Benzene: A Versatile Molecule with Complex Implications
Related Articles: Benzene: A Versatile Molecule with Complex Implications
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Benzene: A Versatile Molecule with Complex Implications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Benzene: A Versatile Molecule with Complex Implications
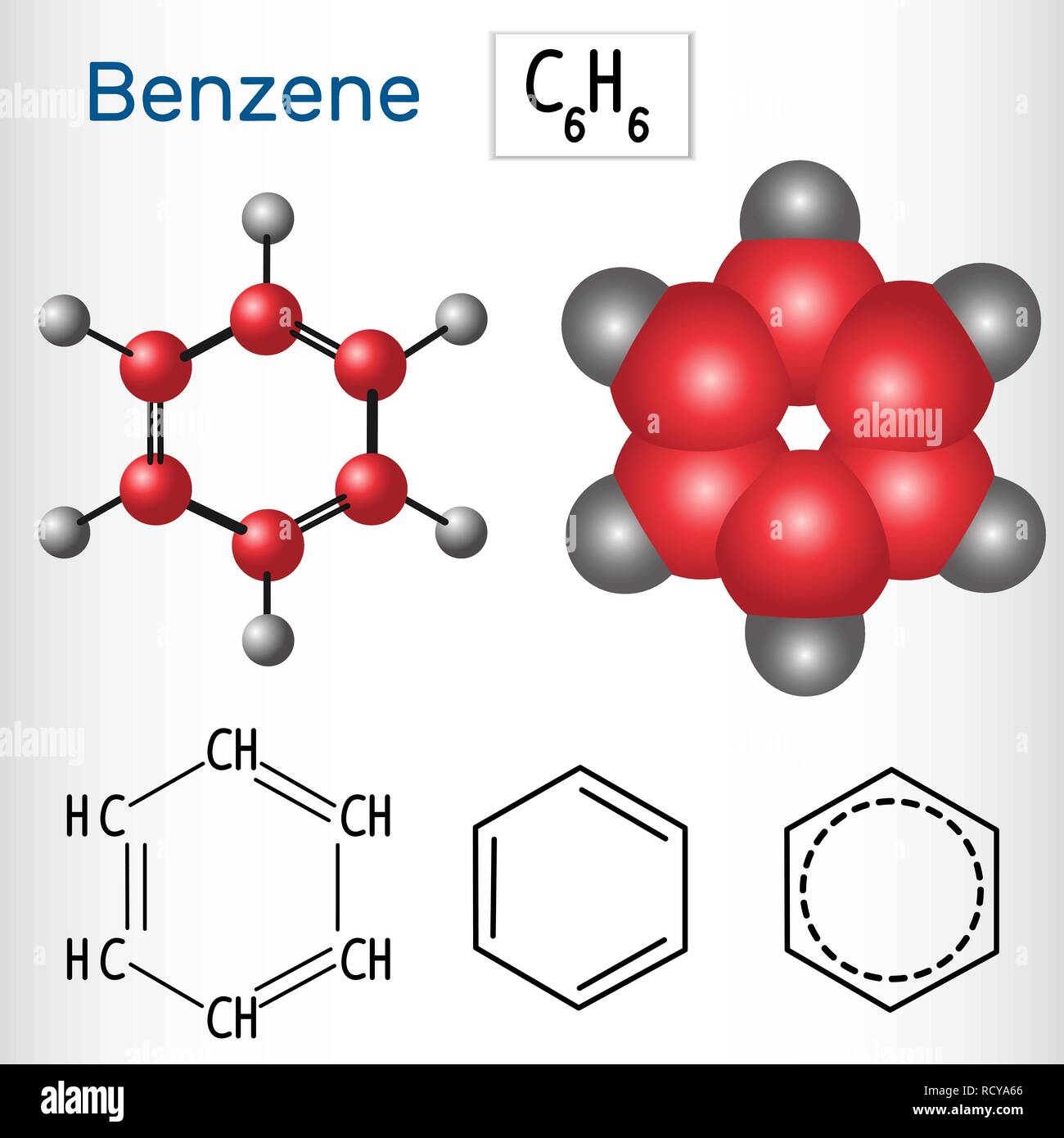
Benzene, a colorless, highly flammable liquid with a sweet odor, is a fundamental building block in the chemical industry. Its unique molecular structure, a six-carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds, grants it remarkable stability and reactivity, making it a versatile component in numerous products. However, despite its widespread applications, benzene’s carcinogenic nature has raised concerns, necessitating a careful understanding of its presence in various consumer goods and industrial processes.
The Importance of Benzene in Chemical Synthesis:
Benzene’s unique molecular structure, known as an aromatic ring, is responsible for its exceptional stability and reactivity. This stability allows it to withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. Its reactivity, on the other hand, enables it to readily participate in chemical reactions, serving as a precursor for countless other compounds.
Applications of Benzene in Everyday Products:
Benzene’s versatility shines through in its diverse applications, contributing to the production of a wide range of everyday products. Some key examples include:
- Plastics: Benzene is a crucial ingredient in the production of various polymers, including polystyrene, which finds use in packaging, insulation, and disposable cups.
- Synthetic Rubber: Benzene is a key component in the synthesis of synthetic rubber, used in tires, hoses, and other rubber products.
- Dyes and Pigments: Benzene derivatives are widely used in the production of dyes and pigments, adding vibrant colors to textiles, paints, and other materials.
- Detergents and Cleaners: Benzene-based surfactants are employed in detergents and cleaning agents, aiding in the removal of dirt and grime.
- Pharmaceuticals: Benzene is a starting material for the synthesis of numerous pharmaceuticals, including aspirin, penicillin, and other essential medications.
- Pesticides: Benzene derivatives are used in the production of certain pesticides, aiming to control pests and protect crops.
- Explosives: Certain benzene derivatives, like trinitrotoluene (TNT), are employed in the manufacture of explosives.
Concerns Regarding Benzene Exposure:
Despite its widespread use, benzene poses significant health risks, primarily due to its carcinogenic nature. Exposure to benzene, even at low levels, can lead to a range of adverse health effects:
- Leukemia: Benzene is a known human carcinogen, primarily linked to the development of leukemia, a type of blood cancer.
- Bone Marrow Suppression: Benzene can damage bone marrow, the tissue responsible for producing blood cells, leading to anemia and other blood disorders.
- Reproductive Issues: Benzene exposure has been associated with reproductive problems, including infertility and birth defects.
- Neurological Effects: Benzene can affect the nervous system, leading to headaches, dizziness, and impaired cognitive function.
Regulation and Minimizing Exposure:
Recognizing the potential health hazards of benzene, regulatory agencies worldwide have implemented strict regulations to limit its exposure. These measures include:
- Occupational Safety Standards: Workplace safety regulations aim to minimize worker exposure to benzene in industries where it is used.
- Air Quality Monitoring: Monitoring programs track benzene levels in ambient air to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Product Labeling: Regulations require the labeling of products containing benzene, informing consumers about potential risks.
- Research and Development: Ongoing research focuses on developing alternative chemicals and processes that minimize or eliminate benzene use.
FAQs Regarding Benzene in Products:
Q: Are all products containing benzene harmful?
A: Not all products containing benzene pose immediate health risks. The level and type of benzene exposure, as well as individual susceptibility, play a crucial role in determining potential health effects.
Q: How can I minimize my exposure to benzene?
A: While complete avoidance of benzene is challenging, certain steps can minimize exposure:
- Avoid using products with known benzene content.
- Ensure adequate ventilation when handling products containing benzene.
- Follow safety guidelines provided by manufacturers.
- Support efforts to reduce benzene use in products.
Q: Are there alternatives to benzene in product manufacturing?
A: Yes, ongoing research and development efforts are exploring alternative chemicals and processes that can replace benzene in various applications. These alternatives aim to maintain the desired properties while minimizing potential health risks.
Tips for Minimizing Benzene Exposure:
- Read product labels carefully: Look for products that explicitly state "benzene-free" or "low benzene content."
- Choose alternatives: Opt for products made with alternative materials or processes that minimize benzene use.
- Ensure proper ventilation: When using products that may contain benzene, ensure adequate ventilation to disperse fumes.
- Avoid prolonged exposure: Limit the time spent handling products containing benzene.
- Wear protective gear: Use gloves and masks when working with products that contain benzene.
Conclusion:
Benzene, a versatile molecule with significant applications in various industries, poses a complex challenge. Its carcinogenic nature necessitates careful consideration and responsible use. While complete avoidance may be impractical, a combination of regulatory measures, consumer awareness, and ongoing research into alternatives can help minimize exposure and mitigate associated health risks. By understanding the potential risks and taking appropriate precautions, individuals can make informed choices and contribute to a safer environment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Benzene: A Versatile Molecule with Complex Implications. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!