A Comprehensive Guide to PFAS-Containing Products
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to PFAS-Containing Products
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to PFAS-Containing Products. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to PFAS-Containing Products

Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of man-made chemicals known for their unique properties, including water and grease resistance, heat stability, and non-stick qualities. These characteristics have made them ubiquitous in numerous consumer and industrial applications. However, their persistence in the environment and potential health risks have raised significant concerns, prompting a growing need to understand the range of products containing PFAS.
A Wide Range of Applications:
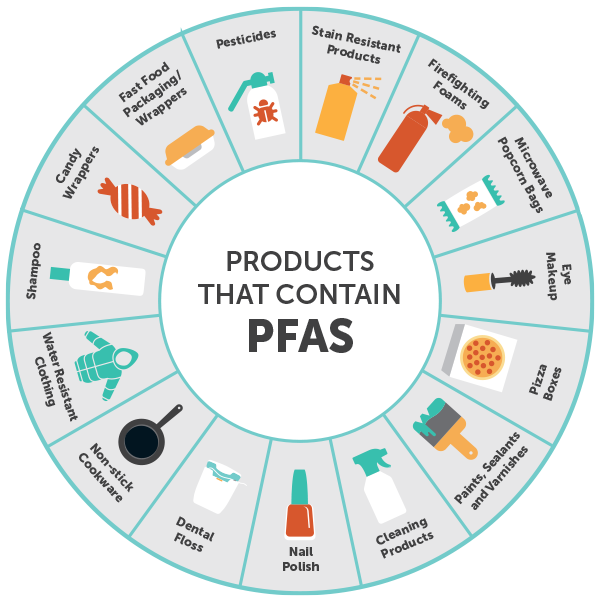
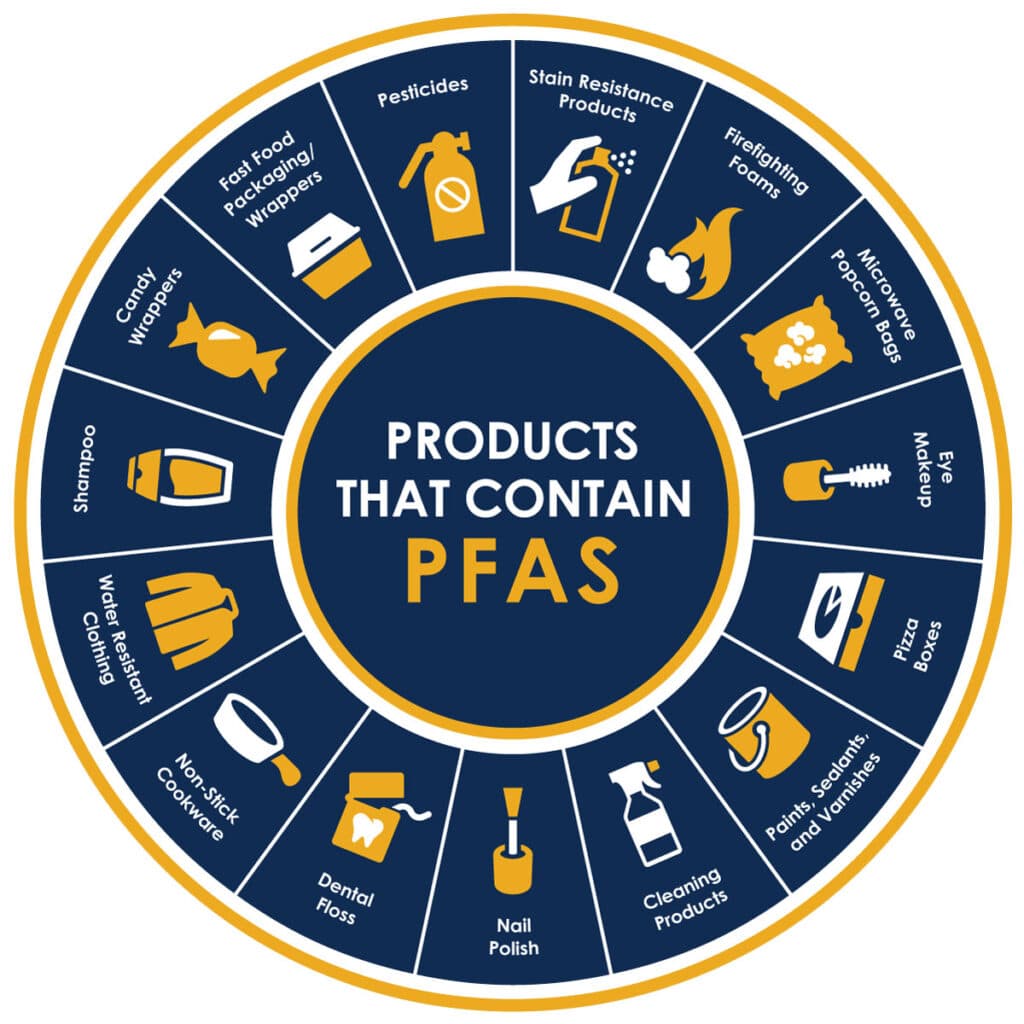
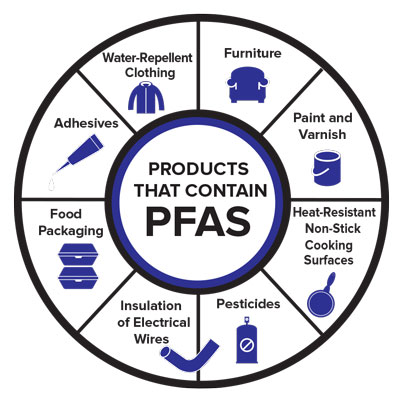
PFAS are found in a diverse array of products, impacting various aspects of modern life. Here’s a breakdown of common categories:
1. Consumer Products:
- Non-stick cookware: PFAS are integral to the non-stick properties of cookware, making them essential for easy cleaning and cooking.
- Food packaging: PFAS are used in food packaging materials like paper wrappers, microwave popcorn bags, and takeout containers to prevent grease and moisture absorption.
- Textiles and clothing: PFAS are incorporated into fabrics to create stain-resistant, water-repellent, and wrinkle-resistant finishes.
- Personal care products: PFAS can be found in shampoos, conditioners, cosmetics, and sunscreens, contributing to water resistance and product longevity.
- Household cleaning products: PFAS are often included in stain removers, carpet cleaners, and other cleaning products to enhance their effectiveness.
- Firefighting foam: A significant application of PFAS is in firefighting foam, particularly for suppressing flammable liquids.
- Paints and coatings: PFAS are incorporated into paints and coatings to improve water resistance, durability, and stain resistance.
2. Industrial Applications:
- Manufacturing: PFAS play a crucial role in various manufacturing processes, including electronics, semiconductors, and plastics production.
- Aeronautics and aerospace: PFAS are used in aircraft components, such as hydraulic fluids and seals, due to their high performance under extreme conditions.
- Automotive industry: PFAS are used in automotive components, including brake fluids and engine oil, for their thermal stability and resistance to degradation.
- Electronics: PFAS are incorporated into electronic components like circuit boards and displays for their electrical insulating properties.
The Importance of Understanding PFAS-Containing Products:
The widespread use of PFAS necessitates a clear understanding of their potential environmental and health impacts. These chemicals are highly persistent and can accumulate in the environment, posing a threat to human and ecological health.
Environmental Concerns:
- Water contamination: PFAS can leach from manufacturing facilities, landfills, and contaminated sites, contaminating groundwater and surface water.
- Bioaccumulation: PFAS can accumulate in the bodies of animals and humans over time, leading to potential health risks.
- Persistence: PFAS are highly persistent and can remain in the environment for decades, making them a long-term environmental concern.
Health Concerns:
- Immune system suppression: Studies have linked PFAS exposure to weakened immune responses, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
- Hormonal disruption: PFAS can interfere with hormone regulation, potentially impacting reproductive health and development.
- Liver and kidney damage: Exposure to high levels of PFAS has been linked to liver and kidney damage.
- Cancer risks: Some studies suggest a potential link between PFAS exposure and certain types of cancer, although more research is needed.
Addressing the Concerns:
The growing awareness of PFAS risks has led to efforts to regulate their use and minimize environmental contamination.
- Regulatory measures: Governments around the world are implementing regulations to limit the production, use, and disposal of PFAS.
- Alternative technologies: Researchers are developing alternative chemicals and technologies to replace PFAS in various applications.
- Public awareness: Educating the public about the risks of PFAS and promoting responsible product choices is crucial in mitigating their impact.
FAQs about PFAS-Containing Products:
Q: How can I identify PFAS-containing products?
A: It is not always easy to identify PFAS-containing products solely by looking at them. However, certain clues can help. Products labeled as "non-stick," "stain-resistant," "water-repellent," or "grease-resistant" may contain PFAS. Check product labels for specific ingredients like PFOA, PFOS, and other PFAS chemicals.
Q: What are the safest alternatives to PFAS-containing products?
A: Several alternatives to PFAS are being developed and marketed. Look for products made with silicone, ceramic, or other materials that do not contain PFAS. Choose products with labels like "PFAS-free," "PFOA-free," or "PFOS-free."
Q: What can I do to minimize my exposure to PFAS?
A:
- Choose PFAS-free products: Opt for products that do not contain PFAS whenever possible.
- Avoid using non-stick cookware at high temperatures: High temperatures can increase the risk of PFAS leaching from cookware.
- Use reusable containers and avoid single-use packaging: Minimize your reliance on food packaging containing PFAS.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after handling products that may contain PFAS: This helps prevent ingestion and absorption through the skin.
- Support regulations to limit PFAS use: Advocate for policies that restrict the production, use, and disposal of PFAS.
Tips for Reducing PFAS Exposure:
- Read product labels carefully: Pay attention to ingredient lists and look for products labeled as "PFAS-free."
- Consider alternatives: Explore alternatives to PFAS-containing products, such as silicone baking mats, ceramic cookware, and natural fabrics.
- Use caution with non-stick cookware: Avoid using non-stick cookware at high temperatures and replace damaged cookware promptly.
- Wash food items thoroughly: Wash fruits and vegetables before consuming them to remove any potential PFAS residue.
- Minimize the use of disposable products: Opt for reusable containers and bags to reduce your reliance on single-use packaging.
Conclusion:
PFAS are ubiquitous in our modern world, but their persistence and potential health risks require careful consideration. Understanding the range of products containing PFAS is crucial for making informed choices and minimizing exposure. By promoting awareness, supporting regulations, and choosing alternatives, we can work towards a future where PFAS contamination is minimized, and human and environmental health are protected.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to PFAS-Containing Products. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!