Empowering Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Products for the Deaf and Hearing Impaired
Related Articles: Empowering Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Products for the Deaf and Hearing Impaired
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Empowering Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Products for the Deaf and Hearing Impaired. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Empowering Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Products for the Deaf and Hearing Impaired

The world of technology has rapidly evolved, offering a plethora of innovative solutions that cater to diverse needs. Among these advancements, products designed for the deaf and hearing impaired stand out as powerful tools for empowerment and inclusion. These products bridge communication gaps, foster independence, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals experiencing hearing loss. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse range of products available, outlining their functionalities, benefits, and considerations for effective use.
Hearing Aids: Amplifying Sound and Enhancing Clarity
Hearing aids remain a cornerstone of hearing loss management. These miniature devices amplify sound, allowing individuals to perceive sounds that would otherwise be inaudible.
Types of Hearing Aids:
- Behind-the-Ear (BTE): A common type, BTE devices are worn behind the ear and connected to a mold that fits in the ear canal. They offer flexibility in adjusting volume and sound settings.
- In-the-Ear (ITE): ITE aids are custom-molded to fit inside the ear. They are discreet and offer a comfortable fit.
- Completely-in-Canal (CIC): CIC devices are the smallest type, fitting entirely within the ear canal. They are virtually invisible and offer a natural sound experience.
- Receiver-in-Canal (RIC): RIC aids feature a small receiver that sits in the ear canal, while the main component remains behind the ear. They offer a balance of sound quality and discretion.
Benefits of Hearing Aids:
- Improved Speech Understanding: Hearing aids amplify sound, making it easier to understand speech in various environments.
- Enhanced Social Interaction: By improving hearing ability, hearing aids facilitate communication and engagement in social settings.
- Reduced Cognitive Strain: Hearing aids minimize the effort required to understand speech, reducing cognitive fatigue and improving focus.
- Safety and Awareness: Hearing aids alert individuals to important sounds, such as alarms, traffic, and approaching individuals.
Considerations:
- Professional Fitting: Hearing aids require professional fitting and adjustment to ensure optimal performance.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning and battery replacement are crucial for maintaining the functionality of hearing aids.
- Cost: The cost of hearing aids varies depending on features and technology.
- Adjusting to Hearing Aids: Individuals may need time to adjust to the sounds amplified by hearing aids.
Cochlear Implants: Restoring Hearing for Profound Deafness
Cochlear implants are advanced devices that bypass damaged portions of the inner ear, directly stimulating the auditory nerve. They provide a sense of hearing for individuals with profound hearing loss, who cannot benefit from traditional hearing aids.
How Cochlear Implants Work:
- External Components: A microphone captures sound, a speech processor converts sound into electrical signals, and a transmitter sends these signals to the internal component.
- Internal Component: A surgically implanted receiver and electrode array convert electrical signals into impulses that stimulate the auditory nerve.
Benefits of Cochlear Implants:
- Sound Perception: Cochlear implants enable individuals to perceive sound and develop speech understanding.
- Improved Communication: Implants facilitate communication, allowing individuals to participate in conversations and social interactions.
- Language Development: Cochlear implants can help children with profound deafness develop language skills.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Implants improve access to information, social connections, and overall well-being.
Considerations:
- Surgical Procedure: Cochlear implant surgery requires a significant commitment.
- Rehabilitation: Extensive rehabilitation is necessary to learn how to interpret the sounds received through the implant.
- Cost: Cochlear implants are a significant financial investment.
- Individual Variability: The success of cochlear implants varies depending on factors such as age, the extent of hearing loss, and individual adaptation.
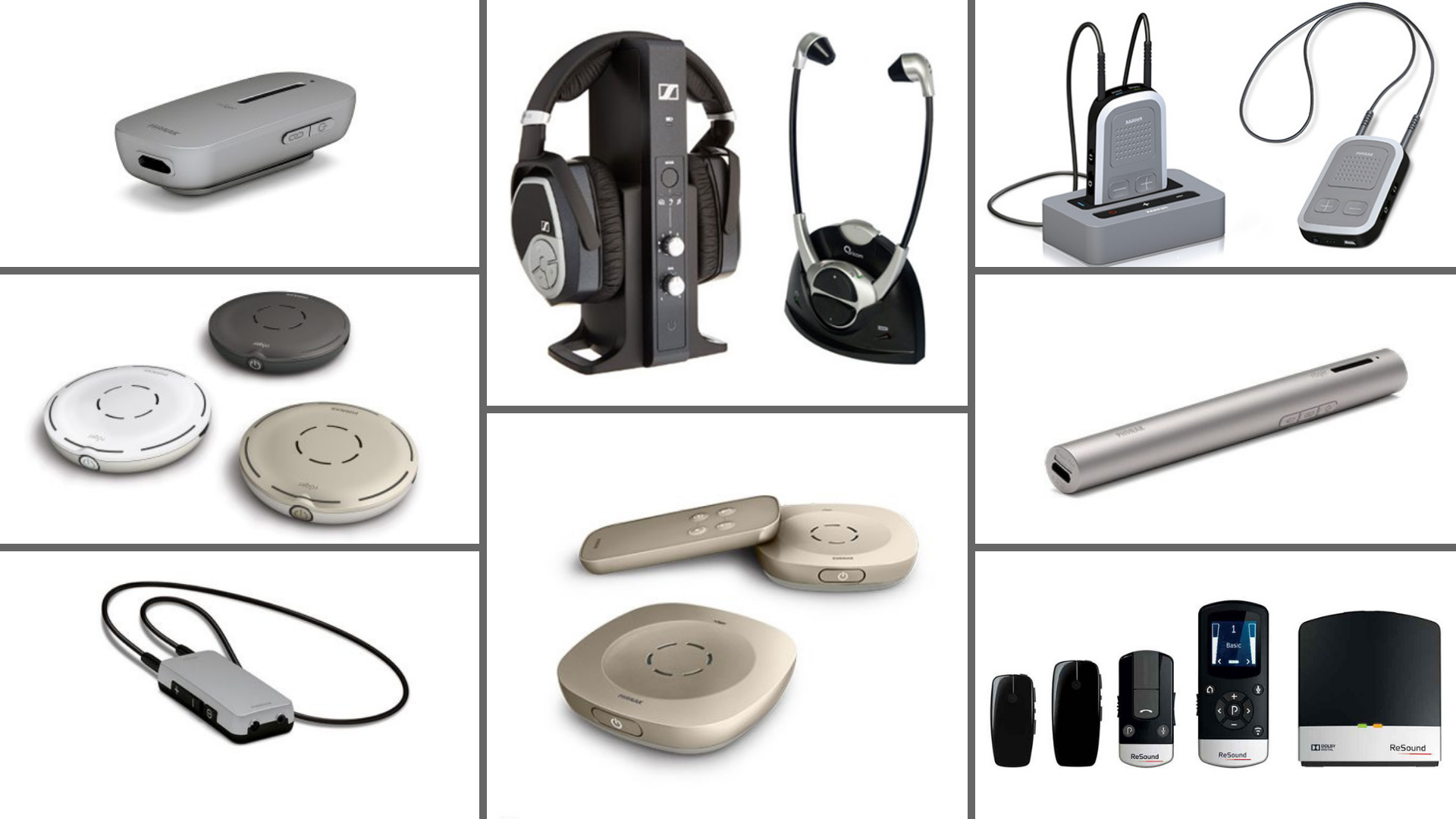
Assistive Listening Devices: Enhancing Sound in Specific Environments
Assistive listening devices (ALDs) are specialized tools that amplify sound in specific environments, making it easier for individuals with hearing loss to participate in conversations and activities.
Types of ALDs:
- Personal FM Systems: These systems use a transmitter to broadcast sound to a receiver worn by the individual with hearing loss.
- Infrared Systems: Infrared systems transmit sound through infrared beams, often used in theaters and auditoriums.
- Loop Systems: Loop systems use a wire loop to transmit sound to hearing aids equipped with a T-coil.
- Tabletop Amplifiers: Tabletop amplifiers amplify sound from a source, such as a television or stereo system.
Benefits of ALDs:
- Improved Sound Clarity: ALDs enhance the audibility of sound in noisy or challenging environments.
- Increased Participation: ALDs allow individuals with hearing loss to participate in conversations and activities more easily.
- Reduced Fatigue: ALDs reduce the effort required to understand speech, minimizing cognitive strain.
- Versatility: ALDs are available in various forms to suit different needs and environments.
Considerations:
- Compatibility: Ensure compatibility between ALDs and hearing aids or other devices.
- Placement and Setup: Proper placement and setup of ALDs are crucial for optimal performance.
- Cost: The cost of ALDs varies depending on features and technology.
Captioning and Subtitling: Making Media Accessible
Captioning and subtitling provide text displays of spoken dialogue, making media content accessible to individuals with hearing loss.
Types of Captioning:
- Closed Captioning: Closed captions are displayed on a television screen and can be turned on or off by the viewer.
- Open Captioning: Open captions are permanently embedded in the video and are always visible.
- Real-time Captioning: Real-time captioning provides live text displays of spoken dialogue, often used in presentations and conferences.
Benefits of Captioning:
- Improved Content Accessibility: Captioning makes media content, including movies, television shows, and online videos, accessible to individuals with hearing loss.
- Enhanced Comprehension: Captioning provides a visual representation of spoken dialogue, improving comprehension, particularly in noisy environments.
- Language Learning: Captioning can aid in language learning by providing a visual representation of spoken words.
Considerations:
- Accuracy: The accuracy of captions is crucial for effective communication.
- Availability: Captioning availability varies depending on the media source and platform.
Sign Language Interpreters: Facilitating Communication for the Deaf Community
Sign language interpreters bridge communication gaps between individuals who use sign language and those who do not.
Role of Sign Language Interpreters:
- Facilitation of Communication: Interpreters translate spoken language into sign language and vice versa, enabling effective communication in various settings.
- Accessibility in Public Settings: Interpreters ensure accessibility for individuals who use sign language in public spaces, such as schools, hospitals, and legal proceedings.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Interpreters understand the nuances of sign language and cultural differences, promoting respectful and accurate communication.
Benefits of Sign Language Interpreters:
- Improved Communication: Interpreters enable clear and effective communication between individuals who use sign language and those who do not.
- Increased Participation: Interpreters allow individuals who use sign language to fully participate in conversations, meetings, and events.
- Access to Information: Interpreters provide access to information and resources that would otherwise be inaccessible.
Considerations:
- Certification and Qualifications: Ensure that interpreters are certified and qualified to provide accurate and reliable services.
- Availability: The availability of interpreters can vary depending on location and demand.
- Cost: The cost of interpreter services can vary depending on the length of the assignment and the complexity of the task.
Video Relay Services (VRS): Connecting Deaf Individuals with the Hearing World
Video relay services (VRS) use video technology to connect deaf individuals with hearing individuals through a relay interpreter.
How VRS Works:
- Video Connection: A deaf individual initiates a video call with a VRS interpreter.
- Relay Interpretation: The interpreter signs the deaf individual’s message to the hearing individual and vice versa.
- Real-time Communication: VRS enables real-time communication between individuals who use sign language and those who do not.
Benefits of VRS:
- Enhanced Communication: VRS provides a reliable and accessible means of communication for deaf individuals.
- Increased Independence: VRS empowers deaf individuals to communicate directly with hearing individuals without relying on third parties.
- Improved Access to Services: VRS facilitates access to essential services, such as healthcare, education, and employment.
Considerations:
- Technology Requirements: VRS requires access to video conferencing equipment and internet connectivity.
- Availability: VRS availability varies depending on the service provider and location.
- Cost: VRS services may incur costs, depending on the provider and the duration of the call.
Text-Based Communication: Bridging the Communication Gap
Text-based communication tools play a crucial role in facilitating communication for individuals with hearing loss.
Types of Text-Based Communication Tools:
- Text Messaging (SMS): Text messaging allows individuals to communicate through written messages.
- Instant Messaging (IM): IM platforms, such as WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger, enable real-time text-based conversations.
- Email: Email provides a reliable and asynchronous form of communication.
- Video Chat with Captioning: Video chat platforms with captioning features enable visual communication and comprehension.
Benefits of Text-Based Communication:
- Accessibility: Text-based communication is accessible to individuals with hearing loss, regardless of their location.
- Convenience: Text-based communication tools are readily available and easy to use.
- Flexibility: Text-based communication allows for asynchronous communication, enabling individuals to respond at their convenience.
Considerations:
- Digital Literacy: Individuals need basic digital literacy skills to utilize text-based communication tools effectively.
- Privacy and Security: Ensure the privacy and security of personal information when using text-based communication platforms.
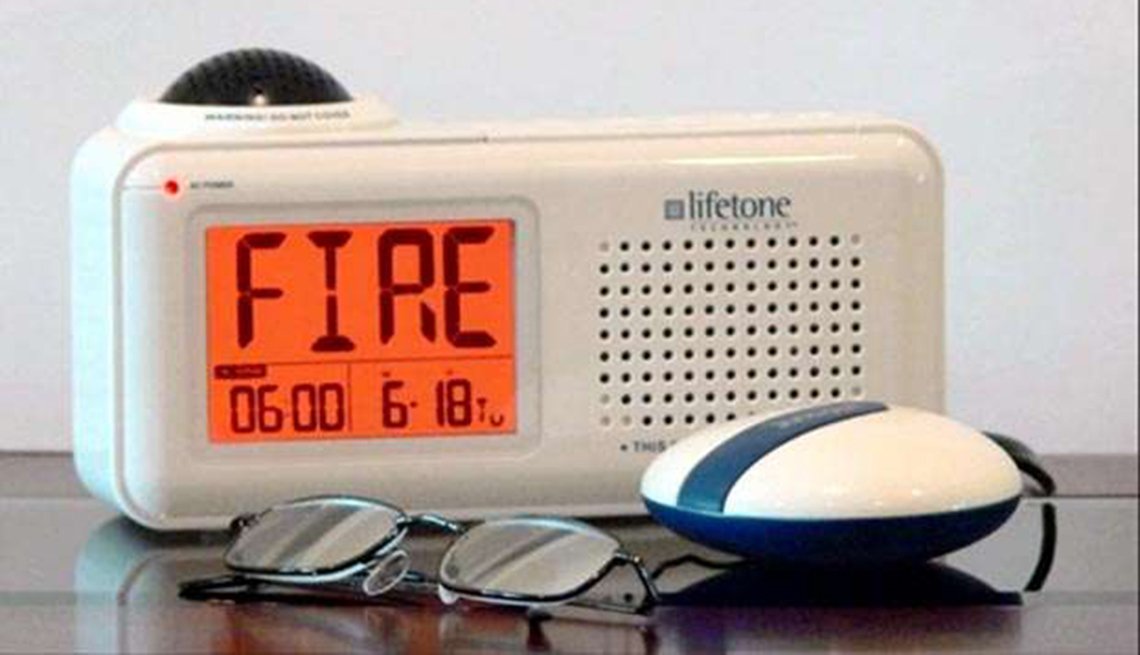
Alerting Devices: Enhancing Safety and Awareness
Alerting devices provide visual or tactile signals for sounds that individuals with hearing loss may not perceive.
Types of Alerting Devices:
- Doorbell and Phone Alert Systems: These systems provide visual or tactile signals when the doorbell or phone rings.
- Smoke and Fire Alarms: Alarms with visual and tactile alerts enhance safety in the event of a fire.
- Baby Monitors: Baby monitors with visual or tactile alerts allow parents with hearing loss to monitor their infants.
Benefits of Alerting Devices:
- Safety and Awareness: Alerting devices enhance safety and awareness by providing alerts for important sounds.
- Independence: Alerting devices allow individuals with hearing loss to live independently and safely.
- Peace of Mind: Alerting devices provide peace of mind, knowing that they will be alerted to important sounds.
Considerations:
- Compatibility: Ensure compatibility between alerting devices and existing systems.
- Installation and Setup: Proper installation and setup are crucial for optimal performance.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance and battery replacement are necessary for reliable operation.
FAQs by Products for the Deaf and Hearing Impaired
Hearing Aids:
-
Q: What is the difference between a hearing aid and a cochlear implant?
- A: Hearing aids amplify sound, while cochlear implants bypass damaged portions of the inner ear, directly stimulating the auditory nerve. Hearing aids are suitable for individuals with mild to severe hearing loss, while cochlear implants are for those with profound deafness.
-
Q: How often do I need to replace my hearing aids?
- A: The lifespan of hearing aids varies depending on the type, usage, and maintenance. Typically, they last 3-5 years.
-
Q: How do I know if I need a hearing aid?
- A: If you experience difficulty understanding speech, particularly in noisy environments, or if you find yourself frequently asking people to repeat themselves, you may benefit from a hearing aid. It’s essential to consult an audiologist for a professional evaluation.
Cochlear Implants:
-
Q: Who is a candidate for a cochlear implant?
- A: Individuals with profound hearing loss who cannot benefit from traditional hearing aids are typically candidates for cochlear implants.
-
Q: How long does it take to adjust to a cochlear implant?
- A: The adjustment period varies, but it can take several months to learn how to interpret the sounds received through the implant.
-
Q: What are the potential risks associated with cochlear implant surgery?
- A: Like any surgical procedure, cochlear implant surgery carries potential risks, including infection, bleeding, and facial nerve damage. However, these risks are relatively low.
Assistive Listening Devices:
-
Q: How do I choose the right ALD for my needs?
- A: The choice of ALD depends on the specific environment and the type of hearing loss. Consulting with an audiologist or hearing aid specialist can help determine the most appropriate device.
-
Q: Are ALDs compatible with hearing aids?
- A: Some ALDs are specifically designed to work with hearing aids, while others may require additional accessories. It’s essential to check compatibility before purchasing.
-
Q: What are the maintenance requirements for ALDs?
- A: Maintenance requirements vary depending on the type of ALD. Some devices may require battery replacement, while others may need regular cleaning.
Captioning and Subtitling:
-
Q: How can I access captioned media content?
- A: Many streaming services and television channels offer closed captions. You can also find captioned videos on YouTube and other online platforms.
-
Q: What is the difference between closed captions and open captions?
- A: Closed captions can be turned on or off by the viewer, while open captions are permanently embedded in the video.
-
Q: How accurate are captions?
- A: The accuracy of captions varies depending on the source and the technology used. Some captions may contain errors or omissions.
Sign Language Interpreters:
-
Q: How do I find a qualified sign language interpreter?
- A: You can contact local organizations that provide interpreter services or search online directories.
-
Q: What types of settings do interpreters work in?
- A: Interpreters work in various settings, including schools, hospitals, courtrooms, and conferences.
-
Q: How much does it cost to hire a sign language interpreter?
- A: The cost of interpreter services varies depending on the length of the assignment and the complexity of the task.
Video Relay Services (VRS):
-
Q: What are the requirements for using VRS?
- A: To use VRS, you need a video conferencing device, such as a computer or smartphone, and an internet connection.
-
Q: Is VRS available 24/7?
- A: VRS services are typically available 24/7.
-
Q: How do I find a VRS provider?
- A: You can search online for VRS providers or contact your local deaf and hard-of-hearing services agency.
Text-Based Communication:
-
Q: What are some tips for effective text-based communication?
- A: Use clear and concise language, avoid slang or jargon, and be mindful of tone and body language, as these can be misinterpreted in text-based communication.
-
Q: What are some considerations for privacy and security when using text-based communication?
- A: Be cautious about sharing personal information online, use strong passwords, and be aware of potential scams.
Alerting Devices:
-
Q: What types of sounds do alerting devices typically alert for?
- A: Alerting devices can alert for a variety of sounds, including doorbells, phones, smoke alarms, and baby cries.
-
Q: How do I know if I need an alerting device?
- A: If you experience difficulty hearing important sounds, such as doorbells or smoke alarms, an alerting device can enhance safety and awareness.
-
Q: What are the installation requirements for alerting devices?
- A: Installation requirements vary depending on the type of device. Some devices may require professional installation, while others can be installed by the user.
Tips by Products for the Deaf and Hearing Impaired
Hearing Aids:
- Tip: Regularly clean your hearing aids with a soft cloth and mild soap.
- Tip: Keep your hearing aids dry and store them in a safe place when not in use.
- Tip: Schedule regular check-ups with your audiologist to ensure your hearing aids are properly fitted and adjusted.
Cochlear Implants:
- Tip: Wear the external components of your cochlear implant as often as possible to maximize sound exposure and language development.
- Tip: Attend rehabilitation sessions to learn how to interpret the sounds received through the implant.
- Tip: Be patient and persistent in your efforts to adjust to your cochlear implant.
Assistive Listening Devices:
- Tip: Experiment with different ALDs to find the one that best suits your needs and environment.
- Tip: Ensure that your ALD is properly positioned for optimal sound reception.
- Tip: Familiarize yourself with the features and settings of your ALD.
Captioning and Subtitling:
- Tip: Enable captions whenever possible to enhance your understanding of media content.
- Tip: Check the accuracy of captions and report any errors to the media provider.
- Tip: Explore online resources for captioned videos and other media content.
Sign Language Interpreters:
- Tip: Request an interpreter for important meetings, appointments, and events.
- Tip: Communicate your needs and preferences to the interpreter to ensure effective communication.
- Tip: Be respectful of the interpreter’s role and expertise.
Video Relay Services (VRS):
- Tip: Familiarize yourself with the VRS system and its features.
- Tip: Use clear and concise language when communicating through VRS.
- Tip: Be patient and understanding as the interpreter relays your message.
Text-Based Communication:
- Tip: Use clear and concise language when texting or emailing.
- Tip: Be mindful of tone and body language, as these can be misinterpreted in text-based communication.
- Tip: Use appropriate punctuation and capitalization to enhance readability.
Alerting Devices:
- Tip: Test your alerting devices regularly to ensure they are functioning properly.
- Tip: Familiarize yourself





![Hearing loss: Tips for better conversations [infographic] Good Samaritan Society](https://www.good-sam.com/resources/-/media/project/good-sam/resources/items/Hearing-loss-infographic.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Empowering Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Products for the Deaf and Hearing Impaired. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!