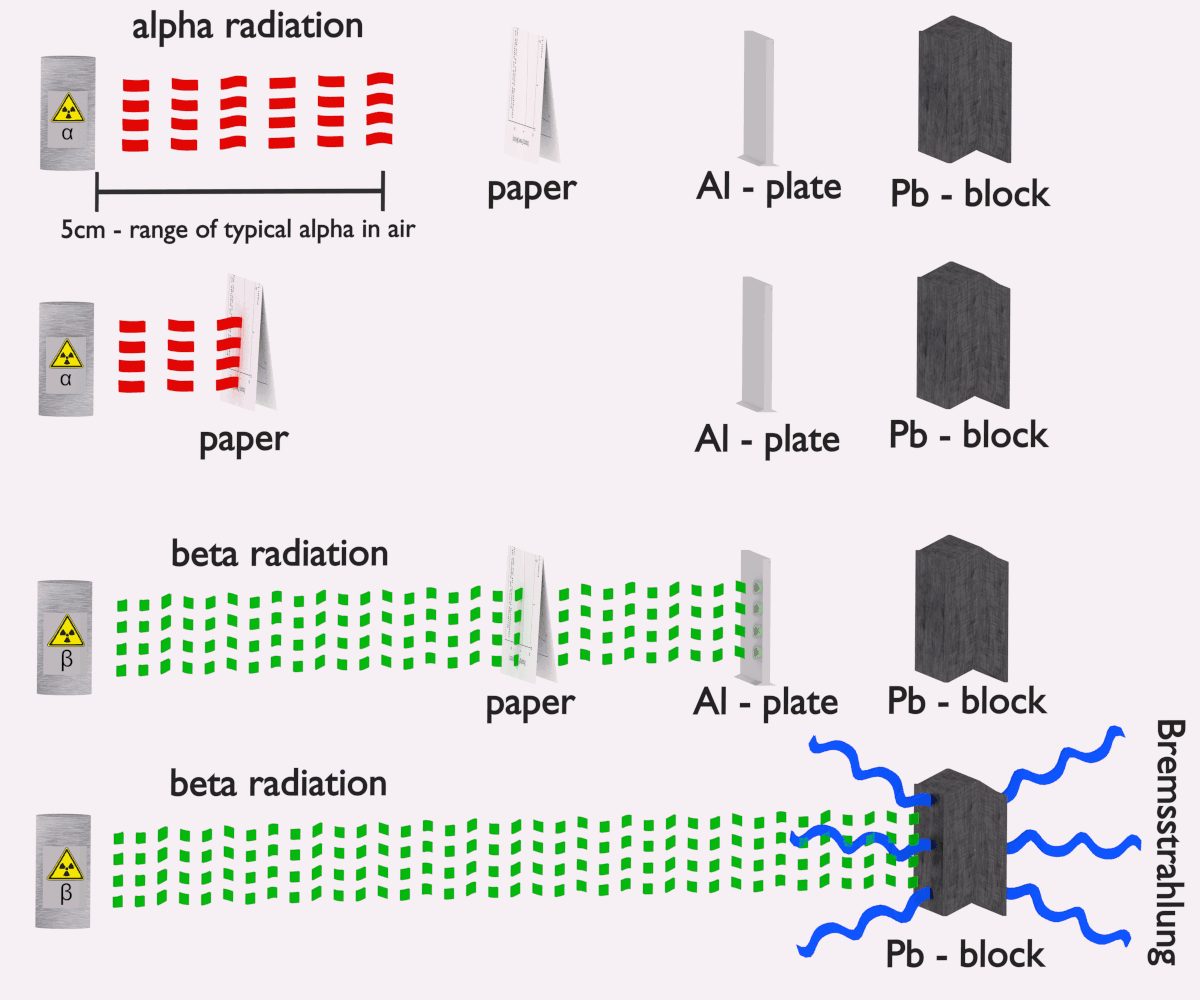
Alpha particles, a type of ionizing radiation, are emitted from the nucleus of certain unstable atoms during radioactive decay. These particles, consisting of two protons and two neutrons, are relatively large and heavy, carrying a double positive charge. While alpha particles possess significant energy, their large size and charge limit their penetration ability, making them less hazardous outside the body. However, when inhaled or ingested, alpha particles can cause significant damage to internal tissues and organs, leading to potential health risks. This article delves into the nature of alpha particles, explores the methods of protection from their harmful effects, and highlights the importance of safeguarding against this invisible threat.
The Nature of Alpha Particles
Alpha particles are emitted from the nuclei of radioactive isotopes during a process known as alpha decay. This decay occurs when an unstable nucleus transforms into a more stable configuration by releasing an alpha particle. The process alters the atomic number of the parent nucleus by two and its mass number by four.
The energy of alpha particles varies depending on the radioactive source, but they typically possess high kinetic energy, ranging from a few MeV (megaelectron volts) to several MeV. This energy is a consequence of the strong electrostatic repulsion between the positively charged alpha particle and the positively charged nucleus it is ejected from.
The Hazards of Alpha Radiation
The primary hazard associated with alpha particles lies in their ability to cause ionization. As alpha particles travel through matter, they interact with atoms, stripping electrons from their shells and creating ions. This ionization process disrupts the chemical bonds within molecules, potentially leading to cellular damage.
Alpha particles are particularly dangerous when ingested or inhaled. Once inside the body, they can directly interact with sensitive tissues, causing damage to DNA and potentially leading to cancer. For instance, exposure to high levels of alpha radiation can lead to lung cancer, bone cancer, and leukemia.
Protecting Against Alpha Radiation
Given the potential hazards of alpha particles, it is crucial to implement effective protection measures. The following strategies are employed to minimize exposure:
1. Distance: Alpha particles have a limited range in air, typically only a few centimeters. Therefore, maintaining a safe distance from radioactive sources is an effective way to reduce exposure.
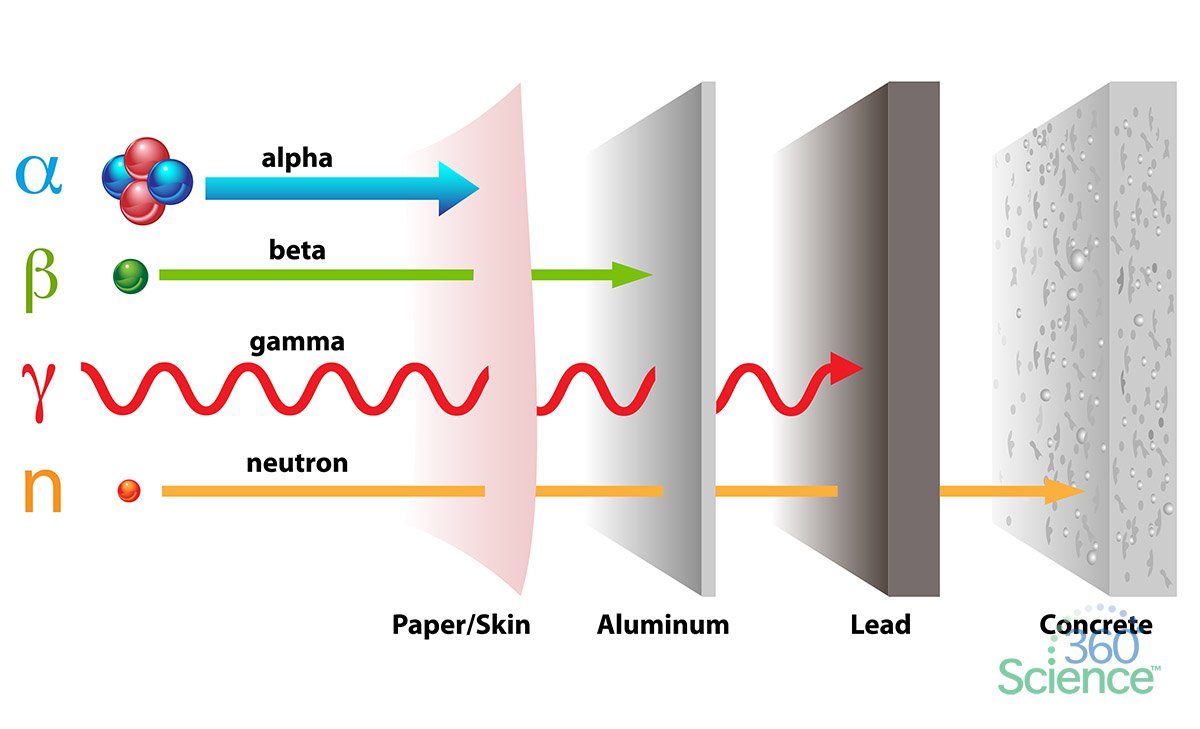
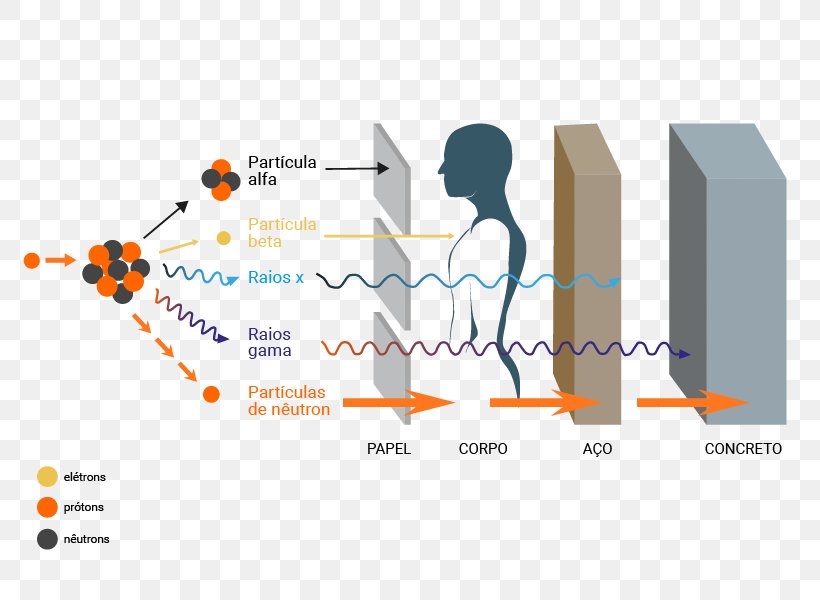
2. Shielding: Alpha particles can be easily stopped by a thin layer of material, such as a sheet of paper, clothing, or even a few millimeters of air. Common shielding materials include:
- Aluminum: Commonly used in nuclear reactors and other industrial settings.
- Lead: A dense material that effectively absorbs alpha particles.
- Concrete: An inexpensive and readily available shielding material.
3. Containment: Radioactive materials emitting alpha particles should be stored and handled in secure, leak-proof containers. This ensures that the particles remain confined and do not escape into the environment.
4. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When handling radioactive materials, appropriate PPE is essential. This includes:
- Gloves: To prevent contact with radioactive materials.
- Respirators: To prevent inhalation of airborne radioactive particles.
- Protective clothing: To minimize skin exposure.
5. Environmental Monitoring: Regular monitoring of the environment for alpha radiation is crucial to ensure that exposure levels remain below safe limits. This involves using specialized detectors to measure alpha particle activity.
6. Minimizing Exposure Time: The shorter the duration of exposure to alpha radiation, the lower the risk of damage. This principle is particularly relevant in occupational settings where workers may be exposed to radioactive materials.
7. Understanding Radioactive Decay: Knowing the half-life of a radioactive isotope is essential for determining the duration of its radioactive activity. This information allows for informed decisions regarding storage, handling, and disposal of radioactive materials.
8. Proper Waste Management: Radioactive waste containing alpha emitters must be managed responsibly. This involves secure storage, treatment, and disposal to minimize the risk of environmental contamination.
9. Public Awareness: Raising public awareness about the hazards of alpha radiation and the importance of protective measures is crucial. This helps individuals make informed decisions regarding their exposure to radioactive materials.
FAQs on Alpha Particle Protection
Q: Are alpha particles a threat outside the body?
A: Alpha particles are not a significant threat outside the body due to their limited range in air. They can be stopped by a thin layer of material, such as clothing or a sheet of paper. However, they can pose a danger if inhaled or ingested.
Q: What are the long-term health effects of alpha radiation exposure?
A: Long-term exposure to alpha radiation can lead to various health issues, including cancer, genetic mutations, and other chronic diseases. The severity of these effects depends on the dose and duration of exposure.
Q: How can I protect myself from alpha radiation in my home?
A: Alpha radiation is not a common threat in residential settings. However, if you are concerned about exposure, you can minimize the risk by:
- Ensuring that smoke detectors and radon detectors are functioning properly.
- Testing your home for radon levels.
- Avoiding contact with radioactive materials.
Q: What are the symptoms of alpha radiation exposure?
A: Symptoms of alpha radiation exposure can vary depending on the dose and duration of exposure. They may include:
- Skin redness and irritation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
- Bleeding
- Lung damage
Q: How can I dispose of radioactive materials safely?
A: Radioactive materials should never be disposed of in regular trash or sewage systems. They should be disposed of according to local regulations and guidelines.
Tips for Protection from Alpha Radiation
- Always follow safety procedures when handling radioactive materials.
- Wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, respirators, and protective clothing.
- Maintain a safe distance from radioactive sources.
- Store radioactive materials in secure, leak-proof containers.
- Monitor the environment for alpha radiation levels.
- Minimize exposure time to radioactive materials.
- Consult with a radiation safety expert if you have any concerns.
Conclusion
Alpha particles, while invisible to the naked eye, represent a significant threat to human health, particularly when inhaled or ingested. By understanding the nature of alpha radiation and implementing appropriate protection measures, individuals and organizations can minimize the risks associated with this type of ionizing radiation. From maintaining safe distances to employing proper shielding and containment strategies, comprehensive protection measures are crucial to ensure the safety and well-being of all. Continuous vigilance, responsible handling of radioactive materials, and ongoing research into the effects of alpha radiation are essential for mitigating the potential hazards associated with this invisible threat.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shielding from the Invisible Threat: Understanding and Mitigating Alpha Particle Radiation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!