Shielding Against Electromagnetic Pulses: Safeguarding Critical Infrastructure and Technology
Related Articles: Shielding Against Electromagnetic Pulses: Safeguarding Critical Infrastructure and Technology
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Shielding Against Electromagnetic Pulses: Safeguarding Critical Infrastructure and Technology. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shielding Against Electromagnetic Pulses: Safeguarding Critical Infrastructure and Technology

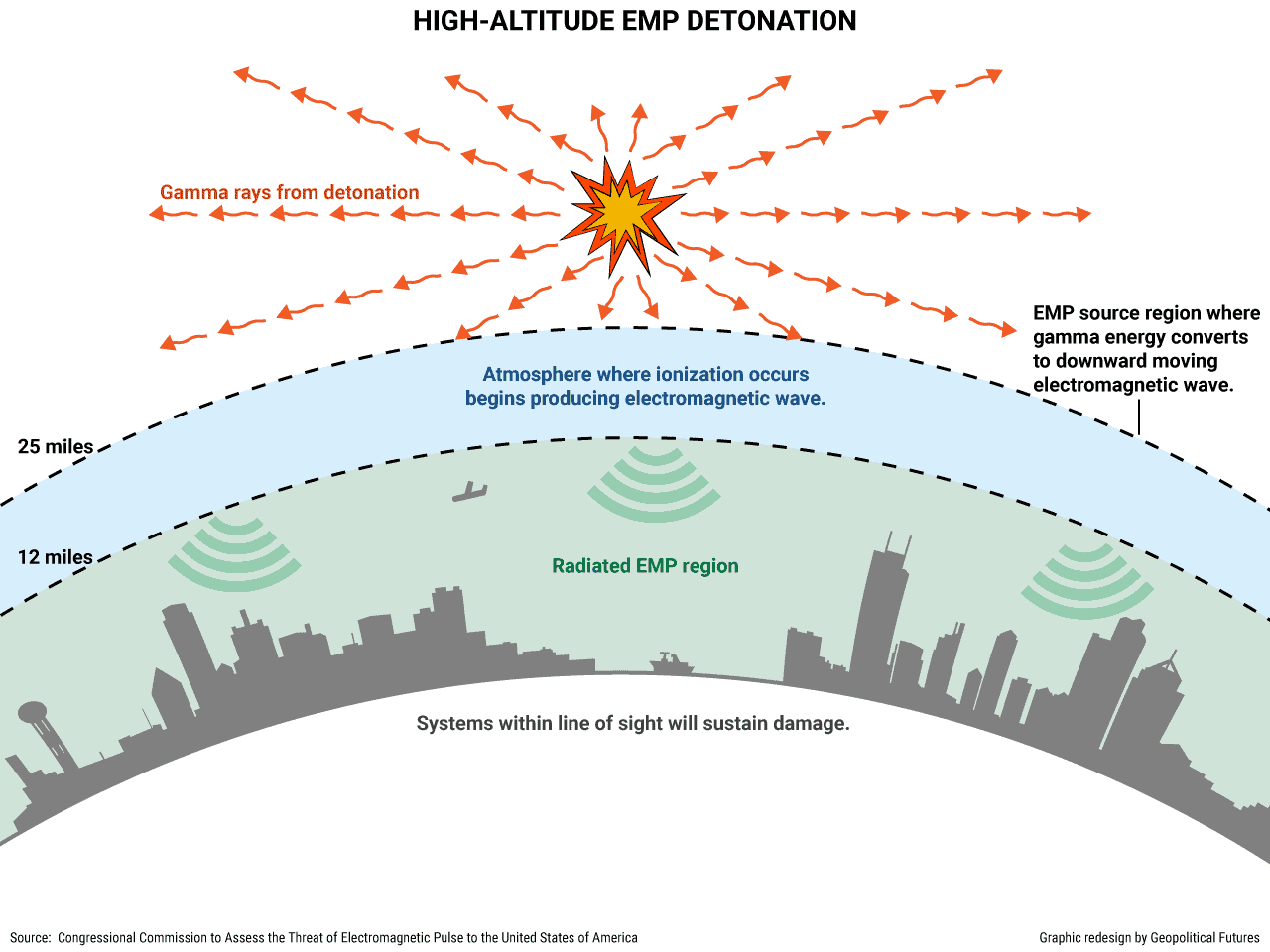
Electromagnetic pulses (EMPs) are sudden bursts of electromagnetic energy that can disrupt or damage electronic devices and systems. These pulses can originate from natural sources like solar flares or from man-made sources such as nuclear detonations. The devastating consequences of an EMP event on modern society, heavily reliant on interconnected technology, necessitate robust protection measures.
Understanding the Threat:
EMPs pose a significant threat to critical infrastructure and technology, potentially causing widespread disruption and economic damage. The impact of an EMP event can be categorized into three primary effects:
- Direct Effects: The immediate impact of an EMP on electronic devices, primarily through induced currents and voltages that can damage or destroy sensitive components.
- Indirect Effects: Disruption of power grids and communication networks, leading to cascading failures and widespread outages.
- Long-Term Effects: The economic and social consequences of prolonged disruptions to essential services, including healthcare, transportation, and financial systems.
Protection Strategies:
Protecting against EMP effects requires a multi-layered approach, encompassing both physical hardening and electromagnetic shielding.
1. Hardening Electronic Systems:
- Circuit Design: Incorporating robust circuit designs with surge protection devices and shielded components can enhance the resilience of electronic systems to EMP transients.
- Component Selection: Utilizing radiation-hardened components designed to withstand high levels of electromagnetic radiation can significantly improve system survivability.
- Redundancy and Backup Systems: Implementing redundant systems and backup power sources can mitigate the impact of EMP-induced failures by providing alternative functionality.
2. Electromagnetic Shielding:
- Faraday Cages: Enclosing sensitive equipment within conductive enclosures, known as Faraday cages, can effectively block electromagnetic waves, preventing penetration and protecting the devices within.
- Shielded Enclosures: Utilizing shielded enclosures with conductive materials and specialized coatings can effectively attenuate EMP radiation, reducing the impact on electronic systems.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding and bonding techniques ensure that any induced currents are safely dissipated to the earth, preventing damage to equipment.
3. Strategic Planning and Response:
- EMP Vulnerability Assessment: Identifying critical infrastructure and systems vulnerable to EMP effects is essential for developing targeted protection measures.
- Emergency Response Plans: Establishing comprehensive emergency response plans for EMP events ensures swift and coordinated actions to mitigate the impact and restore essential services.
- Public Awareness and Education: Raising public awareness about EMP threats and the importance of preparedness can facilitate community resilience and minimize potential panic.
Benefits of EMP Protection:
Investing in EMP protection measures offers several significant benefits:
- Enhanced Security: Protecting critical infrastructure and technology from EMP threats strengthens national security and safeguards against potential disruptions.
- Economic Stability: Minimizing the economic impact of EMP events ensures the continuity of essential services and promotes economic recovery.
- Public Safety: Protecting critical infrastructure, including healthcare facilities and emergency response systems, enhances public safety and reduces potential risks.
- Technological Advancement: Continued development of EMP protection technologies fosters innovation and advances in electronic design and shielding techniques.
FAQs on EMP Protection:
1. What are the common sources of EMPs?
EMPs can originate from natural sources such as solar flares and geomagnetic storms, as well as man-made sources such as nuclear detonations, high-altitude electromagnetic pulse (HEMP) weapons, and powerful radio frequency transmitters.
2. How can I protect my home from an EMP?
Protecting your home from an EMP requires a multi-pronged approach. Consider implementing measures like Faraday cages for sensitive electronics, surge protectors for electrical outlets, and backup power sources.
3. What are the key elements of an effective EMP protection plan?
An effective EMP protection plan should include:
- Vulnerability assessment: Identifying critical systems and infrastructure.
- Hardening measures: Implementing circuit design improvements, shielded enclosures, and radiation-hardened components.
- Emergency response protocols: Establishing clear procedures for managing disruptions and restoring essential services.
- Public awareness campaigns: Educating the public about EMP threats and preparedness measures.
4. Are there any government regulations regarding EMP protection?
While specific EMP protection regulations may vary depending on the region and industry, several government agencies, including the Department of Homeland Security and the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), provide guidance and recommendations for EMP preparedness.
5. What is the role of technology in EMP protection?
Technology plays a crucial role in EMP protection. Advancements in materials science, circuit design, and electromagnetic shielding techniques continue to enhance the effectiveness of protection measures.
Tips for EMP Protection:
- Identify Critical Systems: Determine which electronic systems and infrastructure are most crucial to your well-being and daily operations.
- Implement Hardening Measures: Incorporate surge protectors, shielded enclosures, and radiation-hardened components where possible.
- Maintain Backup Systems: Ensure you have backup power sources and redundant systems in place to mitigate disruptions.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about EMP threats and protection strategies by consulting relevant resources and government guidelines.
- Prepare Emergency Kits: Assemble emergency kits containing essential supplies, including food, water, first-aid, and communication devices.
Conclusion:
Protecting against EMP effects is essential for safeguarding critical infrastructure and technology, ensuring economic stability, and maintaining public safety. By implementing a comprehensive approach that encompasses hardening electronic systems, electromagnetic shielding, and strategic planning, societies can mitigate the devastating consequences of EMP events and build resilience against this emerging threat. As technology evolves and dependence on electronic systems continues to grow, investing in EMP protection remains a critical priority for securing a more resilient and sustainable future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shielding Against Electromagnetic Pulses: Safeguarding Critical Infrastructure and Technology. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!