Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Household Products: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Household Products: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Household Products: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Household Products: A Comprehensive Overview
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Household Products: A Comprehensive Overview
- 3.1 Prevalence of PFAS in Household Products
- 3.2 Health and Environmental Concerns Associated with PFAS
- 3.3 Regulatory Measures and Alternatives
- 3.4 FAQs Regarding PFAS in Household Products
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Household Products: A Comprehensive Overview
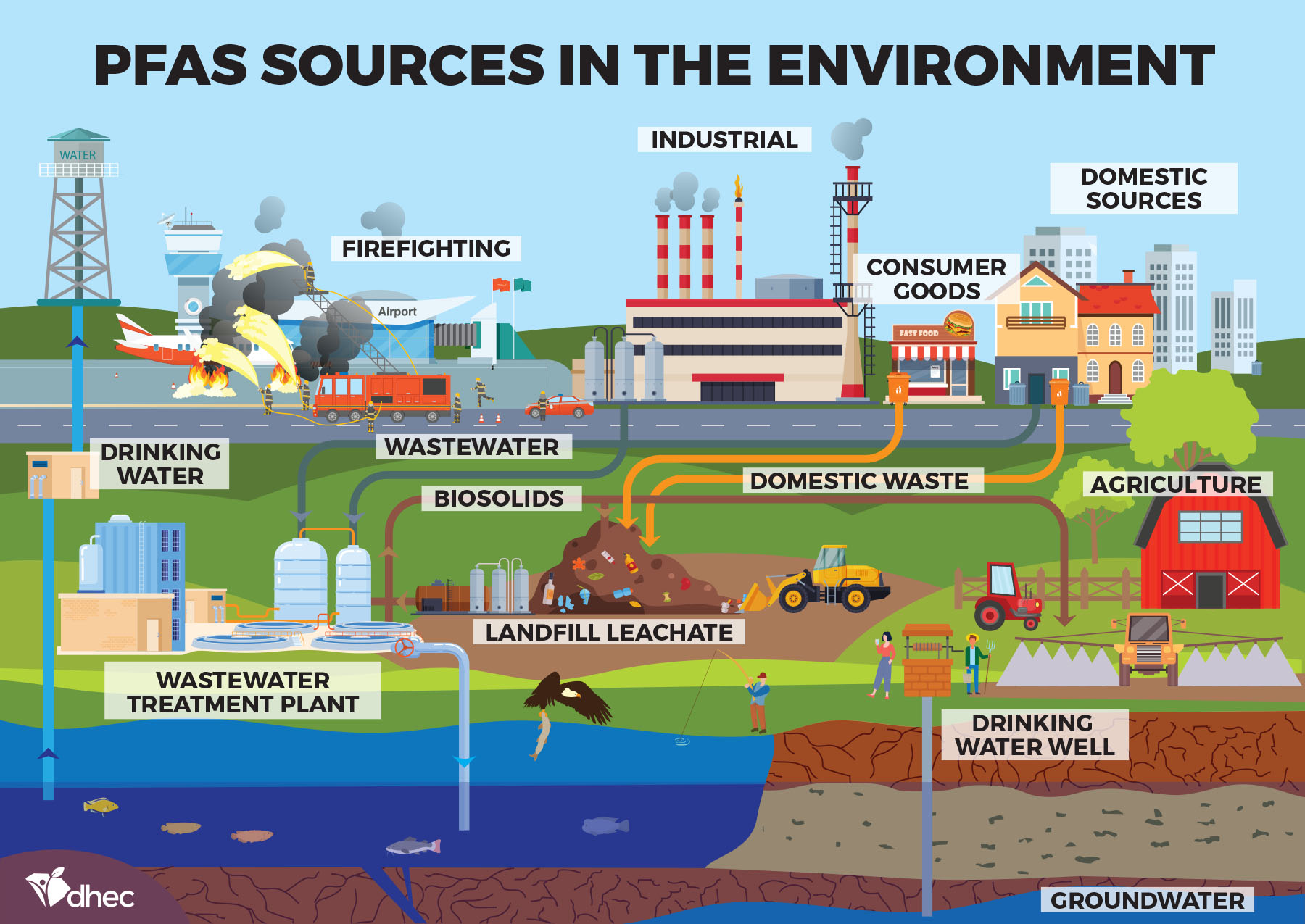
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a large and diverse group of synthetic chemicals that have become ubiquitous in modern society. Their unique properties, including resistance to heat, oil, and water, have made them highly valuable for various industrial and consumer applications. However, these very properties that make them desirable also contribute to their persistence in the environment and their potential for bioaccumulation in the food chain.
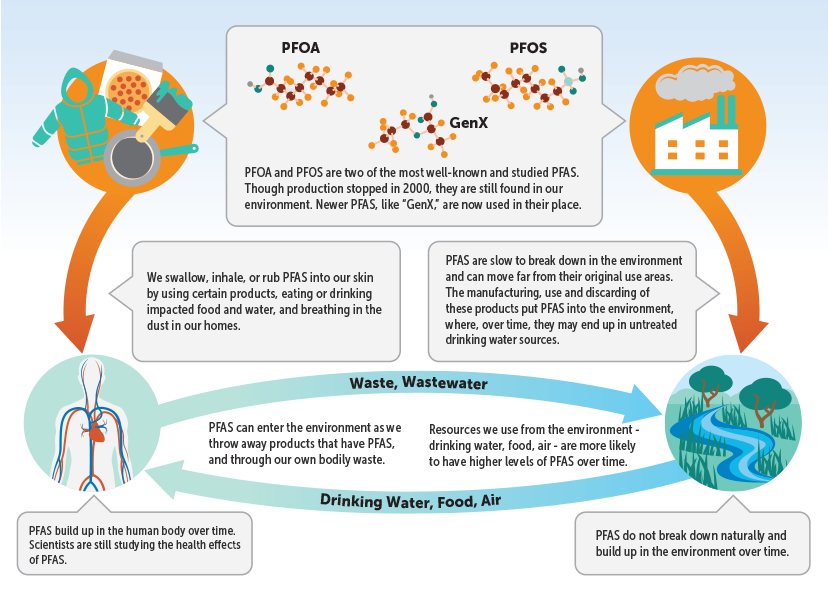
PFAS are often referred to as "forever chemicals" due to their exceptional stability and resistance to degradation. This persistence poses significant environmental and health concerns, as they can accumulate in the environment, water sources, and even human bodies. While PFAS are found in a wide array of products, this article focuses specifically on their presence in household products and the potential implications for human health and the environment.
Prevalence of PFAS in Household Products
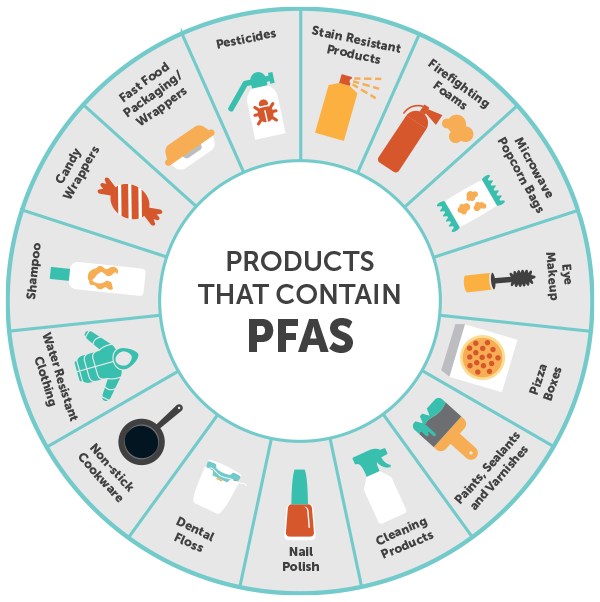
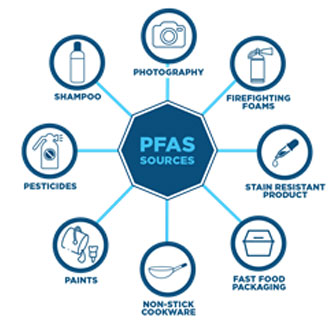
PFAS can be found in a surprisingly wide range of everyday household products, including:
- Non-stick cookware: PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), commonly known as Teflon, is a widely used PFAS in non-stick cookware. Its ability to prevent food from sticking and its resistance to high temperatures make it ideal for cooking.
- Food packaging: PFAS can be found in food packaging materials, such as microwave popcorn bags, pizza boxes, and takeout containers. They help to prevent grease and moisture from penetrating the packaging, extending shelf life and maintaining food quality.
- Personal care products: PFAS are used in cosmetics, shampoos, conditioners, and other personal care products. They can act as emulsifiers, thickeners, and anti-foaming agents, contributing to the desired texture and performance of these products.
- Cleaning products: PFAS are often included in stain removers, carpet cleaners, and other household cleaning products. Their ability to repel water and oil makes them effective at removing stains and dirt.
- Textiles and clothing: PFAS are incorporated into fabrics to create water-resistant and stain-resistant properties, commonly found in outdoor wear, raincoats, and upholstery.
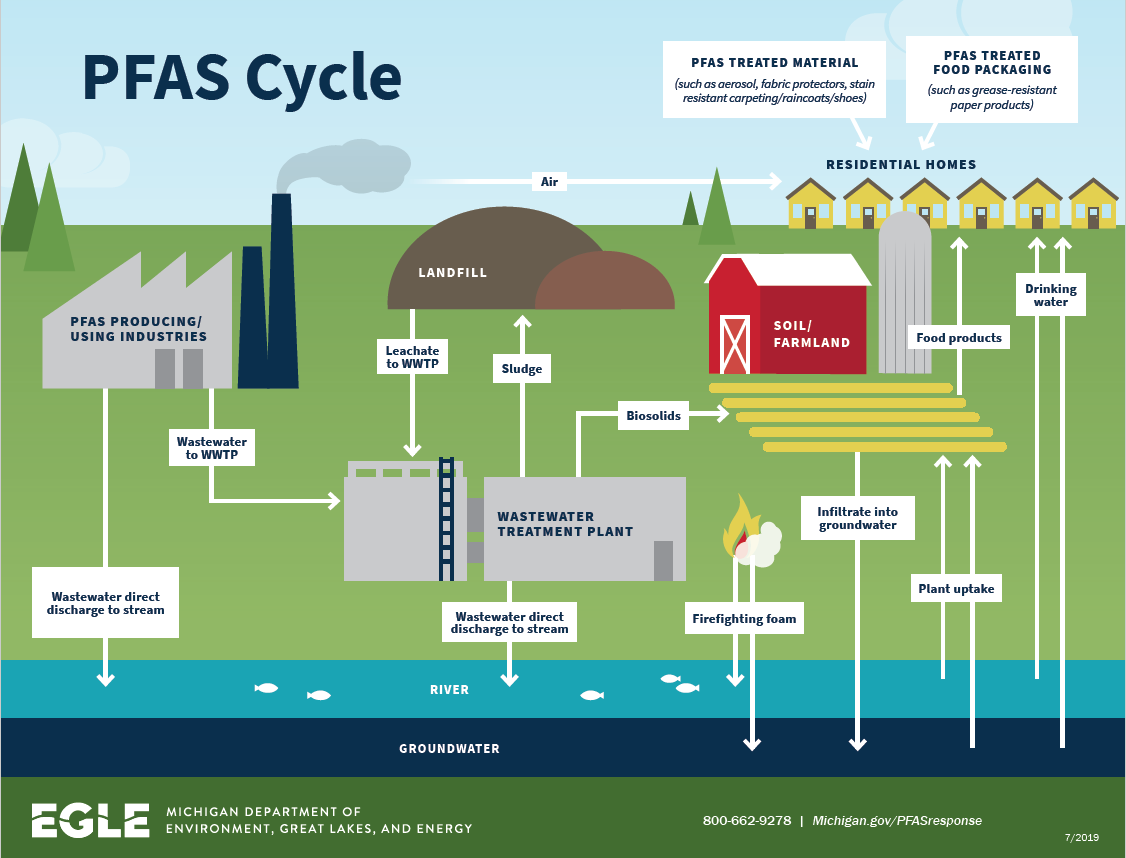
- Firefighting foam: PFAS are used in firefighting foams to suppress flammable liquids, particularly in aviation and industrial settings. However, their use has led to significant environmental contamination due to their persistence and potential for leaching into groundwater.
Health and Environmental Concerns Associated with PFAS
The widespread use of PFAS has raised serious concerns about their potential impact on human health and the environment. While research continues to expand our understanding of the risks associated with PFAS, several key areas of concern have been identified:
- Immune system suppression: Studies have shown that PFAS can interfere with the immune system, potentially increasing the susceptibility to infections and diseases.
- Hormonal disruption: Some PFAS have been linked to hormonal disruption, potentially affecting the development and function of the endocrine system.
- Liver and kidney toxicity: PFAS can accumulate in the liver and kidneys, potentially causing damage to these organs.
- Developmental effects: Exposure to PFAS during pregnancy has been associated with developmental delays and other adverse effects in children.
- Cancer risk: Some PFAS have been classified as "likely to be carcinogenic to humans," suggesting a potential link to cancer development.
- Environmental persistence: PFAS are highly persistent in the environment, meaning they do not break down easily and can accumulate in soil, water, and air. This persistence can lead to widespread contamination, affecting ecosystems and wildlife.
- Bioaccumulation: PFAS can accumulate in the food chain, leading to higher concentrations in animals at the top of the food web, including humans.
Regulatory Measures and Alternatives
Recognizing the potential risks associated with PFAS, regulatory agencies worldwide have taken steps to address their use and manage their environmental impact.
- Phase-out and restrictions: Several countries and regions have implemented bans or restrictions on the use of specific PFAS in certain products. These regulations aim to reduce the overall exposure to these chemicals and minimize their environmental impact.
- Product labeling: Some jurisdictions require manufacturers to label products containing PFAS, providing consumers with information to make informed choices.
- Monitoring and research: Continued research and monitoring are crucial to understand the full extent of PFAS contamination and to develop effective strategies for mitigation and remediation.
- Alternative materials: Scientists and industry are actively developing alternative materials and technologies to replace PFAS in various applications. These alternatives aim to provide similar functionality without the associated health and environmental risks.
FAQs Regarding PFAS in Household Products
Q: How do I know if a product contains PFAS?
A: Product labeling is often the best source of information. Look for terms like "PFOA-free," "PFOS-free," or "PFAS-free" on product packaging. However, it’s important to note that not all products are required to disclose PFAS content, and some labels may be misleading.
Q: Are all PFAS harmful?
A: Not all PFAS are equally harmful. Some PFAS are more persistent and toxic than others. However, due to the complexity of the chemical group, it’s generally advisable to minimize exposure to all PFAS as a precautionary measure.
Q: What can I do to reduce my exposure to PFAS?
A: Here are some tips for minimizing exposure to PFAS in household products:
- Choose PFAS-free products whenever possible. Look for products labeled as "PFAS-free" or "PFOA-free."
- Use alternative cooking methods. Consider using cast iron cookware, stainless steel, or ceramic cookware instead of non-stick cookware.
- Choose reusable food containers. Avoid using microwave popcorn bags and other food packaging that may contain PFAS. Opt for reusable containers made from glass, stainless steel, or silicone.
- Read product labels carefully. Pay attention to ingredient lists and look for PFAS-related terms.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after handling products that may contain PFAS.
- Avoid using stain removers and other cleaning products that contain PFAS.
Q: What about the PFAS already in my home?
A: If you have concerns about PFAS in your home, consult with a qualified professional, such as a certified environmental consultant, for guidance on potential mitigation strategies.
Conclusion
PFAS are a complex and concerning group of chemicals that have become ubiquitous in household products. Their persistence, bioaccumulation, and potential for adverse health effects have raised significant concerns. While research continues to uncover new information about the risks associated with PFAS, it is crucial to take steps to minimize exposure and promote the development of safer alternatives. By making informed choices about the products we use and supporting regulations that restrict PFAS use, we can work towards protecting human health and the environment from the potential harm of these "forever chemicals."



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Household Products: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!